Leo Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Leo Constellation
Abbreviation: Leo
Symbolism: The Lion
R.A. position: 12h 26m 07s
Dec. position: 25° 59′ 16″
Distance from Earth: Average distance is 1535 light-years
Brightest star: Regulus
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −65°
The Leo Constellation is a well-known constellation and a favorite of amateur astronomers. It features a number of bright stars, including Regulus.
Leo the Lion stands proudly in the sky and has a fascinating story with roots in Greek mythology. You can observe Leo in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
Leo is the 5th of the Zodiac constellations and is one of the oldest identified by ancient astronomers.
Characteristics
How far is the Leo constellation from earth?
Like most constellations, constellation Leo is made up of numerous stars and deep sky objects.
When observed from planet Earth, the constellation looks as if all the objects lie on the same plane.
In fact, each object is at a different distance from the earth.

- The Leo constellation brightest star is Regulus, which is around 80 light-years from Earth (1). The famous Leo Triplet lies about 35 million light-years from Earth.
- Denebola is the second brightest star in Leo. It is located approximately 35.9 light-years distant from Earth.
- An interesting star in Leo astronomy is called Wolf 359. This red dwarf is only a mere 7.78 light-years distant. Although it is so close, it is a tiny star that emits about 0.1% of the Sun’s energy, and can only be seen through a telescope.
