What is the carbon cycle?
What is the carbon cycle?
Carbon is the backbone of life on Earth. We are made of carbon, we eat carbon, and our civilizations—our economies, our homes, our means of transport—are built on carbon. We need carbon, but that need is also entwined with one of the most serious problems facing us today: global climate change.
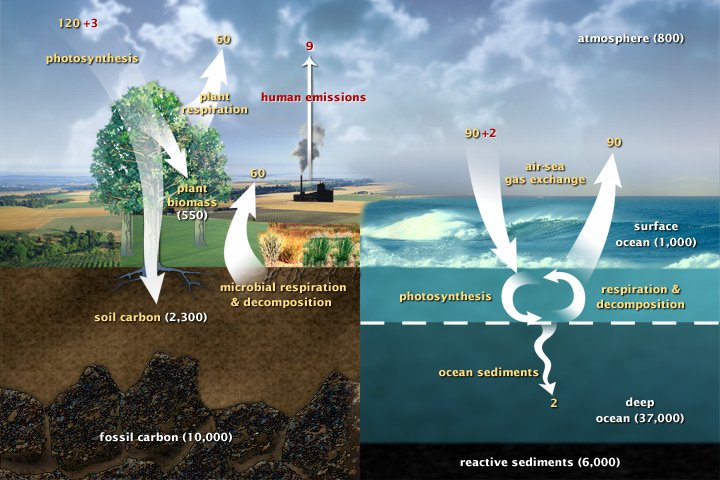
Image source Nasa
Forged in the heart of aging stars, carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the Universe. Most of Earth’s carbon—about 65,500 billion metric tons—is stored in rocks. The rest is in the ocean, atmosphere, plants, soil, and fossil fuels.
Carbon flows between each reservoir in an exchange called the carbon cycle, which has slow and fast components. Any change in the cycle that shifts carbon out of one reservoir puts more carbon in the other reservoirs. Changes that put carbon gases into the atmosphere result in warmer temperatures on Earth.
Deep carbon cycle
Although deep carbon cycling is not as well-understood as carbon movement through the atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere, ocean, and geosphere, it is nonetheless an incredibly important process. The deep carbon cycle is intimately connected to the movement of carbon in the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
If the process did not exist, carbon would remain in the atmosphere, where it would accumulate to extremely high levels over long periods of time. Therefore, by allowing carbon to return to the Earth, the deep carbon cycle plays a critical role in maintaining the terrestrial conditions necessary for life to exist.




![12 Best Budget Telescopes in 2024 [Maximum Value for Money]](https://www.planetguide.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/refreactor-telescope-768x461.jpg)
![12 Best Telescopes for Kids in 2024 [Toddlers to Teens]](https://www.planetguide.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Depositphotos_2254021_l-2015-768x512.jpg)