Aquarius Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Aquarius Constellation
Abbreviation: Aqr
Symbolism: The Water-Bearer
R.A. position: 20h 38m 19.1706s – 23h 56m 23.5355s
Dec. position: -03.3256676° – −24.9040413°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 395 light-years
Area: 979 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Sadalsuud (β Aqr)
Visible at: Latitudes between +65° and −90°
Best viewed: During the month of October at 9.00 pm
The Aquarius constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as The Water-Bearer. Aquarius is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek times and is associated with Prince Ganymede, captured by the God Zeus and carried off to Mount Olympus to become a cup-bearer.
Aquarius is the 10th largest of the 88 known constellations and can be found in the sky by locating Pisces the Fish and Capricornus the Sea-Goat. Aquarius is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the spectacular Saturn and Helix nebulas.
Read on to learn more about the constellations Aquarius and interesting Aquarius constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
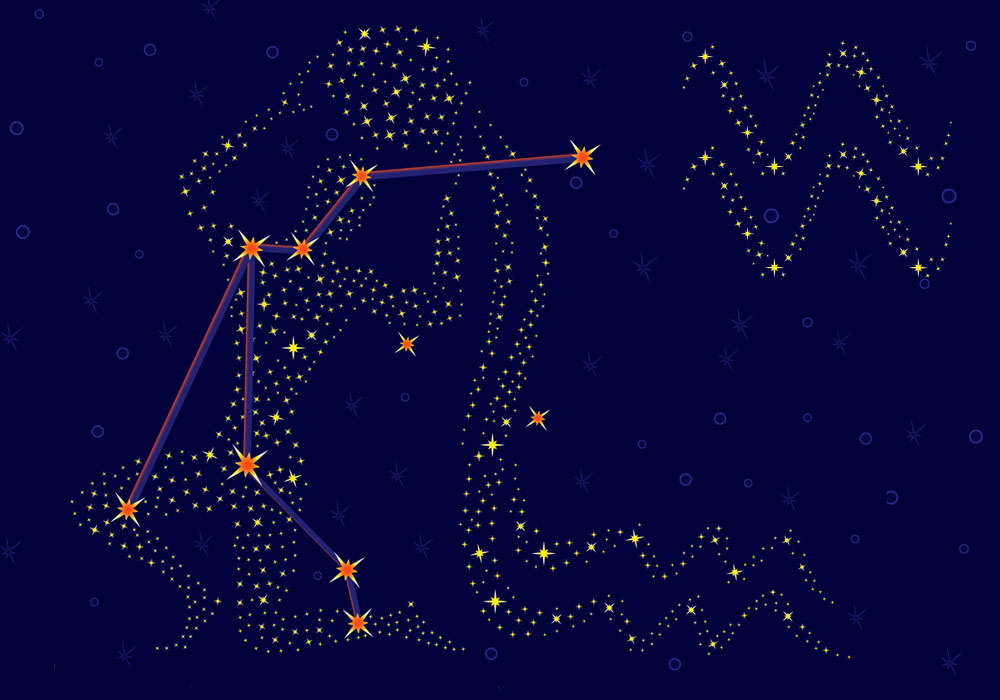
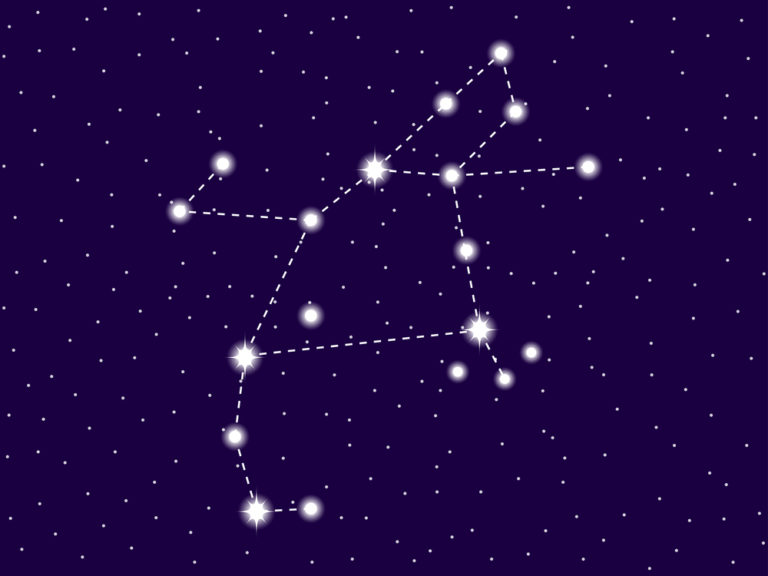
Aquarius constellation
Aquarius is a large constellation located in the southern celestial hemisphere. It has medium to bright stars with fascinating names like Sadalsuud and Sadalmelik.