Taking into account the main stars and their individual distances, the average distance of Leo from the Earth is 1535 light-years.
What does the Leo constellation look like?
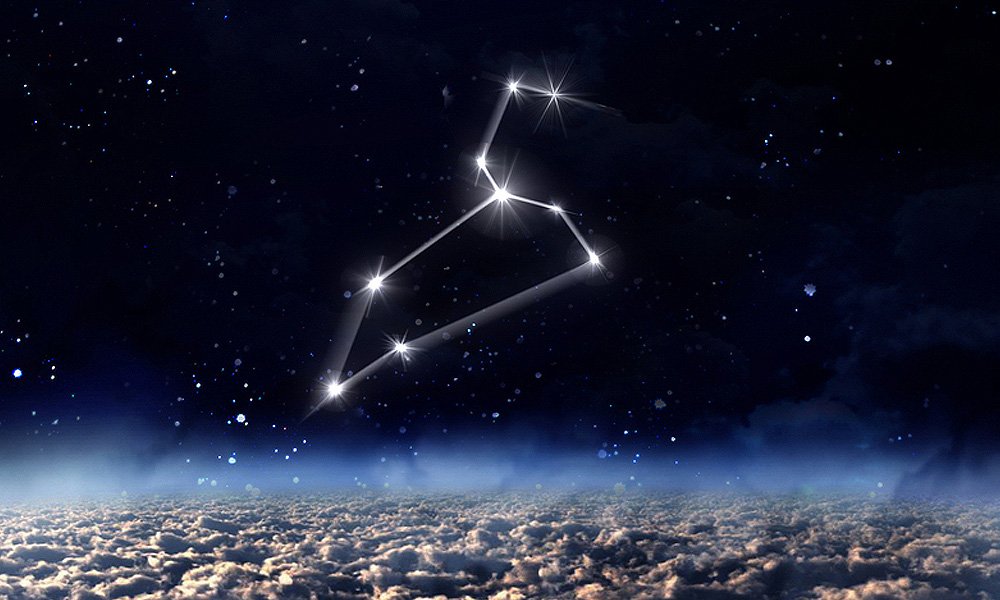
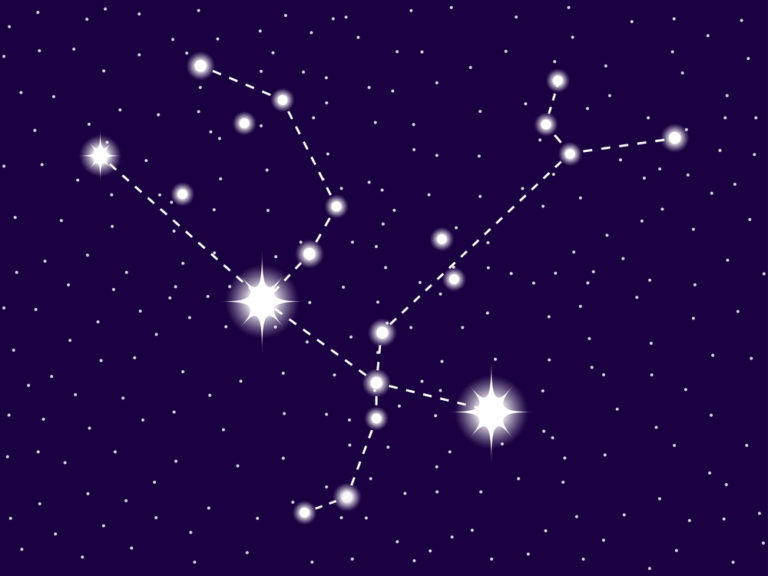
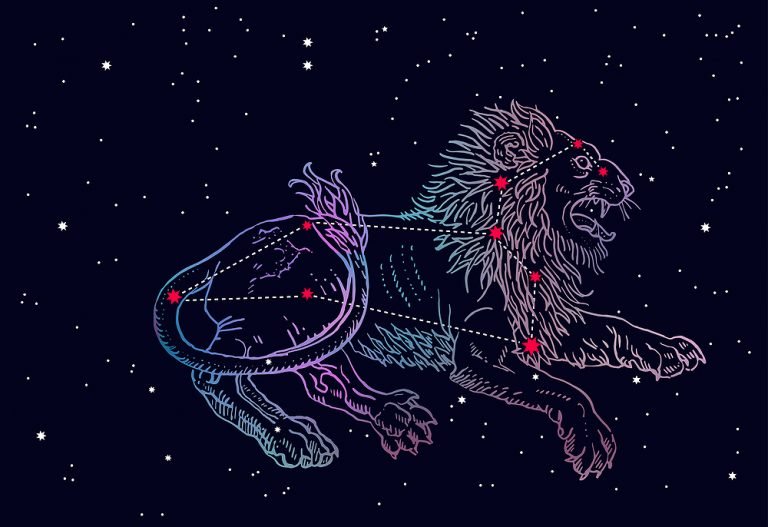
The Constellation Leo is a large lion, crouching in the sky with his foot raised, ready to pounce on any creature that comes close to him!
In the northern hemisphere, the Lion stands upright. His huge head is identified by an asterism of stars, known as the Sickle (2).
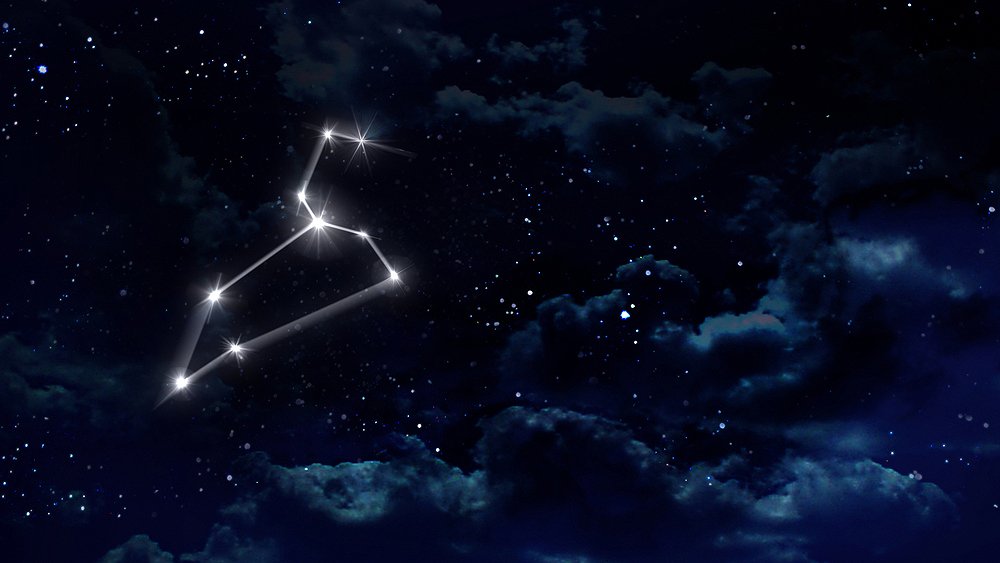

- An asterism is a collection of stars within a larger constellation that form a pattern. They are usually easily identified and help star-gazers to create a bigger picture.
- The Sickle forms the head of the Lion and looks very much like a question mark. At the base, imagine a line to the left that extends across his back to his tail.
- Following an imaginary line down from the Sickle, you find Regulus. Regulus marks the position of his front leg.
Once you locate the Sickle – the Lion comes to life. Give it a try. Remember that in the southern hemisphere, the Lion crouches upside-down.
How old is the Leo constellation?
The earliest records of Leo the constellation is thought to have come from the Mesopotamians as early as 4000BC (3).
Around 1200BC, the ancient Greeks associated Leo with the Lion of Nemean, who was slain by Hercules.
In ancient Chinese history, as long ago as 2300BC, astronomers identified some of the stars of the Leo constellation as part of their constellation Xuanyuan, the Yellow Dragon.

