Aries Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Aries Constellation
Abbreviation: Ari
Symbolism: The Ram
R.A. position: 01h 46m 37.3761s – 03h 29m 42.4003s
Dec. position: 31.2213154°–10.3632069°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 123.5 light-years
Area: 441 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Hamal (Alpha Arietis)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −60°
Best viewed: During the month of December at 9.00pm
The Aries constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as the Ram. Aries is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek Mythology. Aries is the second smallest zodiac constellation.
It has a fascinating story and offers some amazing spiral galaxies that lie millions of light-years away. With bright stars Hamal, Hamal, Sheratan, and the famous 41 Arietis, there are exciting viewing nights ahead for home stargazers.
Read on to learn more about the Aries constellation story and interesting Aries facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
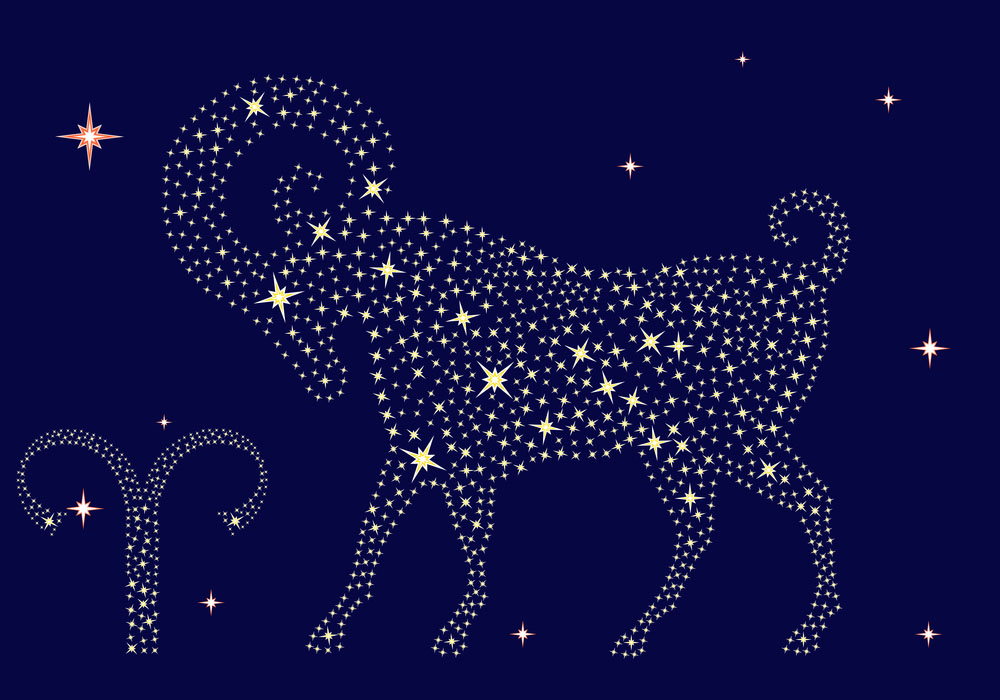
Aries constellation
Aries is an exciting constellation that is found in the northern sky. The Ram is a mythical creature with powers to fly. He gallops across the sky on a mission to save the twins, Phrixus and his sister, Helle, from their evil stepmother.
The Aries (constellation) is the second smallest of the zodiac constellations and the 39th overall in size. It occupies an area of 441 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Pisces the Fish, and Taurus the Bull. Aries bordering constellations that are not part of the Zodiac are Cetus, Triangulum, and Perseus (1).

For home astronomers, the Aries constellation ram offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains bright stars Hamal, Sheratan, and the famous 41 Arietis. It also offers the stunning spiral galaxies NGC 772 and NGC 972. For those wanting to experiment with astrophotography, NGC 1156 is a beautiful dwarf irregular galaxy that offers amazing images resembling cherry blossoms.
In the case of Aries, both the constellation and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The story of Aries dates back over 3000 years to Greek mythology (2).