Aquarius comes from the Greek myth of Prince Ganymede, captured by the God Zeus and carried off to Mount Olympus to become a cup-bearer. After Zeus became tired of the boy, he placed him into the sky where he continues to pour water out of his vessel.

The Aquarius (constellation) is the 10th largest constellation. It occupies an area of 979 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Pisces the Fish and Capricornus the Sea-Goat. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Pegasus, Equuleus, Delphinus, Piscis Austrinus, and Cetus.
For home astronomers, Aquarius the water bearer constellation offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains the fascinating star TRAPPIST-1 which has 7 orbiting planets similar to Earth. It also contains the amazing Saturn Nebula and the beautiful Helix Nebula, known as ‘The Eye of God’ (1).
In the case of Aquarius, both the Aquarius constellations and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The Aquarius constellation story dates back over 3000 years.
What does the Aquarius constellation look like?
You may be asking – what is Aquarius? Aquarius is a handsome young boy who was given eternal youth and life by the God Zeus. But, many pictures depict him as a much older and wiser man with a long flowing beard!
The water bearer constellation is a full bodied-man, unlike some other constellations that are only formed by half the person or creature. Aquarius stands upright in the sky. Balancing in the crook of his left arm is a large vessel, urn, or amphora. A prominent pattern of stars, known as an asterism, defines the urn.
These stars are the “Water Jar” and form a Y-shape. The jar is filled with water that continuously pours out, and flows down past his feet. Some stories say that the water is feeding the fish in the constellation of Piscis Austrinus, although we know that fish do not drink water!
Imagine the Aquarius galaxy with his huge legs slightly bent to support the weight of this massive urn. In his right hand, he sometimes holds the Norma Nilotica, a rod for measuring the depth of the River Nile (2). To complete the image of the water bearer, dress him in a flowing robe that swirls around his waist and over his hips.
How far is the Aquarius constellation from earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. In reality, this is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some stars may be as close as 40 light-years. Deep-sky objects may be as far as 60 million light-years away.
To give some idea, Sadalsuud is the brightest star in Aquarius and is about 540 light-years away. Sadalmelik is a G-type yellow supergiant, about 800 light-years away. Skat, also known as Delta Aquarii, is a blue-white star about 160 light-years away from our Solar System. Sadachbia, also known as Gamma Aquarii, lies about 158 light-years away. Sadaltager is a binary star about 103 light-years away. The famous R Aquarii is about 650 light-years away.
Much further away is the Saturn Nebula, at 3000 light-years. The Aquarius Dwarf galaxy is 3.1 million light-years away and the beautiful Helix Nebula is just under 700 light-years away.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the Aquarius star constellation from Earth is about 395 light-years. If you consider the deep sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years!
Zodiac family
The Aquarius symbol is the 11th sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between 20 January and 19 February. It is one of three Air signs, the others being Gemini and Libra.
The Aquarius zodiac constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Pisces the Fish, swim on the side of the water urn. Capricornus the Sea-Goat, lies below God’s feet.

The area of the sky in which Aquarius is found is known as the Sea. All these constellations are connected to water. In Greek mythology, although Aquarius is in the sky next to Pisces and Capricornus, he is not connected to them in any mythological Aquarius stories.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, the Aquarius constellation lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. The Sun passes through Aquarius each year from around 20 January to 18 February.
Here are some more Aquarius facts! The world is moving into the Age of Aquarius. The famous song, written in 1967 by 5th Dimension featured in the musical Hair.
Features
Major stars in Aquarius
Here is a list of the major Aquarius stars. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in Aquarius? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most interesting Aquarius constellation star names.