The famous Greek astronomer Ptolemy identified the constellation in the Almagest (4) in the second century AD.
Scientifically, the constellation contains objects that are millions of years old. Here are a few Leo constellation facts – the brightest star Regulus is about 1 billion years old.
- The next brightest star Denebola is a young star with an age of only 400 million years.
- The Wolf 359 star has an age of less than 1 billion years. It became famous when it was mentioned in an episode of The Outer Limits.
Zodiac family
Leo is the fifth sign of twelve in the Zodiac family. It represents people born between July 22 and August 22. Leo is a fire sign, together with Aries and Sagittarius.
People born under this sign are known to have great self-confidence and strong personalities.

Leo the Lion has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Cancer, the Crab lies below it on the right side, and Virgo, the Virgin, is found on its left side (5).
In the Zodiac family, Leo and Cancer, the Crab have a connection. They were both slain by Hercules as he carried out tasks assigned to him as punishment.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, Leo zodiac lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the course of a year.
Leo is located in the eastern celestial hemisphere, together with Pisces, Aries, Taurus, Gemini, and Cancer (6).
Features
Stars in Leo constellation
Leo, the constellation is made up of numerous stars. Some Leo constellation stars are brighter than others and many are identified for their unique attributes.
How many stars in Leo? Leo has 9 main stars and 13 stars with planets.
What is the brightest star in the Leo constellation? The brightest star in Leo is known as Regulus.

This star is also notable because it is one of the brightest stars in the sky and is about 4 times bigger than our sun.
Regulus is a four-star system and is around 80 light-years from Earth, which in astronomical terms is close! Regulus is also known as Alpha Leonis.
Also notable in the Leo star constellation is Algieba, also known as Gamma Leonis (7). This is a two-star system around 130 light-years from Earth. The two stars orbit around one another at a distance of about 16 billion miles.
In the Leo constellation, you will find an asterism called the Sickle. This star pattern is made up of 6 stars – Epsilon Leonis, Rasalas, Adhafera, Algieba, Eta Leonis, and Regulus.
The 6 stars with Regulus at the base, form an easy-to-find pattern of a question mark and define the large head of the Lion (8).
Deep sky objects in Leo constellation
Leo (constellation) features a number of interesting deep sky objects.
The first is the Leo Triplet. Also known as M66 Group, this is a group of interacting spiral galaxies.
The Leo Triplet is a great sight for astronomers as they can be seen in a single view through a basic telescope.

The galaxies in the group are called Messier 65, Messier 66, and NGC 3628. This triplet lies about 35 million light-years from Earth (9).
Another interesting deep sky object in the Leo constellation is the Leo Ring (10). This huge cloud of helium and hydrogen gas forms a hazy light in the sky.
It was discovered by accident in 1983 by a group of astronomers, Schneider et al., while they were looking at another unrelated object in the sky.
The Leo Ring is thought to have been created during the Big Bang. The Big Bang Theory is a scientific explanation of how the Universe began, based primarily on mathematical formulas and models.
Exoplanets in Leo constellation
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars other than our sun. Exoplanets are exciting to astronomers as they may present conditions similar to Earth, and perhaps the possibility of life!
In 2008, astronomers discovered an interesting dying red giant star known as HD 102272.

Image credits: NASA
This star has 2 planets that orbit it. One is about the size of Saturn and the other the size of Jupiter. The star and its exoplanets are about 1200 light-years away from Earth. (11)
Another interesting discovery in 2010 shows a large planet called GJ 436b. It is about 22 times the size of Earth.
This planet is different from our planets in that it orbits over the poles of its star, rather than the equator.
The potential existence of water is always an exciting find when looking for life in space. In 2017, scientists discovered an exoplanet called K2-18b.
Because it orbits in the zone of a red dwarf star that may be habitable, there is a chance that it contains water or ice. (12)
Location and visibility
Where is Leo constellation?
Leo is a great constellation for new astronomers to find in the sky. It contains one of the brightest stars in the sky and a distinctive sickle shape that you can make out without the use of a telescope.
Leo occupies an area of 947 square degrees and is the 12th largest constellation. It is located in the second quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ2.