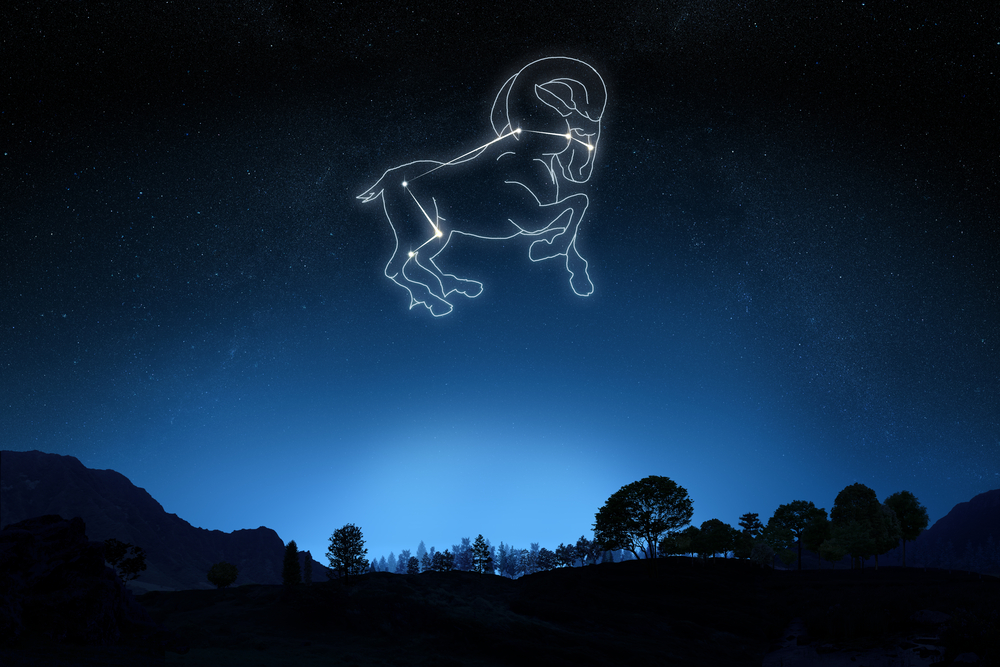
What does Aries constellation look like?
With many bright stars at strategic points, the Ram is a constellation that you can draw with your eye in the sky. The constellation Aries looks like a huge ram leaping across the sky. He is a full-bodied animal, unlike some constellation creatures who are only half-formed.
The ram has two massive horns on his head, depicted by the stars Sheratan and Mesarthim. His front legs point forward in a galloping stance. The back legs are drawn up to give the animal speed. You can imagine the Ram looking backward over his shoulder – perhaps he is checking that Taurus the Bull is not following him as he rushes to save the twins Phrixus and Helle. The star Botein marks the belly of the Ram and forms part of the famous triangle that lies on his hindquarters.
If you look at the star pattern that defines Aries astronomy, you see a shape that resembles a flattened X, with the left side much longer than the right side. Aries constellation star names (3):
- Hamal
- Sheratan
- 41 Arietis
- Mesarthim
- Botein
- Epsilon Arietis
- Lambda Arietis
- Zeta Arietis
How far is Aries constellation from earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be “close’ to Earth at less than 100 light-years distant. Others are millions of light-years away.
To give some idea, Hamal is the brightest star and lies about 66 light-years away. Sheratan is a binary star system and is 59.6 light-years from Earth. Gamma Arietis lies at a distance of 164 light-years away. Delta Arietis, is about 168 light-years from us. 41 arietis, a triple-star system is 160 light-years away.
Constellations are not only made up of stars. They also contain deep sky objects like Messiers and Nebula. In the Aries zodiac constellation, NGC 972 lies about 50 million light-years from Earth.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Aries constellation from Earth is 123.5 light-years. If you consider some of the deep sky objects, the distance can increase to be millions of light-years.
Zodiac family
Aries is the first sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between March 20 to April 19. It is one of three fire signs, the others being Sagittarius and Leo. Fire signs are strong and passionate with a great desire to learn.
