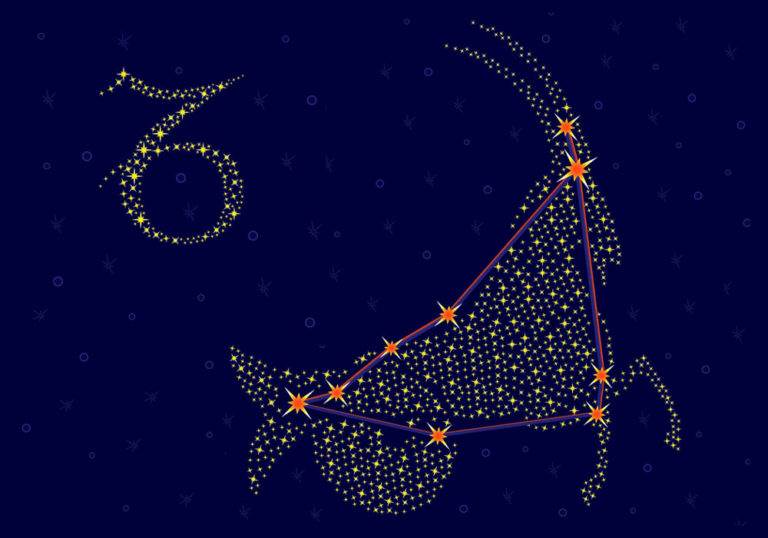
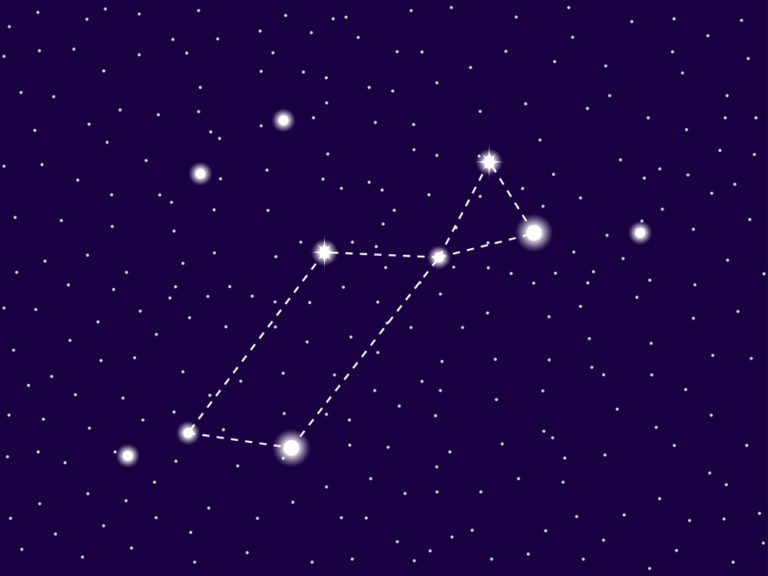
Cygnus Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Cygnus Constellation
Abbreviation: Cyg
Symbolism: The Swan, or the Northern Cross
R.A. position: 20.62h
Dec. position: +42.03°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 577 light-years
Area: 804 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Deneb (α Cyg)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −40°
Best viewed: During the month of September at 9.00pm
The Cygnus constellation is the 16th largest in the sky. It is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek times. It is associated with the beautiful Queen Leda, and Zeus, King of the Gods, who had an undying love.
Cygnus can be found in the sky by locating the constellations of Lyra or Vulpecula. Cygnus is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the spectacular Fireworks Galaxy, a favorite amongst stargazers.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
Cygnus constellation
The constellation Cygnus is a large constellation located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It has many bright stars that are well known, including the star Deneb, which is the head of the Northern Cross.
The Swan comes from the Cygnus greek mythology story of the beautiful Leda, who bore twin sons for Zeus, hatched from an egg. Zeus had disguised himself as a swan to rescue Leda, and in his happiness, he placed the swan into the sky.