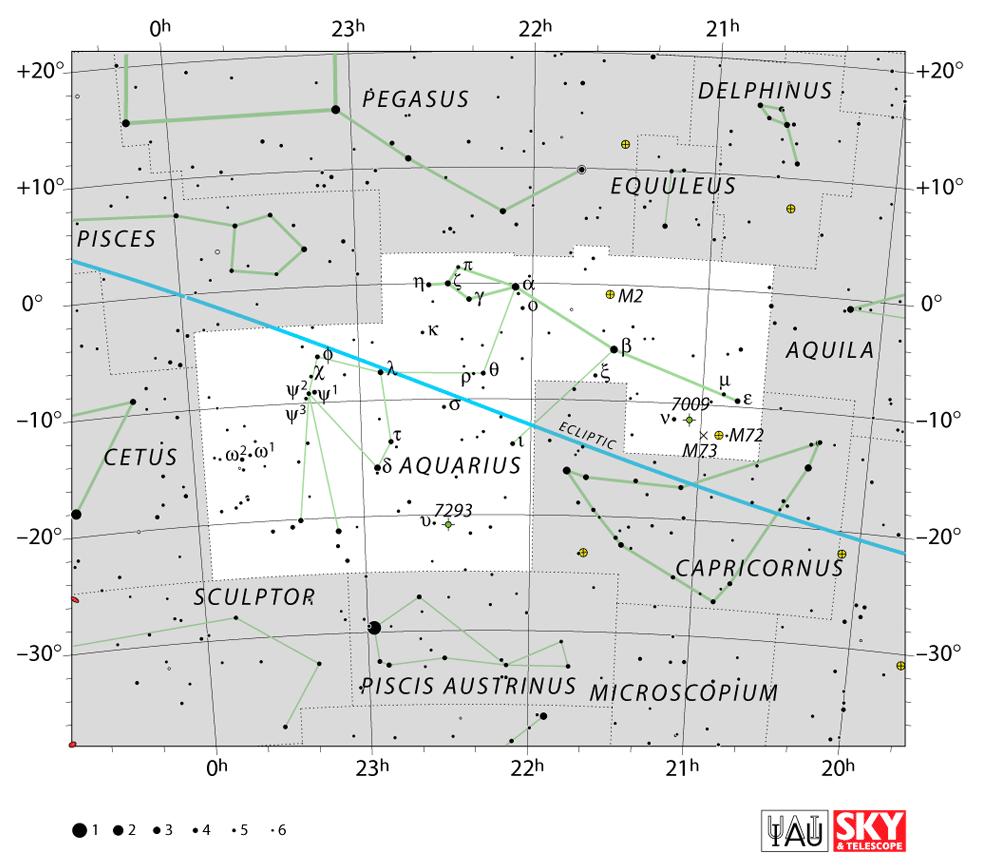
Here are the major Aquarius constellation stars and Aquarius star map (3)
- M2
- M72
- M73
- Sadalsuud
- Sadalmelik
- Skat
- Sadaltager
- Lambda Aquarii
- Albali
- Sadachbia
- Eta Aquarii
- Tau-2 Aquarii
- Ancha
- Phi Aquarii
- Iota Aquarii
- Psi-1 Aquarii
- Psi-2 Aquarii
- Omega-2 Aquarii
- Nu Aquarii
- Pi Aquarii
- Mu Aquarii
- Sigma Aquarii
- Omega-1 Aquarii
- Psi-3 Aquarii
- Situla
Sadalmelik – α Aquarii (Alpha Aquarii)
Sadalmelik is a yellow supergiant. It is 3000 times brighter than our Sun. The star has an apparent magnitude of 2.95 and lies 800 light-years away from our Solar System. The name of this Aquarius star comes from the Arabic “sa’d al-malik”, meaning “luck of the king”. Alpha aquarii lies on the right shoulder of the Aquarius water bearer.
Sadalsuud – β Aquarii (Beta Aquarii)
Sadalsuud is a rare yellow supergiant and is Aquarius brightest star. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.87 and is about 540 light-years away. Sadalsuud has a radius that is 47.88 times bigger than the Sun and it is 2,200 times brighter. The name comes from the Arabic phrase, sa’d al-suud.