The Aries zodiac constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Pisces the Fish, swim in front of the Ram. Taurus the Bull lies behind and below his back legs.

Aries is leaping through the sky, on a mission to achieve. Although they stand close to one another in the sky, constellation Aries does not connect with Pisces or Taurus in any mythology stories.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, Aries the ram constellation
lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. The Sun passes through Aries space each year from around April 19 to May 14. That is why autumn in the
southern hemisphere, and spring in the northern hemisphere is the wrong time of year for viewing the constellations Aries. You will find that the sun obscures the Ram (4).
Features
Major stars in Aries
Which is the brightest star in the Aries constellation? This is the first question new stargazers ask! Read on for an interesting list of the major ram stars and interesting facts about Aries constellation stars.
Hamal – α Arietis (Alpha Arietis)
Hamal is the brightest star in Aries and the 48th brightest star in the night sky. Also known as Alpha Arietis, this K-type orange giant has an apparent magnitude of around 2.04. It is twice as massive as the Sun. The star lies about 66 light-years away. In Arabic, Hamal means Lamb. The name comes from the Arabic phrase, rās al-ħamal, which means “head of the ram”.
Hamal is one of the 58 bright stars selected for navigation. Navigational stars are part of a conspicuous asterism or star pattern. Hamal forms a distinctive triangle in the Aries star formation together with nearby stars, Sheratan and Mesarthim in the Aries ram constellation (5).
Sheratan – β Arietis (Beta Arietis)
Sheratan, Beta Arietis, is a binary star system and is the second brightest star in Aries. It lies about 59.6 light-years from Earth and has an apparent magnitude of 2.6. Sheratan marks one of Aries horns.
Sheratan and its partner orbit one another in a time period of 106 days. These stars in Aries constellation are a spectroscopic binary system, which means that a telescope will not resolve the two individual components.
The name derives from an Arabic phrase aš-šarāţān, which means “the two signs,”, referring to the vernal equinox between 2000BC and 100BC. You can see the star without using a telescope (6).
Mesarthim – γ Arietis (Gamma Arietis)
Gamma Arietis is another binary star system located in the Aries (constellation). With a combined apparent magnitude of 3.86, it is the fourth brightest star in Aries. It lies about 164 light-years from Earth. Mesarthim has a radius that is 1.90 times that of the Sun. The name means the ‘fat ram’ and it marks one of the ram’s horns. You can see these stars in Aries without using a telescope. Together with Hamal and Sheratan, it forms the triangle of stars selected for navigation (7).
Botein – δ Arietis (Delta Arietis)
Delta Arietis, also known as Botein, is an orange K-type giant star with an apparent magnitude of 4.35. It has a diameter 13 times that of the sun. The name comes from the Arabic Al Butain and means ‘little belly’ and indicates the belly of the Ram.
Botein is about 168 light-years from Earth. You can see the star in the Aries star constellation without using a telescope. Botein is part of star classifications known as red clump giants. This means that it is generating energy through the fusion of helium at its core (8).
Bharani – 41 Arietis (c Arietis)
41 arietis is a triple-star system in the Aries constellation. The brightest component is a blue-white dwarf star and has the name Bharani. It lies about 160 light-years away from Earth. The apparent magnitude is 3.61 which means you can see it without the need for a telescope. Its estimated age is around 130 million years. Bharani is about 160 times more luminous than our Sun. In Hindu Astronomy, the second lunar mansion has the name Bharani (9).
ε Arietis – Epsilon Arietis
ε Arietis is a binary main sequence white star in the ram constellation. It is made up of two white A-type main sequence dwarfs. The stars lie about 293 light-years from Earth and have a combined apparent magnitude of 4.63. This means that you can see it in dark skies without a telescope. In the city, you probably will not be able to see Epsilon Arietis. This Aries star lies inside the body of the Ram just above the belly star, Botein (10).
