Libra Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Libra Constellation
Abbreviation Lib
Symbolism: The Scales / The Balance
R.A. position: 15h
Dec. position: -15°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 229 light-years
Area: 538 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Zubeneschamali (β Lib)
Visible at: Latitudes between +65° and −90°
Best viewed: During the month of June at 9.00pm
The Libra constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as The Scales or The Balance. Libra is the only zodiac constellation that is an inanimate object. It is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek and Roman times and is associated with the Goddess Astraea.
Libra is the 49th largest of the 88 known constellations and can be found in the sky by locating Virgo the Virgin, and Scorpius the Scorpion. Libra is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the amazing NGC 5792 spiral galaxy.
Read on to learn more about the constellation Libra and interesting Libra constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
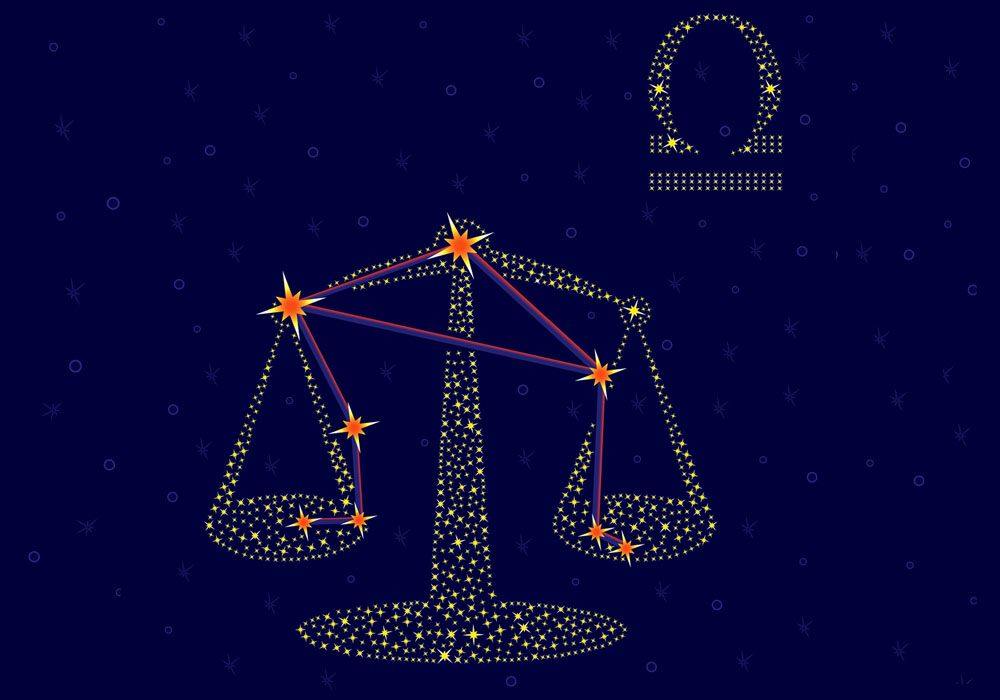
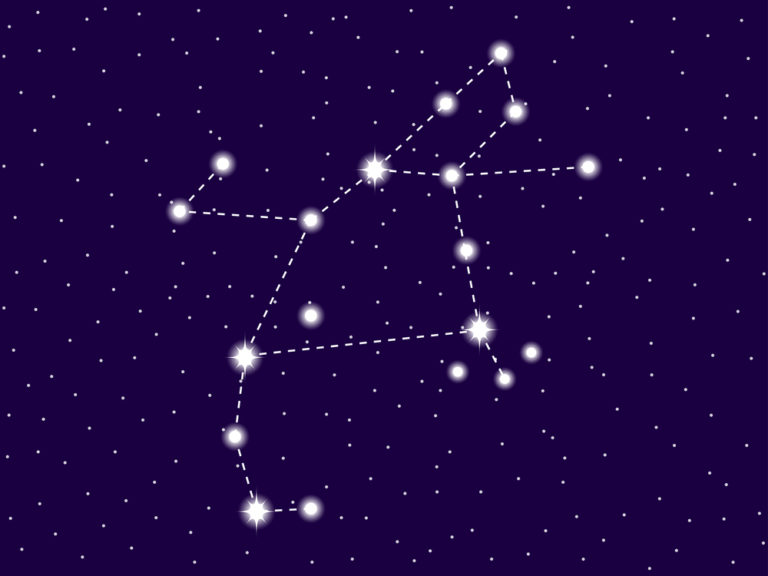
Libra constellation
Libra is a fairly faint constellation located in the southern celestial hemisphere. It has some bright stars with fascinating names like Zubeneschamali and Zubenelgenubi. It also contains the oldest star in the universe – aptly named Methuselah!