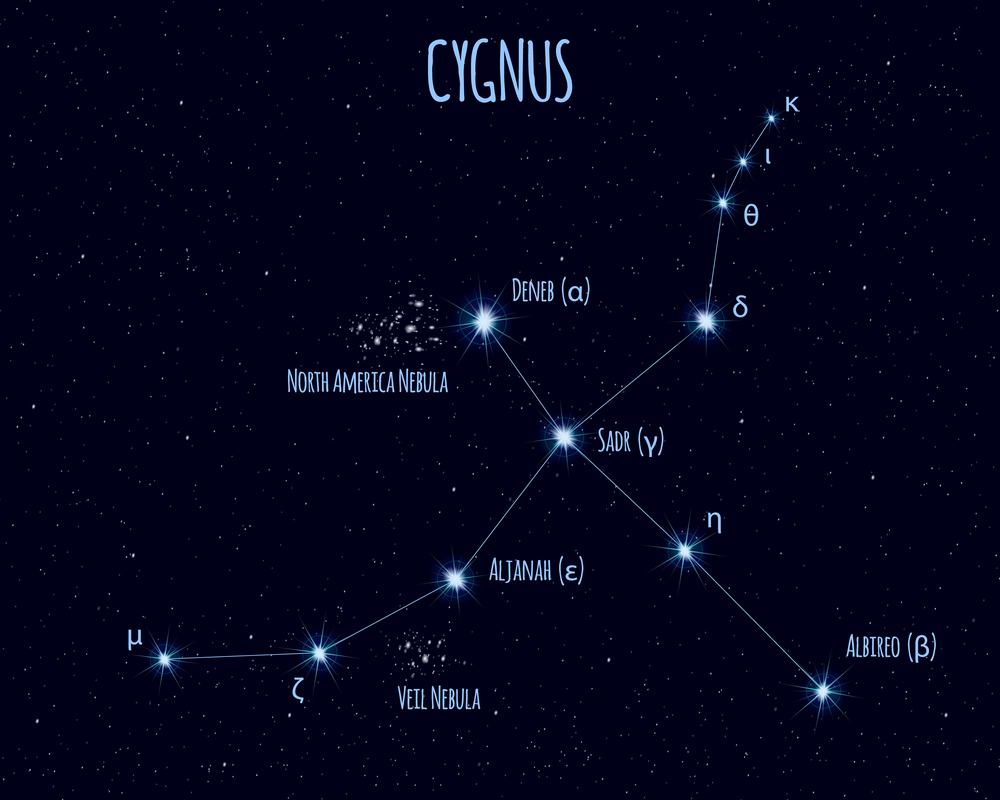
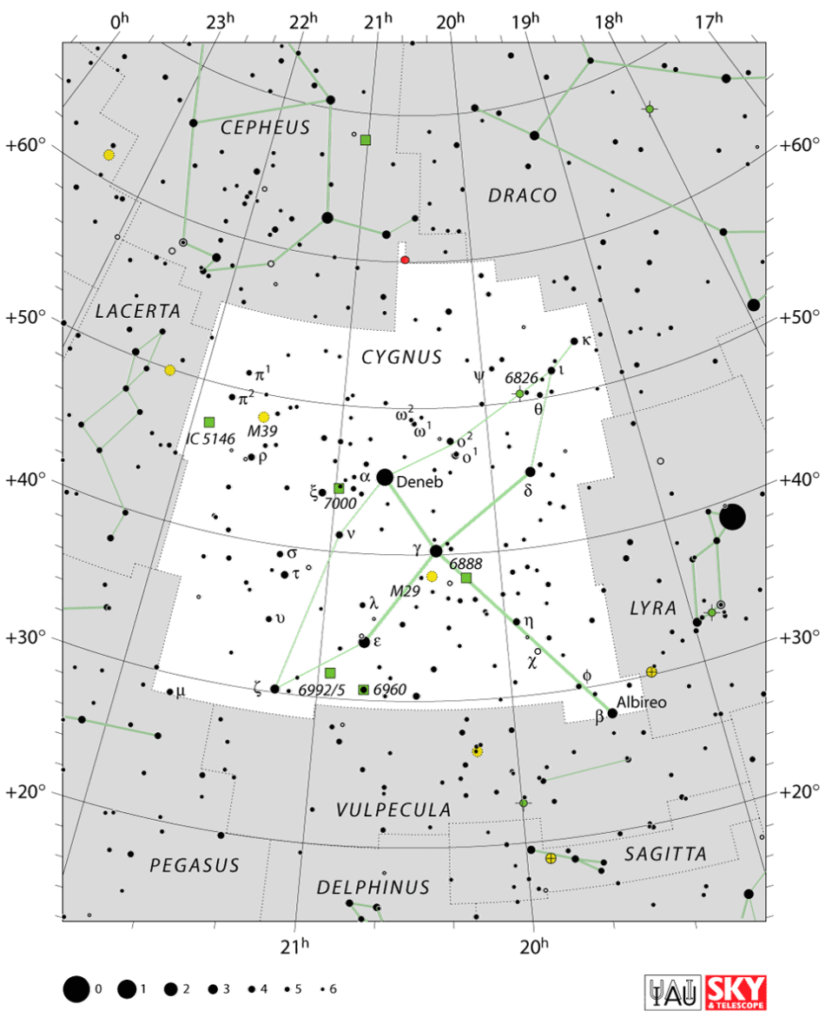
The Cygnus (constellation) occupies an area of 804 square degrees. The neighboring constellations are Cepheus, Draco, Lacerta, Lyra, Pegasus, and Vulpecula. For home stargazers, Cygnus has many exciting stars and deep-sky objects to view.
It contains the amazing Northern Cross asterism, well known around the globe. It also offers the amazing Fireworks Galaxy, the North America Galaxy, and the Cygnus x-1, a source of a-rays in the universe.
Cygnus is not a Zodiac sign, she is a beautiful serene Swan, floating across the sky. The Cygnus star system dates back over 3000 years (1).
What does Cygnus constellation look like?
ICygnus is a beautiful swan. She flies through the heavens, like an Angel, with wings outstretched on either side. When Zeus, King of the Gods, noticed Leda, he fell in love with her.
Disguising himself as a swan, he rescued her from an Eagle. The swan represents a magnificent creature of love, positiveness, and serenity. In the sky, Cygnus is large and imposing. She is a full-body creature, unlike some other constellations that are only half-formed.