Deep sky objects in Aries
NGC 772
NGC 772, is also known as Arp 78. It is an unbarred spiral galaxy that lies about 130 light-years away from Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.3. NGC is a spiral galaxy with spiraling arms, a glowing centre, a mixture of bright specks of star formation, and dark ripples of cosmic dust. It sounds very similar to our Galaxy, the Milky Way! It is different in that it does not have a central bar, hence the description ‘unbarred’ galaxy. In the lamb constellation, it lies southeast of Beta Arietis (11).
NGC 1156
NGC 1156 is a beautiful dwarf irregular galaxy that offers stunning images resembling cherry blossoms. An irregular galaxy does not have the classic shape of a spiral or rounded shape. NGC 1156 is very faint at an apparent magnitude of 12.3 and you need a powerful telescope to see it. The bright ‘blooms’ are known as stellar nurseries. These are active regions where new stars are being born. Scientists believe that the galaxy had a close encounter with another galaxy in its past. This explains the pockets of gas within NGC 1156 that rotate in the opposite direction to the rest of the galaxy (12).
NGC 972
NGC 972 is a spiral galaxy that lies in the northern corner of the Aries constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 12.1 and lies about 50 million light-years from Earth. The size of the galaxy is about 70,000 light-years across. NGC 972 was discovered on September 11, 1784, by the German-British astronomer William Herschel. Scientists believe that the presence of huge star-forming regions in NGC 972 are probably the result of a merger with a gas-rich companion in the past (13).
NGC 697
NGC 697 is a small but bright galaxy in the constellation of Aries. Using a powerful 10” telescope it looks like an elongated patch of light with a bright center. It lies northwest of Beta Arietis and has an apparent magnitude of 12.7. It is a barred -spiral galaxy and lies about 143 million light-years from the Milky Way. It has a size of about 165,000 light-years across (14).
Exoplanets in Aries
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to Earth, and hence the possibility of life. Aries contains several stars with extrasolar planets.
HIP 14810 b, c, d
HIP 14810 is a G5 type star, orbited by 3 giant planets, each one bigger than 10 times the mass of the Earth. The exoplanets have names HIP 14810b, HIP 14810c, and HIP 14810d. The planets are around 174 light-years from Earth. They orbit their main star with orbital periods of 6,147 and 962 days respectively (15).
Teegarden’s b and c
Teegardens is a main sequence star. Two planets orbit the star, Teegarden’s b and Teegarden’s c. An international team of astronomers from the University of Göttingen announced the discovery on June 18, 2019. These planets are exciting in that they are some of the closest found so far to us at a mere 12.5 light-years away. These planets are the joint fourth-nearest habitable zone exoplanets to Earth (16).
HD 12661 b
HD 12661 b is a gas giant planet orbiting its main star, HD 12661. The main star is a G-type main sequence star, slightly larger than the Sun. HD 12661 b is 2.43 times the size of Jupiter. It takes 262.7 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was announced in the year 2000. HD 12661 also has a second planet known as HD 12661 c. it is 1.57 times the mass of Jupiter (17).
HD 20367 b
HD 20367 b is a planet discovered in 2002, with a mass slightly bigger than Jupiter. It orbits its mother star HD 20367, every 500 days. The mother star is about the same size as our Sun. The planet is about 85 light-years away from Earth (18).
Meteor showers in Aries
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show and makes for great viewing if you can get away from city lights.
May Arietids
The May Arietids occur between 22 May and 2 July. The peak is around 8 June. This shower radiates from the star Epsilon Arietis. The speed of the meteors is 39 km/s.
Autumn Arietids
The Autumn Arietids shower is seen from 7 September to 27 October with the peaks on 9 October. You can expect an hourly rate of 3 to 5 meteors (19).
Delta Arietids
The Delta Arietids meteor shower occurs between 8 December and 2 January. Meteors travel at speeds of 29km/s. The closest star to the radiant point is HD 59640. This shower was discovered in 1959 by analyzing photographic meteor orbits (20).