This aquarian star meaning is “luck of lucks”. Beta Aquarii appears as a single star to the naked eye, however, it has two optical companions, making it a triple star. They are more distant and smaller and are not gravitationally bound with Sadalsuud. The star is about 110 million years old. Sadalsuud lies on the left shoulder of Aquarius (4).
Skat – δ Aquarii (Delta Aquarii)
Skat is one of the most interesting stars in Aquarius. It is also known as Delta Aquarii, and is a blue-white star with an apparent magnitude of 3.269. It lies about 160 light-years away from our Solar System. Skat is the 3rd brightest star in Aquarius. The name comes from the Arabic as-saq. This Aquarius star meaning is leg or shin, and the star lies at the right leg of the water-bearer. Delta Aquarii is the radiant point of the well-known meteor shower, the Delta Aquariids which you can see between mid-July to mid-August (5).
Sadachbia – γ Aquarii (Gamma Aquarii)
Sadachbia, also known as Gamma Aquarii, is a blue star that lies about 158 light-years away. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.84 and you can see it without using a telescope. The name comes from the Arabic phrase sa’d al-axbiyah, which means “luck of the homes”, referring to tents in this case. The 13th century Persian astronomical writer Al Kazwini called the star Al Sa’d (6). The star lies at the right arm of the water-bearer, at the inner edge of the urn.
Sadaltager – ζ Aquarii (Zeta Aquarii)
Sadaltager is a binary star of Aquarius with an apparent magnitude of 4.42. It lies about 103 light-years away. The brighter component is Zeta-2 Aquarii and is a yellow-white main sequence dwarf. The companion star, Zeta-1 Aquarii, is a yellow-white subgiant. If you look through a telescope, you can see both stars as separate entities. The name comes from the Arabic “sa’d al-tajir”, meaning “luck of the merchant”.
R Aquarii
R Aquarii is one of the stars of Aquarius that is of great interest to astronomers. It lies about 650 light-years away and is known as a symbiotic binary. This is a star system that comprises two stars surrounded by a large cloud of gas, called a nebula. In this case, the two star types are a white dwarf and a red giant. In this complex relationship, the white dwarf is stripping matter from its larger companion. The photo shows large spurts, loops, and trails of matter as this process takes place. The star system has an apparent magnitude of 7.69 (7).
Deep-sky objects in Aquarius
Messier 2 (M2, NGC 7089)
M2 lies north of the star Sadalsuud, Beta Aquarii. It is a spectacular globular cluster containing about 150,000 stars. The age of the cluster is around 13 billion years. The Universe is about 13.8 billion years old, which means that the cluster formed when the Universe was very young. M2, like other deep-sky objects, travels in the sky. It is moving toward us at about 5.3 kilometers per second.
M2 is one of the largest globular clusters known, with a diameter of 175 light-years. It lies about 37,500 light-years away and has an apparent magnitude of 6.3. The cluster was discovered by different astronomers, namely Italian astronomer Jean-Dominique Maraldi in 1746, Charles Messier in 1760, and German astronomer William Herschel, who was the first to resolve the stars in the cluster in 1783 (8).
Messier 72 (M72, NGC 6981)
M72 lies just below an imaginary line drawn from Sadalmelik to Sadalsuud, the two brightest stars in the constellation Aquarius. It is a globular cluster, about 54,570 light-years from Earth. The French astronomer Pierre Méchain discovered M72 in 1780. Charles Messier included the cluster in his catalog as a faint nebula and not as a cluster.
The cluster has an apparent magnitude of 9.35 and is about 106 light-years in diameter. It is around 9.5 billion years old. With a small telescope, you can see Messier 2 as a faint gas cloud, A larger telescope resolves the image and you can see it as a cluster (9).
Messier 73 (M73, NGC 6994)
Messier 73, also known as NGC 6994 is an asterism of four stars that appear close to each other, but are not connected in any way. They are all at different distances from the Earth and are moving in different directions. M73 has an apparent magnitude of 9.0 and lies about 2,500 light-years from Earth.
Charles Messier discovered the object in 1780. The stars of M73 are very faint and not easy to observe with the naked eye. To see the Y-shape clearly you need a minimum of a 4-inch telescope (10).