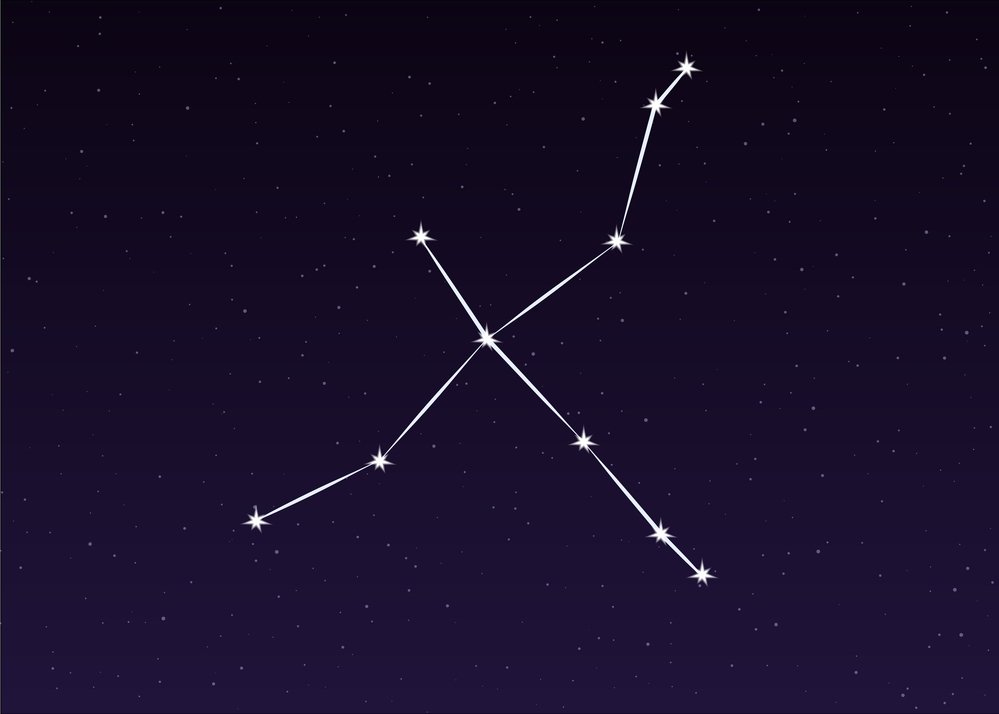
In the sky, the constellation of Cygnus is depicted by a number of bright stars. Most notably, they form a well-defined cross, also known as the Northern Cross. The famous star, Deneb, lies at the head of the Cross. Sadr lies in the middle.
For many people, Cygnus is the Cross, rather than the Swan. It is easy to see the Cross, as each arm is defined by the bright stars Rukh and Gienah.
If you love mystical stories, imagine a glorious swan with a long neck pointing slightly down and forwards. Her tail is stretched out behind her as she flies. On either side, huge wings help her glide silently amongst the stars. To complete the image, color the swan in a snow-white color – a stunning apparition in the sky.
How far is Cygnus constellation from earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. In reality, this is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some stars may be as close as 40 light-years. Deep-sky objects may be as far as millions of light-years away.

To give some idea, Cygnus brightest star, Deneb is 1,400 light-years away from Earth. Sadr, the star at the intersection of the Cross is about 1,800 light-years distant from the earth. Gienah is 72.7 light-years away and Rukh, also known as Farwaris, is 170 light-years away.
Albireo is a binary star system that lies about 380 light-years away. Zeta Cygni is a yellow star that lies about 151 light-years away from Earth. Tau Cygni is closer at only 68.2 light-years away.
The distance from Earth to Messier 29, an open cluster, is about 4,000 light-years. The spectacular Fireworks Galaxy is a massive 22 million light-years away from Earth.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the Cygnus constellation from Earth is about 577 light-years. If you consider the deep-sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years.
Features
Major stars in Cygnus
Cygnus is also known as the Northern Cross. Five bright stars define the Cygnus cross. Sadr is the central star of the Northern Cross, also formed by the bright Deneb, Albireo, Aljanah, and Fawaris. Deneb, Sadr and Albireo form the pole of the cross, while Aljanah and Fawaris mark the crossbeam.
Read on to learn more about each of these fascinating stars of Cygnus.
Deneb – α Cygni (Alpha Cygni)
Deneb is a blue-white supergiant that lies about 1,400 light-years away from Earth. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky. The name Deneb comes from the Arabic dhaneb, meaning “tail”, from the phrase Dhanab ad-Dajājah, which means “the tail of the hen.”
In the Northern Cross, Deneb lies at the head of the Cross. In the swan, Deneb lies at the tail. Together with the bright stars Altair in the constellation Aquila, and Vega in Lyra, Deneb, Cygnus alpha, forms the Summer Triangle, a well-known asterism in the summer sky.
Deneb has an apparent visual magnitude of 1.25. It is almost 60,000 times more luminous than our Sun and is one of the largest white stars known (2).