Epsilon Arietids
This meteor shower occurs between 24 April and 27 May with the peak on 9 May. The meteors radiate outwards from the star Epsilon Arietis. You can expect to see about 4 meteors per hour, traveling at speeds of 23km/s (21).
Daytime-Arietids
The Daytime Arietids are the strongest daylight meteor shower in the year. You can see it between 14 May and 24 June with the peak occurring on 8 June. This shower occurs in daylight hours but offers up to 60 meteors per hour at speeds of 38km/s. so you may spot some! Epsilon Arietis is the closest star to the radiant point of the meteor shower (22).
Aries-Triangulids
The Aries-Triangulids were discovered quite recently in September 1993, when an unexpected shower activity was observed (23).
Location and visibility
Where is Aries constellation located?
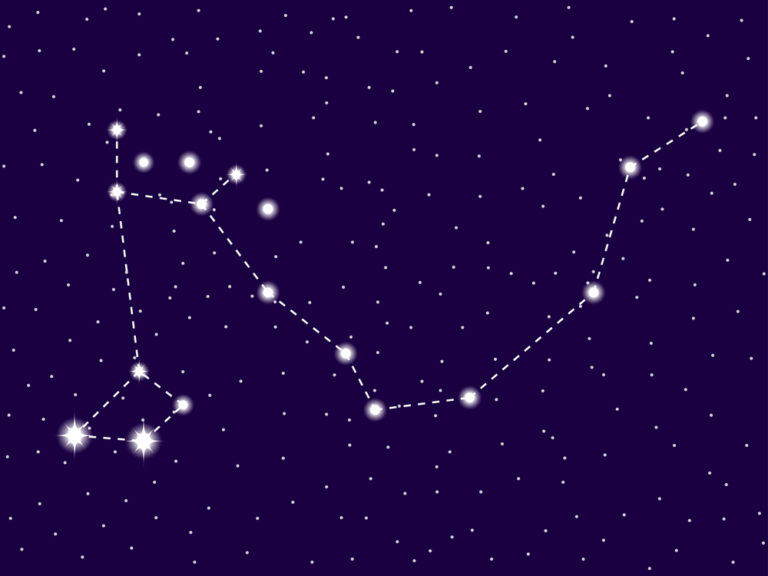
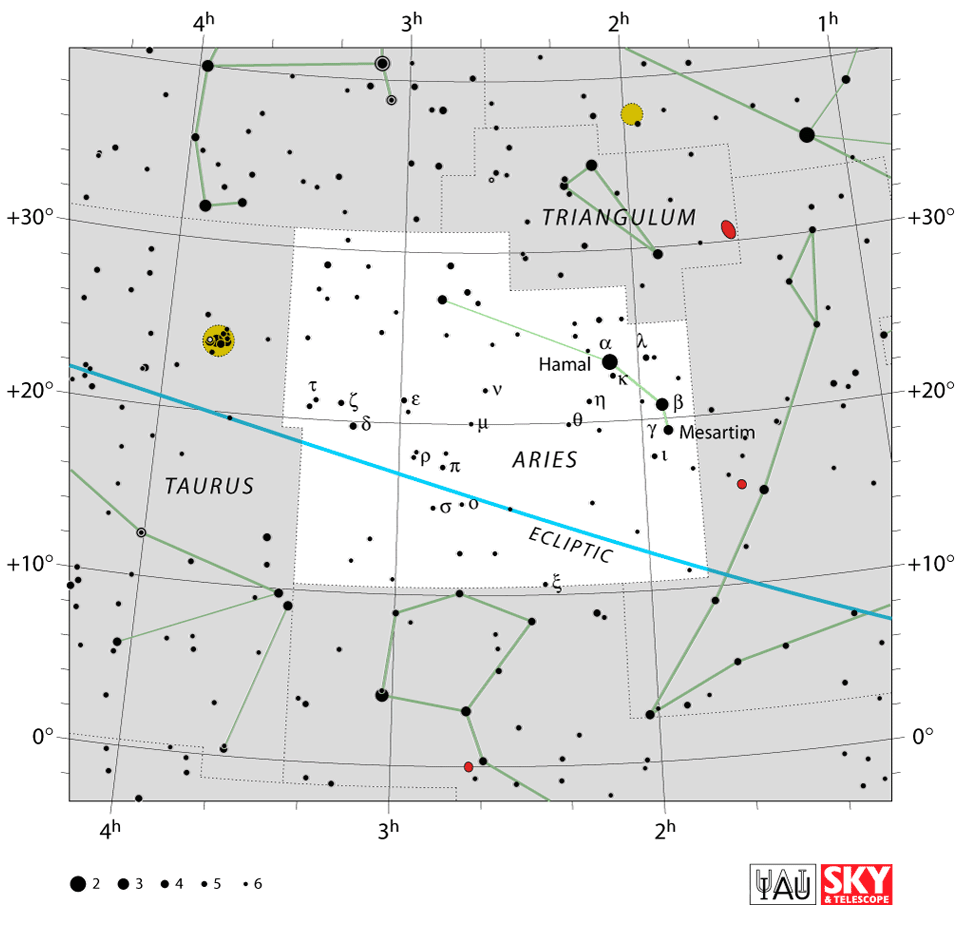
Use this Aries constellation map to see where is where is Aries located in the sky.
Aries the constellation is easy to find once you know what to look for. You can see the bright stars without a telescope. Then you can imagine the Ram leaping across the sky. In Aries the ram mythology, he is on a mission to save the twin brother and sister, Phrixus and Helle, from their evil stepmother, who wanted to kill them.

The ram constellation is the 39th largest constellation in the sky and is predominantly a northern constellation. It is the second smallest of the twelve Zodiac constellations and occupies an area of 441 square degrees. Capricornus is the only constellation smaller than Aries, with a size of 413 square degrees.
The Aries star constellation lies in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ1. A quadrant is a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see Aries in the sky at latitudes +90° and −60°.
To find the Aries ram constellation, you can locate the two neighboring zodiac constellations. Look for Pisces the Fish and Taurus the Bull. The Fish are swimming directly in front of the Ram. Taurus stands behind and below Ram’s back legs. Another tip to see the Aries constellation location is to find the famous Pleiades star cluster near to the bow of Orion. Aries lies to the right of the bright cluster (24).