Saturn Nebula (NGC 7009, Caldwell 55)
The Saturn Nebula, also known as NGC 7009, is a planetary nebula that formed when a low-mass star evolved into a bright white dwarf. The main star has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is about 20 times brighter than our Sun. The surface temperature is about 55,000 K. In comparison, our Sun’s surface temperature is around 5.800 K.
The star offers images of a beautiful fluorescent green light, which comes from the strong ultraviolet radiation that it emits. Through a telescope, it appears to look much like Saturn, giving it the name Saturn Nebula. It lies about 3000 light-years away. Sir William Herschel discovered the Saturn Nebula in the late 18th century.
Helix Nebula (NGC 7293, Caldwell 63)
The Helix Nebula is one the closest bright nebula to Earth, at a distance of 700 light-years. It was discovered in the 19th century by Karl Ludwig Harding. The beautiful shape looks like an eye, giving it the nickname the ‘Eye of God’. The nebula has a size of 2.5 light-years and you can spot it west of Upsilon Aquarii.
A small telescope shows a patch of light and a larger scope resolves it into a beautiful eye shape. The image shows two discs of gas and dust almost perpendicular to one another. Scientists say that this is a complex planetary nebulae that is a product of a binary star system. In this system, one star takes up the material coming off its dying partner (11).
The Aquarius Dwarf (PGC 65367, DDO 210)
The Aquarius Dwarf is an irregular dwarf galaxy that is about 3.1 million light-years away and has a faint apparent magnitude of 14.0. It is one of few galaxies that has a blueshift. Blueshift means that the galaxy is moving towards the Milky Way, as opposed to redshift galaxies that are moving away. It was first cataloged in 1959 by the DDO survey and is a member of the Local Group of galaxies. The majority of stars are around 6.8 billion years old (12).
Exoplanets in Aquarius
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life.
TRAPPIST-1
TRAPPIST-1 is only 40 light-years away from Earth. In May 2016, scientists announced they had found three planet candidates around this star using the Transiting Planets and Planetesimals Small Telescope (TRAPPIST) in Chile. More planets have since been discovered – 7 in total. They are all Earth-sized worlds that are possibly rocky. Because they orbit in the habitable zone, this is an exciting discovery, where water may exist (13).
WASP-6 b
WASP-6 b is an exoplanet that orbits its mother star, WASP-6. WASP-6 is a G-type star, also known as a yellow dwarf. The planet is a gas giant with a mass of 0.37 Jupiters. It takes 3.4 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was announced in 2009.
WASP-47
WASP-47 is a main sequence yellow star. It has 4 exoplanets revolving around it. WASP-47 b, c, d, and e. The star lies about 200 light-years away. The planets have orbital periods of 4 days, 596 days, 9 days, and .78 days respectively. WASP-47 c is a gas giant that is 1.57 the mass of Jupiter and 1.21 its radius. WASP-47 b was discovered in 2012 and is about the same size as a Jupiter.
GJ 876
GJ 876 is a red M-type star with 4 known exoplanets. GJ 876 c is a gas giant exoplanet that orbits the mother star every 30.1 days. It has a mass of 0.7142 Jupiters. GJ 876 b is a much larger gas giant with a mass of 2.2756 Jupiters. It takes 61.1 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was announced in 1998 (14).
Meteor showers in Aquarius
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars. The water bearer offers some spectacular Aquarius showers.
Delta Aquariids
The Delta Aquariids originate close to the star Aquarius Delta Aquarii, also known as Skat. The shower originates from the comet 96P Machholz. It is a long lasting shower that you can see over a few months from July to September. It is best seen in the southern hemisphere and peak viewing times are the two hours before dawn (15).
The shower offers a southern and a northern display.
Southern Delta Aquariids
This shower is active from 12 July to 23 August 23 with the peak activity on 28 and 29 July. You can expect to see around 20 meteors per hour traveling at speeds of 41km/s. George Lyon Tupman noted observations of the southern Delta Aquariids in 1870. He was the Chief Astronomer for the British astronomical expedition to Hawaii to observe the 1874 transit of Venus.
Northern Delta Aquariids
The Northern Delta Aquariids last from 16 July 16 to 10 September 10 with a peak around 15 August. Expect to see an average of 10 meteors per hour, traveling at speeds of 41km/s (16).
Location and visibility
Where is the Aquarius constellation located?