Sadr – γ Cygni (Gamma Cygni)
Gamma Cygni, also named Sadr, is another one of Cygnus main stars. It indicates the intersection of the Northern Cross. It lies on the back of the swan. Between its wings. The traditional name comes from the Arabic word for “the chest” – şadr.
It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.23 and is one of the brightest stars that you can see in the night sky. Sadr is a supergiant star in Cygnus, with a mass of about 12 times that of our Sun, and a radius of 150 times.
Gamma Cygni lies about 1,800 light-years away from Earth. It is surrounded by a diffuse emission nebula, known as the Sadr region (3).
Gienah – ε Cygni (Epsilon Cygni)
Gienah is also known as Aljanah or Epsilon Cygni. It is an orange giant star with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.48. Gienah is 72.7 light-years away from our Solar System. It is 62 times more luminous than the Sun and has a radius of 11 times that of the Sun.
The name is shared with a star in the constellation of Corvus, the Crow. In both cases, the name comes from the Arabic word janāħ, which means “the wing.” Both stars lie in the wings of the birds. In the Northern Cross, Gienah indicates the lower crossbeam.
Rukh – δ Cygni (Delta Cygni)
Also known as Farwaris, or Delta Cygni, Rukh appears as a single star from Earth. But, it is actually a triple star system consisting of a bluish-white giant, a yellow-white star, and an orange main-sequence star. The star system lies 170 light-years from Earth.
The star system has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 2.87. Around the year 11,250, Delta Cygni will become the North Star for about 400 years. The star lies on the wing of the swan and on the upper crossbeam of the Cross.
Albireo – β Cygni (Beta Cygni)
Albireo, Beta Cygni, is also known as the Beak Star. It lies at the head of the Swan and at the base of the Northern Cross. It is the 5th brightest star in Cygnus constellation. Albireo is a binary star system and lies about 380 light-years away. You can see it as one star without using a telescope.
The apparent visual magnitudes of the stars are 3.18 and 5,82 respectively. The Arabians designated the star as Al Minhar al Dajajah, the Hen’s Beak. Astronomers enjoy viewing this star system as it offers the beautiful contrast of a gold-yellow star and its glorious azure blue companion (4).
ζ Cygni (Zeta Cygni)
Zeta Cygni is a yellow star that lies about 151 light-years away from Earth. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.20. It is 119 times brighter than the Sun and has a radius of 14.7 times that of the Sun.
The star has a companion thought to be a white dwarf, named CCDM J21129+3014B. Zeta Cygni lies at the tip of the lower wing of the Swan. It also indicates the end of the lower crossbeam of the Northern Cross (5).
τ Cygni (Tau Cygni)
Tau Cygni is a double Cygnus star. The main star is a yellow-white subgiant star with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.72. The companion star has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.44, which is much fainter.
Together, you can see them in dark skies without using a telescope. The star system lies about 68.2 light-years away from the solar system. Tau Cygni is not a definitive star in the Northern Cross. It lies on the lower Cygnus wing (6).
Deep-sky objects in Cygnus
Messier 39 (M39) – NGC 7092
Messier 29 is an open cluster in the swan constellation, with an apparent visual magnitude of 7.1. It lies about 4,000 light-years away from our Solar System. You can see this deep-sky object with binoculars, but a telescope will give far more exciting views.
The Messier has a triangular shape, with three bright stars marking the corners. Charles Messier discovered the cluster in 1764. It lies near the star Gamma Cygni, to the south and east. The estimated age of the cluster is 10 million years. Messier 39 is a relatively loose cluster. It has 30 confirmed members occupying an area about 7 light-years in diameter (7).
Fireworks Galaxy – NGC 6946 (Arp 29, Caldwell 12)
NGC 6946 is a medium-sized spiral Cygnus galaxy that is super exciting. It lies about 22 million light-years away from Earth. In the past century, astronomers have observed 8 supernovas exploding in the arms of the galaxy, making it live up to its name ‘Fireworks Galaxy’.
The galaxy has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.6 and lies near the border of the constellation Cepheus. It is close to the galactic plane, obscured by the interstellar matter of the Milky Way. NGC 6946 was discovered by the German-born British astronomer Sir Frederick William Herschel in 1798 (8).
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1, a binary star system that is famous for its strong source of X-rays. It offered the first major evidence for the existence of black holes in the Universe. Cygnus X-1 lies about 7,000 light-years from Earth.
This is a binary star system, with a primary Cygnus supergiant, HDE 226868. It revolves around its companion star every 5.6 days. The X-ray emission is thought to be due to matter torn from the primary star that is heated as it is drawn to the black hole (9).
North America Nebula – NGC 7000 (Caldwell 20)
The most famous Cygnus nebula is NGC 7000, also known as the North America Nebula. If you look at images, you see that its shape closely resembles that of the continent of North America, hence the name! The shape is a massive cloud of dust that obscures the nebula.
The North America Nebula has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.00 and lies about 1,600 light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1786. Of interest to astronomers, is the area of great star-formation, known as the Cygnus Wall. In the image of the shape of America, this lies in the region which would be Mexico and Central America (10).