A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. Leo can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -65° (13).
The neighboring constellations are Cancer, Coma Berenices, Hydra, Crater, Leo Minor, Lynx, Ursa Major, Sextans, and Virgo.
Also read: Cancer Constellation & Orion Constellation
How to find Leo constellation?
The August constellation of Leo is easy to find in the night sky, both in the northern and southern hemispheres.
- The easiest starting point is to locate the stars that make up the Lions huge head. This group of stars is known as an asterism and is called the Sickle.
- It forms the shape of a curved sickle, or even easier to look for – is the distinctive shape of a question mark.
- One of the brightest stars in the sky, Regulus, is very easy to see with the naked eye. Work your eye upwards from there, forming the question mark.
- Straight across to the left of Regulus is another bright star called Denebola. This star indicates the Lion’s tail and forms a triangle with Zosma and Chertan.
- The three together form the hindquarters of the Lion. Once you have marked out the head and hindquarters, a little imagination will create the full form of this magnificent creature.
- Virgo lies underneath the Lion’s tail. The constellation of Leo Minor, a small lion, is situated above his head.
When is the Leo constellation visible?
Constellation Leo can be seen in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
In the northern hemisphere, Leo is visible in the southern night sky.
In January – look low on the eastern horizon at around 11 pm. Leo then moves slowly westwards until dawn breaks.

In February, March, and April, the constellation will appear in the eastern sky around 8 pm. It gradually moves higher before dipping towards the horizon. In May and June, Leo will appear high in the western night sky at around 10 pm (14).
In the southern hemisphere, Leo appears upside-down. In February and March, Leo will appear low in the north-eastern sky from around 9 pm. It moves slowly westwards throughout the night before dipping below the horizon at dawn.
In April. May and June, the constellation will appear in the north-eastern sky at around 6 pm, gradually moving towards the north-western horizon.
What is the best way to view it?
If you live in the city, there is a good chance that you will spot the famous Sickle shape in the sky. It can be seen on a clear night as a question mark.
From there, it is easy to find the Leo constellation brightest star, Regulus, at the base of the question mark.
Getting away from city lights is the best way to view any constellation and Leo is no exception.

You will see the stars more clearly and appreciate the joy of star-gazing. Using a powerful pair of binos will give you an even better view of the constellation.
The best way to view Leo is through a telescope.
For beginners, the Dobsonian range of telescopes are well priced and easy to transport. They require minimal setup and can be enjoyed by the whole family.
The SkyWatcher S11620 Traditional Dobsonian 10-Inch telescope offers the most aperture for your money. It makes a great buy for beginners who are becoming serious sky-watchers.
Expect to pay around $850 for a quality instrument that will last a lifetime. The telescope features a massive 10” Newtonian-style aperture.
Also included in the set is a 2” single-speed Crayford-style Focuser with a 1.25” adaptor.
History
Who discovered the Leo constellation?
Leo the Lion was a constellation known to many ancient civilizations. In the history of Leo constellation, it is thought that the Mesopotamians may have had a constellation similar to Leo as early as 4000BC.
The ancient Greeks associated Leo with the Lion of Nemean, who was slain by Hercules. This version dates back to around 1200BC.
In ancient Chinese history, as long ago as 2300BC, astronomers identified some of the stars of the Leo constellation as part of their constellation, the Yellow Dragon, called Xuanyuan. In the Chinese zodiac, the stars that form what we know as Leo, are thought to represent the shape of a horse.
In more modern times, around the second century AD, the Greek astronomer Ptolemy identified the constellation in the Almagest. He also identified 48 other constellations, including Taurus, Gemini, Virgo, and Libra. (15)
When was it first recorded?
Leo the Lion was known to the ancient Greek astronomers as far back as 1200BC. Even earlier than that, it is thought that the Mesopotamians may have had a constellation similar to Leo as early as 4000BC.
Ancient Chinese astronomers identified some of the stars of the Leo constellation as part of their constellation Xuanyuan, the Yellow Dragon. This was dated as far back as 2300BC.
In western astronomy, the first person to identify the Leo constellation was the Greek astronomer Ptolemy who recorded it in the Almagest in the second century AD. (16)
How did the Leo constellation get its name?
The constellation gets its name from the Latin word Leo which means Lion. The Leo constellation story stems from the ancient Greek Mythology of Hercules, son of Zeus.
Hercules was given a series of tasks as punishment for killing six other sons of Zeus. The first task was to slay the Lion of Nemean. After doing this, the Lion was placed into the sky, as he was the King of Beasts.
Other ancient civilizations named the constellation according to their folklore and beliefs. Babylonian astronomers called the constellation The Great Lion and gave it the strange name UR.GU.LA. Regulus, the bright star, was known as the ‘star that stands at the Lion’s breast.’
The Persians knew the constellation as Shir or Ser (17). The ancient Egyptians also knew of Leo the Lion. They worshipped the Lion as the place where the Sun rose after creation.
Its appearance in the night sky coincided with the flooding of the Nile river and the summer solstice.
Mythology
Leo constellation in mythology
Leo, the Lion Constellation, like many other constellations, has a story based on the adventures of the great Hercules, son of Zeus, who was endlessly tormented by Hera, his stepmother.
She hated Hercules and made it her mission to kill him. Living with ongoing attempts on his life eventually drove Hercules insane.