Aquarius is a large constellation with medium to bright stars and you can easily spot once you know what to look for. In dark skies, you can see the main stars without a telescope. Then, you can imagine the Water-Bearer kneeling down with a large urn in his hand.

Where is Aquarius in the sky?
Aquarius is a southern constellation and is the 2nd largest zodiac constellation occupying an area of 979 square degrees. Is it the 10th largest constellation of the 88 named constellations.
Aquarius lies in the fourth quadrant of the southern hemisphere, SQ4. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes +65° and −90°.
To find Aquarius you can locate the two zodiac constellations of Pisces the Fish and Capricornus the Horned-Goat. The Fish are on the west side of the urn.
Capricornus lies underneath the god of Aquarius. The area of the sky in which Aquarius is found is known as the Sea. This area also contains the water-related constellations Pisces the Fish, and Capricornus the Sea-Goat.
When is the Aquarius constellation visible?
Aquarius is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.

Northern hemisphere
If you are in the northern hemisphere – In August and September look low on the eastern horizon around 11pm. In October he will appear low in the eastern horizon around 8pm and then continue towards the western horizon until daybreak.
In November, December, and January, Aquarius is visible much earlier, at around 6pm to 8pm.
A good time to take the children out for some stargazing. If you stay up later and track the Aquarius constellation with a telescope, you will watch it dip below the western horizon at around midnight.
Southern hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere, In October you can spot Aquarius God of water, at around 9pm low on the eastern horizon. In November the constellation will appear in the north-eastern night sky at around 10pm. In December it appears for a short time in the north-west between 11pm and 2am.
Remember – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down. The water-bearer will be throwing his water upwards instead of pouring it downwards! (17).
How to find the Aquarius constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Read on to see how to find the Aquarius constellation.
- To find the Aquarius constellation location, it is easiest to first pinpoint the Great Square of Pegasus
- Imagine a line joining the lower 2 corners of the square, it lies at a diagonal, forming a V-shape
- In line with the V, and to the west, are the two ropes that tie Pisces the Fish together
- So, where is Aquarius? Aquarius stands facing Pisces. Look for the distinct asterism, the Y-shape Aquarius star pattern that forms the Water Jar
- You can also locate Capricornus the Sea-Goat
- Look directly upwards and you will find the legs of Aquarius
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so where is the Aquarius constellation?
- To find the Aquarius location, it is easiest to first find the Great Square of Pegasus
- Imagine a line joining the upper 2 corners of the square, it lies at a diagonal, forming a V-shape
- In line with the V, and to the east, are the two ropes that tie Pisces the Fish together
- Aquarius stands facing Pisces, with the distinct asterism of stars Aquarius, a Y-shape that forms the Water Jar
- You can also locate Capricornus the Sea-Goat
- Look directly downwards and you will find the legs of the Aquarius star constellations
How to view Aquarius Constellation?
Aquarius is a large constellation but does not have the brightest stars in the sky. Getting away from city lights is the best way to see it. You can see the Aquarius water constellations with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make your Aquarius astronomy experience so much more exciting.

For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Aquarius. Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Orion 09007 SpaceProbe 130ST Equatorial Reflector Telescope is a well-priced scope at around $300. It is ideal for a family looking to start stargazing as a hobby. It has a large 5.1-inch aperture. The optical tube weighs only 27 lbs, making it easy to pack into a car. Included in the kit are two Sirius Plossl eyepieces, a 25mm and a 10mm.
You also get a 6×30 FinderScope and a tripod accessory tray. The sturdy EQ-2 equatorial telescope mount and adjustable tripod allow smaller children to see great views of the constellation of Aquarius and learn about the story of Aquarius.
History of observation
Who discovered the Aquarius constellation?
Aquarius history dates back to ancient civilizations of the Greeks, Egyptians, and Sumerians, and was documented in stories, folklore, and myths.
The Greek Aquarius constellation myth dates as far back as 3000BC. It associates with the handsome Trojan Prince, Ganymede, son of Tros of Dardania. He was captured by Zeus and taken to Mount Olympus to be a cup-bearer for the Gods.

Even older than this, around 4000BC, Sumerian astronomers linked the constellation to a youth who was the bearer of a destructive flood that ravaged the entire planet. This may also indicate the Biblical flood of Noah (18).