Pelican Nebula – IC 5070 and IC 5067
The Pelican Nebula is an emission nebula. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.0 and lies about 1,800 light-years away from Earth. The name comes from the fact that its shape resembles a pelican. NASA scientists say that this massive star-forming region will in millions of years, lose its pelican shape and will need a new name.
The nebula lies close to the nearby North America Nebula, separated from it by a large molecular cloud filled with dark dust. In astronomy terms, they are close at about 1,500 light-years apart. The two nebulae are about 1,500 light-years apart. The Pelican Nebula lies near Cygnus brightest star, Deneb. It can be found to the northeast of the star (11).
Sadr Region – IC 1318
The Sadr Region in the Cygnus refers to the hydrogen emission nebula surrounding the star Sadr, Gamma Cygni. Sadr lies at the center of the Northern Cross, or on the back of the swan, between the wings.
The Sadr Region also includes the beautiful Butterfly Nebula, named because its shape resembles a butterfly. Sadr has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.2 and the surrounding nebula is also as bright. There is an estimated distance of 1,800 to 5,000 light-years between the components in the Sadir region (12).
Exoplanets in Cygnus
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life.
HAT-P-11
HAT-P-11 has one exoplanet called HAT-P-11 b. It is a Neptune-like exoplanet with a mass of 26.69 Earths. It takes 4.9 days to complete one orbit of its star. It lies about 124 light-years away from Earth. Discovery was in 2008. This exoplanet excites astronomers as it has an abundance of Helium in its atmosphere.
Jessica Spake, part of Exeter’s Physics and Astronomy department said: “This is a really exciting discovery, particularly as helium was only detected in exoplanet atmospheres for the first time earlier this year.
The observations show helium being blasted away from the planet by radiation from its host star. Hopefully, we can use this new study to learn what types of planets have large envelopes of hydrogen and helium, and how long they can hold the gases in their atmospheres” (13).
KELT-20
KELT-20 is a blue-white star that lies about 373 light-years away from our Solar System. It has an exoplanet known as MASACARA-2 or KELT-20 b. It is a gas giant with a mass of 3.382 Jupiters and takes 3.5 days to complete one orbit of its mother star. Discovery was in 2017.
HD 187123
HD 187123 is a yellow star that lies 157 light-years away from Earth. It has 2 exoplanets revolving around it. The first is HD 187123 b. This gas giant has a mass of 0.523 Jupiters and takes 3.1 days to complete one orbit of its star. The second is HD 187123, a gas giant with a mass of 1.99 Jupiters. It takes 10.4 years to complete one orbit of its star. The exoplanets discovery was in 1998 and 2008 respectively.
Meteor showers in Cygnus
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars.
Kappa Cygnids
The Kappa Cygnids occur between 3 August and 25 August, with the peak around 17 August. You can expect to see around 3 meteors per hour, traveling at speeds of 25km/s. Meteors are blueish-white with short tails. This shower is best viewed in the northern hemisphere.
The radiant point of a shower is the point from which the meteors appear to radiate. In the Kappa Cygnids, the radiant point is between Lyra, Draco, and the Cygnus constellations, close to the star Kappa Cygnus.
The shower was first discovered by the Hungarian astronomer N. de Konkoly on August 11 to 12 in 1874. He was studying the brighter Perseids, when he noticed a few meteors of unknown origin.
In 1877, the English astronomer William F. Denning noticed the k-Cygnids again. He documented this shower as a separate shower from the famous Perseids. The perseids are brighter and offer many more meteors per hour. Kappa Cygnids shower is fairly faint but did appear brighter in 2007 and 2014 (14).
Location and visibility
Where is Cygnus constellation located?
Cygnus is a large constellation with many bright stars and you can easily spot it once you know what to look for. In dark skies, you can see the main stars without a telescope. Then, you can imagine the beautiful mythical white swan silently gliding through the heavens.
Cygnus is a northern constellation and is the 16th largest constellation of the 88 named constellations. It occupies an area of 804 square degrees. Cygnus lies in the fourth quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ4.

A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes between +90° and −40°.
To find the Cygnus location, you can look for the well-defined asterism, or star pattern called the Northern Cross. The Northern Cross lies directly inside the swan constellation. Alternatively, you can look for Pegasus the Winged Horse, by locating the Great Square of Pegasus, which is also easy to spot. The Cygnus star constellation lies above Pegasus in the sky.
Cygnus and Lyra are also connected in the sky. Each offers one of the 3 stars that form the Summer Triangle. Vega in Lyra, Deneb in Cygnus, and Altair in Aquila are the 3 stars in the Triangle. Cygnus belongs to the Hercules family of constellations. These include Aquila, Centaurus, Corona Australis, Hercules, Hydra, Lyra, amongst others. They are all connected to the Great Warrior in Greek Mythology. (15).
When is Cygnus constellation visible?
You can view the Swan constellation in both the northern and southern hemispheres. When is Cygnus visible?

Northern Hemisphere
If you are in the northern hemisphere – In June and July, Cygnus is visible in the north-eastern sky from around 10pm. By 2am the constellation will be directly overhead and will stay high in the sky until daybreak.