When is Aries constellation visible?
As a home stargazer, you may ask – when is Aries visible? Read on to find out. The Aries galaxy is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.

Northern hemisphere
In the northern hemisphere, you can spot Aries constellation in the sky
in the month of October, November and December. In late October, the Ram rises in the east at around 6.00pm and reaches its highest point in the sky at midnight. It then moves to the west until day break. November and December are also good months for viewing Aries the ram. He rises above the eastern horizon at around 6.00pm and reaches the highest point at around 10.00pm.
Southern Hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere, Aries is best seen in spring to mid summer. In fact, the evening rising of the triangle in the Ram, marks the coming of summer for astrologers (25).
In September, October, November, and December, the Aries (constellation) will appear just above the northern horizon at around 9.00pm and move slowly across the sky (26).
How to find Aries constellation?
Although Aries is a fairly faint constellation, it does have bright magnitude stars that will help you to find the Aries location.
Northern Hemisphere
- Most home stargazers can find the three stars in the belt of Orion, so let’s start there!
- Extend a line from upwards to the brightest star you can see – it is Aldebaran, the eye of the bull
- From there, continue your imaginary line and look for the bright cluster of stars known as the Pleiades
- Hop across with a straight line to the right of the Pleiades and you will find the bright star Hamal, at the head of the Ram
- Look for two stars forming a triangle, those are the tips of the horns
- Extending a line backward from Hamal you can imagine the body of the ram with legs underneath
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down.
- Most home stargazers can find the three stars in the belt of Orion, so let’s start there!