The Egyptians also knew of the water bearer around the 3rd century BC. He is the God of the Nile, Hapi, who distributed the waters of life by flooding the River Nile onto the adjacent lands.
In traditional Chinese uranography, around 750BC, the modern constellation Aquarius lies within the northern quadrant of the sky, symbolized as the Black Tortoise of the North. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese means “the precious pitcher constellation” (19).
In recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Aquarius constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is the Aquarius constellation?
Aquarius is an ancient constellation, and Aquarius history dates back to the era of Greek mythology around 3000BC. The constellation depicts
the myth of Aquarius in which Prince Ganymede was captured by Zeus and taken to Mount Olympus to be a cup-bearer for the Gods. After Zeus tired of the boy, he gave him eternal life and placed him into the sky.

A century before this, around 4000BC, Sumerian astronomers linked the Aquarius constellation history to a youth who was the bearer of a destructive flood that destroyed the planet and may be linked to the Biblical flood of Noah (20).
The Egyptian Aquarius dates back to the 3rd century BC. He is the God of the Nile, Hapi, who distributes the waters of life by flooding the River Nile onto the adjacent lands.
Aquarius is also an old Chinese constellation known as far back as 750BC. It lies within the northern quadrant of the sky, symbolized as the Black Tortoise of the North.
How did the Aquarius constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, how did Aquarius get its name?
Like many other signs of the zodiac, Aquarius in greek mythology has Latin roots. The base of the word is ‘aqua’ which means water. ‘Aquarius’ means “water-carrier”. Aquarius also relates to an aquarium, a container for fish.
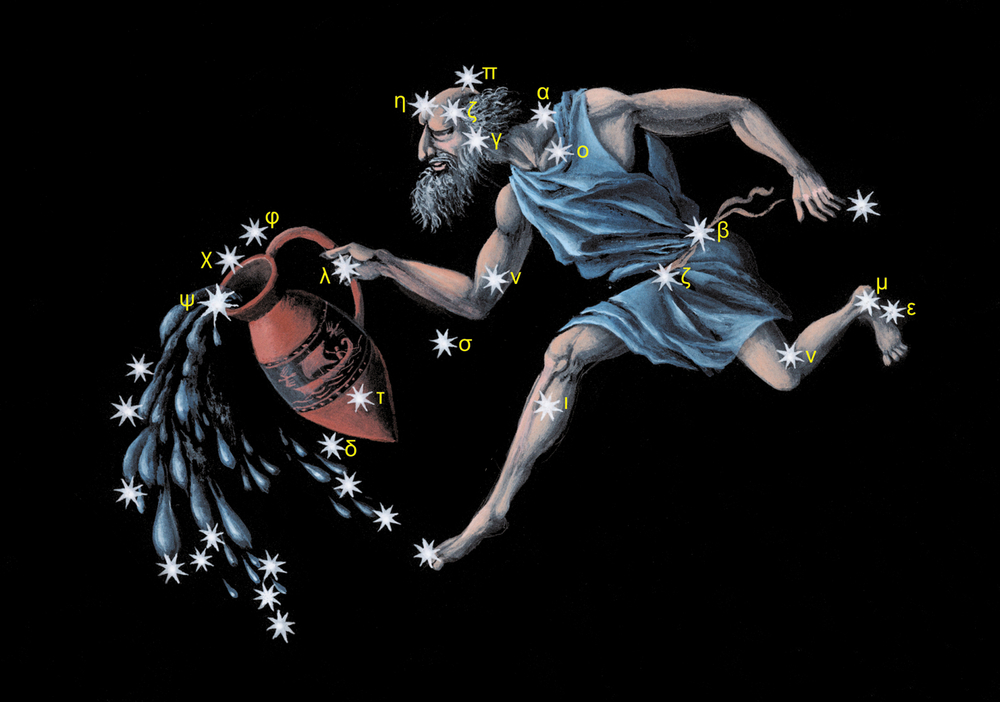

In Aquarius greek mythology, the water carrier, or water bearer, was the young Prince Ganymede, who was captured by Zeus and taken to Mount Olympus to be a cup-bearer for the Gods. He relates to water, as he is constantly pouring water from a vessel that he holds.