In August and September, the constellation appears high in the eastern sky around 9pm. In October and November, Cygnus appears overhead from around 7pm. This is a great time to take the family out for some stargazing to learn about Cygnus the swan story.
In December and January, Cygnus the swan appears high in the western sky from around 6pm and disappears below the horizon before 10pm.
Southern Hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere – In July and August Cygnus is visible low in the north-eastern sky from around 9pm. It stays low on the horizon and moves westwards throughout the night. In September and October, the constellation appears low on the north-eastern horizon from around 7pm. It then disappears below the north-western horizon around midnight.
Remember – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down (16).
How to find Cygnus constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Read on to learn how to find the Cygnus constellation in the sky.
- Cygnus is an easy constellation to find as it has several well-known asterisms, or star patterns
- Look for the Northern Cross! It lies in the middle of the swan.
- In your mind, extend the vertical line of the Cross to form the long neck and tail of the swan
- Extend the horizontal lines of the Cross to form the outspread wings
- Alternatively, you can also locate the Summer Triangle. Look for bright stars Altair, Vega, and Deneb
- Deneb lies in the tail of the swan, Vega is above his upper wing and Altair is in front of his beak
Southern Hemisphere
- Cygnus is an easy constellation to find as it has several well-known asterisms or star patterns
- Look for the Northern Cross! It lies in the middle of the swan.
- In your mind, extend the vertical line of the Cross to form the long neck and tail of the swan
- Extend the horizontal lines of the Cross to form the outspread wings
- Alternatively, you can also locate the Summer Triangle. Look for bright stars Altair, Vega, and Deneb
- Deneb lies in the tail of the swan, Vega is below his lower wing and Altair is in front of his beak
Do you want to know some more interesting Cygnus facts? In the Southern hemisphere, constellations appear upside down. So, the Swan is gliding more upwards than downwards in the sky!
How to view Cygnus Constellation?
The swan constellation Cygnus is the 18th largest constellation in the sky. It has many well-defined stars that you can see with the naked eye. By locating these stars, you can imagine the beautiful swan floating across the sky, serene and peaceful. You will also see the well-known Northern Cross, a major feature of the night skies.
Cygnus belongs to the Hercules family of constellations. They all have stories in Greek Mythology related to the Great Warrior Hercules. Some of the other constellations in this group are Aquila, Centaurus, Corvus, Crux, Hydra, Lupus, Lyra, Serpens, and Triangulum Australe.
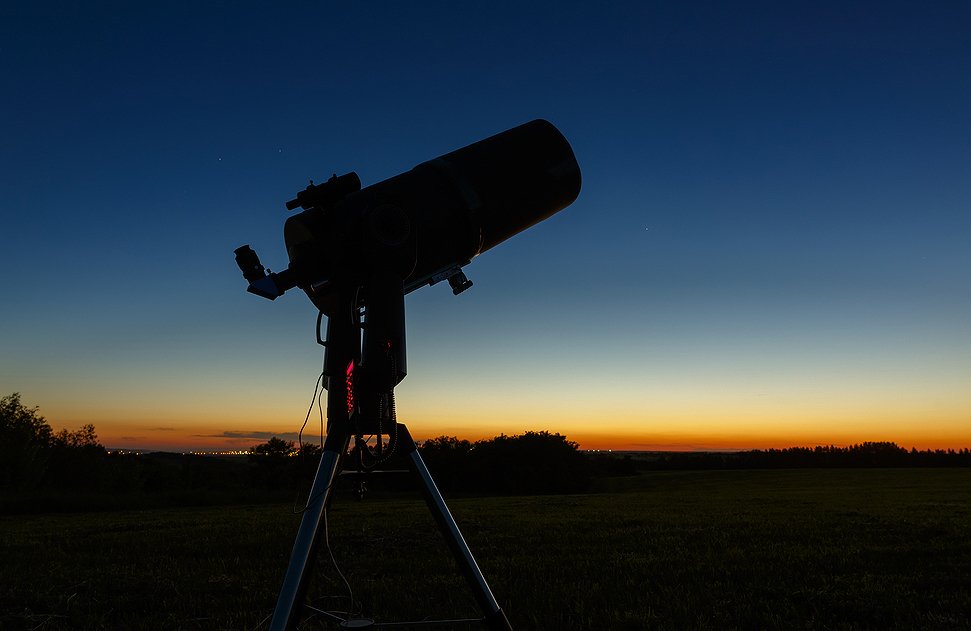

The best way to see Cygnus the swan constellation is to get away from the city lights and pollution. You can use a pair of binos, but a telescope will make the experience so much more exciting. For family viewing, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of the Cygnus swan.
Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Celestron NexStar 4SE Telescope has a fun bright orange tube – very trendy! It offers a 4” aperture, which gives stunning views of Cygnus constellation stars and deep-sky objects. It comes with a fully automated GoTo mount and a database of more than 40,000 celestial objects.
For a family, this is a great travel scope as it automatically locates and tracks objects for you. Using the SkyAlign feature, you can center the eyepiece on any three bright objects, and the NexStar SE aligns to the night sky, ready to locate Cygnus for you. It is so easy that kids can do it.