In his rage, he killed six sons of Zeus. When Hercules regained his sanity, he was forced to carry out twelve dangerous tasks as punishment.
The first of these tasks was to kill a lion that was terrorizing the city of Nemea. The Lion had a golden coat that was impenetrable by classic weapons. Hercules did not know this and unsuccessfully tried to slay the lion with a bow and arrow.
Hercules then approached the Lion’s cave with another plan. He blocked off one of the entrances and faced the Lion inside, beating him with a club and then strangling him to death.
Eratosthenes, an ancient Greek astronomer, wrote in his records of the Leo constellation myth that the Lion was placed among the constellations because he was the King of the Beasts.
What does Leo constellation symbolize?
Lions in mythology are creatures of great power and strength. He is indeed the King of Beasts. The Lion is feared by all.
The lioness has huge amounts of perseverance, endurance, and stamina, stalking her prey silently before racing in for the kill.
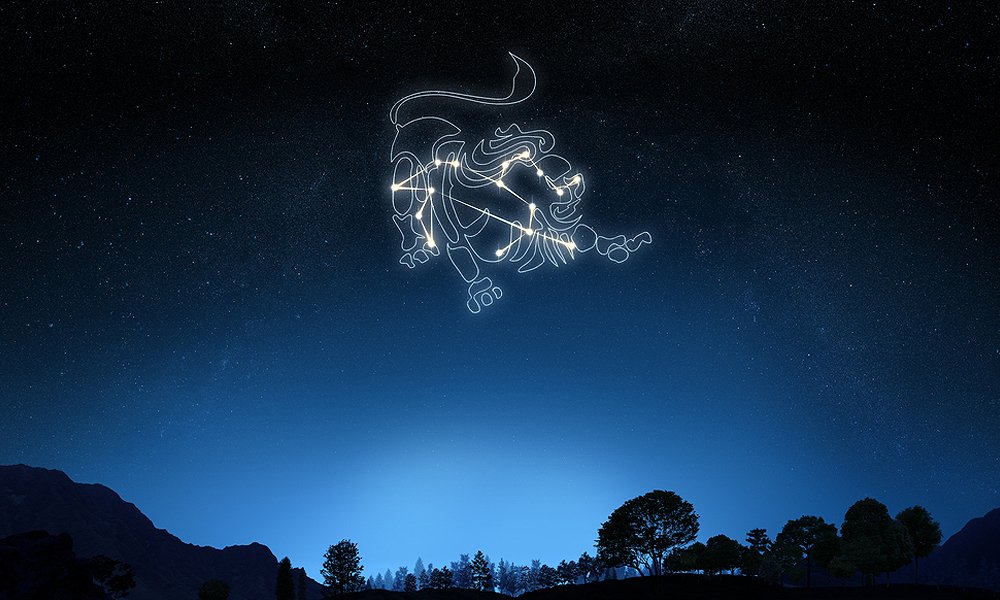

The Lion represents courage, wisdom, pride, and authority. In the law of the jungle, very few creatures will do battle with a lion.
As a spiritual animal, the Leo meaning of the Lion represents strength and the ability to overcome difficulties.
People born under the sign of the Lion have great personal strength, perseverance, and assertiveness. They are often leaders – Barack Obama is a perfect example.
Leo Starseeds personify the ability to excel faster than others and become leaders in their fields. Starseeds are highly evolved souls who have great powers of wisdom.
Future
Astronomers are constantly searching for life in the universe. As telescopes become more powerful, they focus on exoplanets in constellations.
Leo offers many exoplanets that will become very exciting to explore in the future.
Meteor showers make awesome viewing if you are lucky enough to be in an area where they are visible.

The Leonids, like all meteor showers, are named after the constellation from which they appear to radiate.
The radiant, or center of the shower, lies in the constellation of Leo the Lion, giving it the name Leonids.
This year, the shower will peak between the 17th and 18th of November. Plan to have your telescope ready for a night of spectacular star gazing!