- Extend a line from downwards to the brightest star you can see – it is Aldebaran, the eye of the bull
- From there, continue your imaginary line and look for the bright cluster of stars known as the Pleiades
- Hop across with a straight line to the left of the Pleiades and you will find the bright star Hamal, at the head of the Ram
- Look for two more stars forming a triangle, those are the tips of the horns in the Aries constellation mythology
- Extending a line upwards from Hamal you can imagine the body of the ram with legs pointing upwards!
How to view Aries Constellation?
To get the best views of any of the Zodiac constellations, it is preferable to get away from city lights and pollution. You can see the main Aries constellation stars with the naked eye or with a pair of binoculars.
But, to really get fabulous views, you need a telescope! For home stargazers, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you amazing images of the sheep constellation.

Depending on your budget, plan to spend between $250 to $900 on an instrument that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Celestron AstroFi 90 Telescope is a refractor telescope that will take you from beginner to intermediate levels. It has connectivity to iPhone and also offers integrated WiFi. Using the Celestron SkyPortal App, you can easily find any Aries stars you want.
Just tap the screen and the telescope automatically moves to the sky object and the screen displays information about it. It features a 90mm refractor with fully coated glass optics. It comes with two Kellner eyepieces, a 25mm, and a 10mm, and a Star Diagonal Finderscope. The tripod has an adjustable height, great for smaller children to use with ease.
History of observation
Who discovered Aries constellation?
Many ancient cultures have folklore and myths that are thousands of years old, telling stories about the Aries origin.
The ram was a prized animal to the nomad Bedouin tribes in the Middle East. It was also documented in the Book of Wonders, a 14th and 15th century Arabic manuscript.

In ancient Egyptian astronomy around the 3rd century BC, Aries was the god Amon-Ra, who was depicted as a man with a ram’s head and represented creativity and fertility. Ram-headed sphinxes are found at the entrance to the temple of Amun at Thebes. The bodies of rams were mummified and dressed in gilded masks and even jewelry.
The most famous mythology of Aries is found in Greek mythology dating back to 3000BC. In the story, the Ram is a flying creature who saves the twins, Phrixus and Helle, children of a Boeotian king. Their stepmother wanted to kill them, but the Ram placed them on his back and flew to Colchis.
The famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Aries constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD (27).
How old is Aries constellation?
Aries is an ancient constellation that dates back to the age of greek mythology Aries around 3000BC. The Aries constellation story tells of twins, Phrixus and Helle who had to escape from their evil stepmother. The Ram saved them, by allowing them to ride on his back as he flew with them to Colchis.
The ancient Egyptians knew the Ram constellation around the 3rd century BC. In this Aries the ram myth, he is the God Amon-Ra, and is known as a man with a ram’s head.

The ancient city of Meroë in Sudan was the administrative center for the kingdom of Cush, around 750 BC. It became a prosperous region and survived a Roman invasion. The Ram Aries in mythology dominates these ancient pyramids of Meroë (28).
Ancient Chinese astronomers around 750BCE also knew the Ram. In traditional Chinese uranography, the constellation Aries is located within the western quadrant of the sky. It is symbolized as the White Tiger of the West. The name of the constellation in modern Chinese is bái yáng zuò, which means “the white sheep constellation” (29).
In biblical times, the Book of Genesis 22:10-13, written by Moses, speaks of the Ram. “Then Abraham lifted his eyes and looked, and there behind him was a ram caught in a thicket by its horns. So Abraham went and took the ram, and offered it up for a burnt offering instead of his son”.
How did the Aries constellation get its name?
You may ask – Aries is a constellation named after what animal? The answer is a Ram! So, what does Aries mean? It is a simple translation, in Aries etymology, the word comes from the Latin which means Ram.

Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. You may ask – what is the Aries constellation meaning? The Ram is a powerful creature with great strength. Using his magical powers in the Aries story, he rescued the twins Phrixus and Helle and flew with them on his back to safety. Unfortunately, Helle fell off and drowned in the sea.