This scope features a 1325mm focal length. It comes with a camera control feature and shutter release cable. With this feature, you can try your hand at taking photos with a digital SLR camera. The Celestron NexStar 4SE Telescope is easy to transport and set up. At under $600 it is perfect for a family weekend get-away for some stargazing.
History of observation
Who discovered Cygnus constellation?
Cygnus constellation history dates back to ancient civilizations of the Greeks, Hindus, and Polynesians, and was documented in stories, folklore, and myths.
Cygnus history dates as far back as 3000BC. It associates with the Greek mythology Queen Leda, seduced by Zeus, disguised as a beautiful swan. She bore him two twin sons, Pollux and Castor, who later became the constellation Gemini (17).

The Cygnus constellation story was also known to the Hindu astronomers. The time period between 4:24 AM to 5:12 AM is called the Brahmamuhurtha, which means “the moment of the Universe” and correlates with the Cygnus constellation. This is a good time to meditate and complete tasks.
Cygnus was known to Chinese astronomers as far back as 750BC. Because it stretches along the Milky Way, it is a river and a heavenly bridge between celestial kingdoms. In modern Chinese astronomy, Cygnus lies in the area of the sky known as the Black Tortoise of the North.
The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is tiān é zuò, meaning “the swan constellation”. In ancient Polynesia, around 1200AD, astronomers called it Tuula-lupe (18).
In more recent times, Cygnus was one of the original 48 constellations formulated by Ptolemy in his 2nd-century work, the Almagest. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Cygnus constellation?
Ara Pacis was an open-air altar built in Rome about 2,030 years ago for Augustus, the first Roman emperor. The mother figure’s open veil forms an arch shape with a dragon to her right, also representing Draco. At the left is a swan representing Cygnus.
Cygnus is an ancient constellation that dates back to the era of Greek mythology around 3000BC. The constellation depicts the myth of Leda and the King of the Gods, Zeus. Zeus disguised himself into a beautiful swan to woo Leda. She fell in love and bore him two sons, Castor and Pollux from an egg.

Cygnus is also an old Chinese constellation known as far back as 750BC. It has a lovely story representing a heavenly bridge between celestial kingdoms. In modern Chinese astronomy, Cygnus lies in the area of the sky known as the Black Tortoise of the North. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is tiān é zuò, the Cygnus meaning is the “the swan constellation”.
In Biblical times, around 1200BC and 165BC, the Hebrews wrote about Swans. The Israelites could not eat swans as they were one of the unclean birds – “And the swan, and the pelican, and the gier eagle” Leviticus 11:18 KJV. Swans in Biblical times also represented true and faithful love. “Now to the married I command, yet not I but the Lord: A wife is not to depart from her husband”. I Corinthians 7:10 (19).
How did the Cygnus constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology.
The words Cygnus and cygnet, a young swan, are from the Latin word Cygnus, meaning ‘swan’. In Greek mythology, there are four characters with variations of the name Cycnus or Cygnus.
In Greek, kuknos, is the word for swan. The swan in Greek mythology was Zeus, King of the Gods, in disguise. He transformed into a swan to woo the beautiful Leda and gain her love.
If you ask – what does Cygnus mean? The Cygnus name meaning is Swan.
The English word swan comes from the Indo-European root *swen- meaning ‘To sound’. Derivatives are all related to sound -resonate, sonic, sonnet, unison, sonar, sonata, sonorous. In ancient tales, Swans sang a beautiful swan song when they were dying (20).
Cygnus is also known as the Northern Cross. This is because it is identified by a star pattern that forms a Cross in the Sky. Sadr is the central star of the Northern Cross. Deneb marks the top of the pole and Albireo marks the base. Aljanah and Fawaris mark the ends of the crossbeam.
Mythology and meaning
Cygnus myth
Like many constellations, there are different stories about the Cygnus constellation myth.

Myth 1
The most well-known is the story of Leda, Queen of Sparta. Zeus, King of the Gods, was greatly attracted to Leda. He was a master of disguise and would turn into different creatures to get near to the lady he desired.
One day, a large eagle attacked Leda. Zeus disguised himself as a swan and took the queen under his wings. Leda later produced two eggs that bore a set of twins from each.
From one egg brothers, Castor and Pollux emerged, From the other, the twin sisters Helen of Troy and Clytemnestra were born. To celebrate the births, Zeus placed the swan amongst the stars to create the constellation Cygnus.
Myth 2
Another story tells of Cycnus, a close friend of Phaeton, the mortal son of the Sun God Helios. The two were racing across the sky and came too close to the Sun. Their chariots burned up and they fell to Earth. Cycnus found the body of his friend trapped at the bottom of the River Eridanus.
He made a pact with Zeus – if God gave him the body of a swan, he would only live as long as a swan does. Once transformed, Cycnus could dive into the river and send Phaeton’s soul to the afterlife. In Cygnus greek mythology, Cycnus’ sacrifice moved Zeus, and he placed his image in the sky.
Myth 3
In another Cygnus myth, the swan was sacred to the God Apollo. Large flocks inhabited the river Eridanos in Hyperborea where they encircled God’s holy shrine, singing hymns.