The constellation also has Indo-European roots. So what does Aquarius mean? The root *akw-a, means water, as in flowing water. Derivatives are aquatic, aquamarine, aqueduct, all related to water. The Aquarius nickname or abbreviation is ‘aqr’.
Aquarius is also related to Aquila, the Latin word for Eagle. Zeus disguised himself as an eagle to capture the prince. The eagle was also placed into the sky and became the constellation Aquila (21).
Mythology and meaning
Aquarius myth
Like many of the constellations, there are different Aquarius mythology stories.
In the ancient stories of Greek Gods, the Aquarius constellation mythology tells the story of a handsome Trojan Prince, Ganymede, son of Tros of Dardania, founder of Troy. Ganymede was herding sheep when Zeus, King of Gods, noticed him and was fascinated by his beauty.

Zeus disguised himself as an eagle. He captured the boy and took him to Mount Olympus to become a companion for Zeus and an Aquarius greek god cup-bearer for the Gods. Zeus gave the prince immortality and eternal youth. His father, Tros, was not happy, but Aquarius God Zeus pacified him by offering beautiful horses as a gift.
After time, Zeus became bored with Ganymede and placed him into the sky as the constellation Aquarius. In this Aquarius greek myth, Zeus also placed the eagle in the sky, forming the constellation Aquila (22).
In the Sumerian mythology of Aquarius, the youth was the bearer of a destructive flood that ravaged the entire planet, linking to the Biblical flood of Noah. This version of Aquarius myths tells of Aquarius holding the vessel from which the floodwaters flowed down from heaven onto the Earth.
You may ask – who was Aquarius in Egyptian mythology? Aquarius Egyptian mythology links the constellation to the God of the Nile, Hapi.
This generous God distributed the waters of life, and the urn symbolized the fountain of good fortune. In this Aquarius story, he holds the Norma Nilotica, a rod for measuring the depth of the River Nile (23).
What does Aquarius symbolize?
As you see in the above picture, Aquarius is the water bearer, a symbol of the Gods bringing nourishment to the Earth in the form of life-giving water. The Aquarius sign is progressive, independent, intelligent, unique, and idealistic. Aquarians can be the best socializers or the most hidden, solitary recluse. The symbol represents a character that is assertive, analytical, and very original. Aquarians desire to be different.

Their elemental sign is air, the same as that for Gemini and Libra. Air signs are intellectual and curious. Aquarius has a fixed modality, representing the power of sustaining. The role of fixed signs is to secure and stabilize the planet after the cardinal signs. Aquarians have very strong opinions.
On the negative side, Aquarius meaning wants to have things their way, or they become uncomfortable or unhappy. Aquarius is slow to change and often spends a lot of time trying to change people, which clashes badly with other strong zodiac signs. They can be emotionally detached and rebellious (24).
Many people ask – what is the Aquarius planet? Uranus is the planet that rules the personality of the water bearer. You may also ask – what is the god Aquarius? Aquarius is not a god, he is a prince who was given eternal life by God Zeus.
Here are some famous Aquarius personalities – Abraham Lincoln, Oprah Winfrey, Galileo Galilei, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Yoko Ono, and Michael Jordan (25).
Future of Aquarius constellation
Aquarius is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study.
The star R Aquarii is changing as we speak. It is part of a binary star system comprising a white dwarf and a red giant. The white dwarf is stripping matter from its larger companion, by absorbing the outer layers of material. This results in spectacular images seen through a telescope. Scientists call this the ‘death throes’ of the stars, and they will become 1000 times brighter than our Sun before burning out (26).

Another intriguing event is a bright star that suddenly ‘disappeared’ from the constellation. Scientists believe that it was blocked by a large cloud of dust, or it turned into a black hole. If this happened, it bypassed the stage of becoming a supernova. This may be the first time that scientists see such an event. The star, PHL 293B, lies in the Dwarf Galaxy, 75 million light-years away (27).
The Helix Nebula has a white dwarf at its center that is in the final stages of dying. As it dies, it explodes and throws ultra-violet gas, dust, clouds, and cosmic matter. Planets around the star are swallowed up, tossed around, and may even crash into one another. This leads to a spectacular show when viewed through a telescope (28).