The Hebrew word for the ram symbol, the horn, is shofar, from Hebrew shophar, ‘ram’s horn’. It relates to the Arabic sawafiru, which also means ‘ram’s horns’. The shofar was blown at mount Sinai, when the Torah was given, and came from the ram that was sacrificed in place of Isaac.
Here is an interesting story answering the question – how did Aries get its name? Another derivative of the word Aries, comes from the word Ares, which relates to the planet Mars. Mars is the ruling Aries planet of the zodiac sign. The word Aries in Greek comes from the word Κριός, Krios (30).
Mythology and meaning
Aries myth
In Greek myth, the Aries symbol is the Golden Ram. Phrixus and his twin sister, Helle, were the children of a Boeotian king. The children’s stepmother, Ino, hated them and plotted to get rid of them. She devised a plan to ensure that the wheat crops would fail and plunge the land into famine.

In the Aries legend, the local farmers, frightened of famine, asked a nearby oracle for assistance. Ino bribed the messengers sent to the oracle to lie and tell people that the oracle required the sacrifice of Phrixus and Helle to stop the famine. Their natural mother, Nephele, sent a flying Ram to rescue the children. During the escape flight, Helle fainted and fell off the Ram into the Sea and drowned. To this day, according to the Aries constellation myth, the area is known as the Hellespont, the sea of Helle.
Phrixus survived the trip to Colchis, where King Aeëtes, the son of the sun god Helios, took him in. He had a happy life and married the King’s daughter, Chalciope. To show his gratitude, Phrixus sacrificed the Ram to Zeus and gave the king the fleece of the Ram. In a further story of Aries constellation history, Jason and his crew of Argonauts, set out on a quest to retrieve the Golden Fleece.
What does Aries symbolize?
Here are some more fascinating Aries constellation facts.
Aries mythology symbolizes a Ram, a flying, swimming creature of great power. Aries is the first sign of the Zodiac and as such it symbolizes leaders, innovators, and those who get things done. Aries will surmount incredible obstacles and achieve the impossible, as the Ram did in the Aries myth when saving Phrixus and Helle from their stepmother, Ino.

Aries is one of the four cardinal signs. The cardinal signs align with the start of a season when the sun makes its annual passage through them. Aries represents the start of the spring season. In Aries history, Ares is the son of Zeus and Hera. He is the Aries god of War, as he represents the violent and physical aspects of the battle.
People born under this sign tend to be passionate, motivated, and confident. They are often leaders who inspire communities and nations. They have a positive and cheerful disposition. With an Aries background, weakness is to have the relentless determination and never give us. This may sound great, but it can be difficult to deal with if you are a partner in a relationship with an Aries.
Here are some famous Aries personalities – Thomas Jefferson, Leonardo da Vinci, Vincent van Gogh, Elton John, Lady Gaga, and Maria Sharapova (31).
Future of Aries constellation
Although Aries is an ancient constellation, it was not officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union until 1922. Astronomer Eugène Delporte defined its boundAries 1930. In terms of modern astronomy – it is a new constellation.
Over millions of years, stars and deep-sky objects change the form, move or even explode. Aries is of great interest to scientists and astronomers as it contains regions that are actively forming stars.

This means that even now, new stars are being born. NGC 972 is a spiral galaxy that lies about 50 million light-years from Earth. Scientists believe that the presence of huge star-forming regions in NGC 972 are probably the result of a merger with a gas-rich companion in the past (32).
Arp 78 is an exciting galaxy, in that it resembles our Milky Way. Scientists are studying Arp 78 to see if there are any possible exoplanets with conditions to sustain life as we know it. The galaxy lies about 100 million light-years away.Beta Arietis, known as Sheratan is a binary star with two components very close to one another.
They are so close, that even a powerful telescope cannot separate them. Because they are so close, the stars are subjected to the immense gravitational force that will cause their collapse. The higher mass star will die first. Then, the second star will explode and shrink into a white dwarf. This will be fast in terms of the universe – it could take a couple of billion years! (33).