The Hyperborean people transformed into swans when they became old, The normally silent swan sang a beautiful sweet song as death approached, which is probably the most beautiful Cygnus the swan myth (21).
What does Cygnus symbolize?
In the mythology of Cygnus, the Swan is linked to Leda, Queen of Sparta. Zeus, King of the Gods, was greatly attracted to Leda. He was a master of disguise and would transform into different creatures to get near to the lady he desired.
In this case, he became a beautiful swan. Leda later produced two twins from an egg and twins Castor and Pollux were born. To celebrate the births, Zeus placed the swan amongst the stars.
The swan Cygnus symbol represents beauty, grace, elegance, and love. It also symbolizes balance and divination. Swans remind us of flying angels and as such have a spiritual meaning.

Swans can help you see into the future. They are closely connected to water and offer creativity, depth. and fluidity. Everything about a swan is calm, relaxed, and beautiful. It is serene and strong. In Cygnus mythology, Leda’s births were mystical and magical. The twins emerged from an egg, making the story even more fascinating.
If you see a swan in your dreams, you need to slow down and take stock of your life situation. Let the swan guide you to better days and allow the Angel in the Swan to protect you. The Swan brings joy and happiness and signals a time to leave behind all that is bad and negative.
Leda was a joyful soul, and only did good in her life. The Swan radiates positive energy and good karma. Let your inner beauty shine, like Leda in the Cygnus story and like the magnificent creature in the sky. The Swan is the ultimate symbol of Love. A pairing of male and female swans will last forever (22).
Future of Cygnus constellation
Cygnus is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study. It has many interesting stars that are changing their form and can be studied as this happens.
Deneb is one of the 3 stars in the Summer Triangle. In around the year 9800AD, the star Deneb will become our Northern Star. The current Northern Star is Polaris in Ursa Minor. Due to the Earth’s axial precession, different stars take this position over thousands of years.
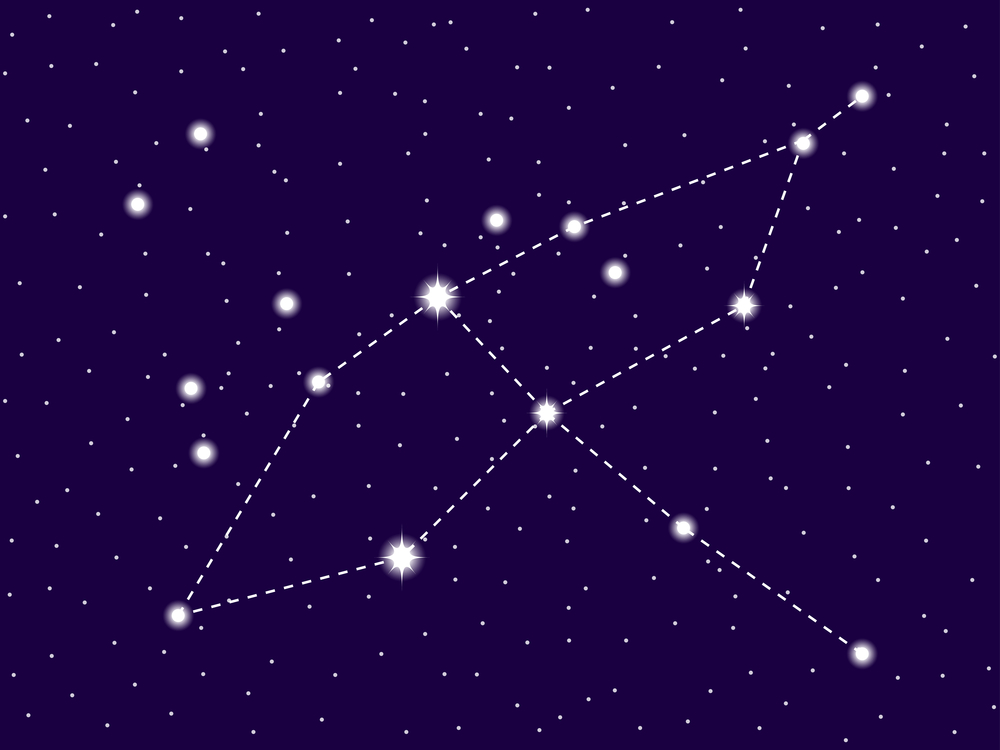
In a couple of million years, Deneb will explode as a supernova. Astronomers believe that the star has stopped fusing hydrogen at its core, and is cooling and expanding. It may become an extremely luminous red giant or a luminous blue variable. Unfortunately, we won’t be around to know! (23).
Another star of Cygnus that is interesting is Sadr. Gamma Cygni) has reached the supergiant stage of its stellar evolution. That means that its radius has expanded and will continue to expand to many times its former size.
Because Sadr supergiant in Cygnus, is so massive, more than 300 times the size of the Sun, it will one day go supernova and illuminate a big portion of the night sky. This will happen even though it is such a young star (24).
Albireo is also considered a supernova candidate. Scientists say that it is difficult to predict when this may happen but it could be in the year 3.870.000. At that time, it will be as close as 80 light-years to the Solar System (25).