The Scales are the only zodiac sign that is not a living creature and is not part of the iconic Greek mythology legends. The Scales balance in the sky with two pans suspended by arms on a horizontal lever.
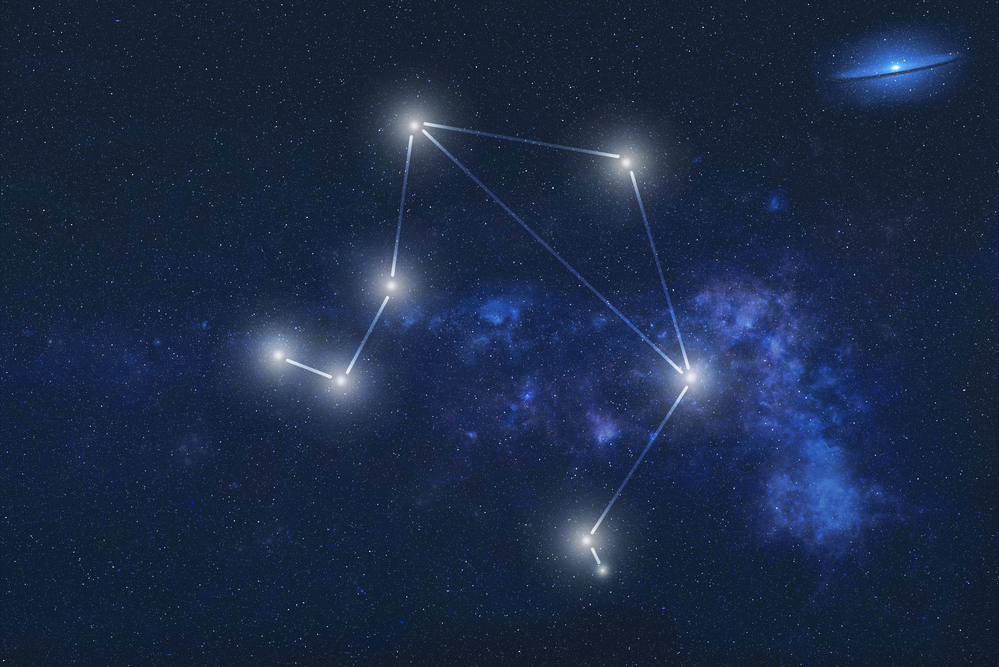

The Libra (constellation) is the 49th largest constellation. It occupies an area of 538 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Virgo the Virgin and Scorpius the Scorpion. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Lupus, Hydra, Serpens Caput, and the corner of Centaurus.
For home astronomers, the scales constellation offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains the fascinating star Gliese 581 which has orbiting planets that are similar to Earth. It also offers the beautiful spiral barred galaxy NGC 5885 that lies about 80 million light-years away (34).
In the case of Libra, both the Libra constellations and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The Libra constellation story dates back over 3000 years.
What does Libra constellation look like?
You may be asking – what is Libra? Libra is a scale! With many bright stars at strategic points, Libra is a constellation that you can draw with your eye in the sky.
The constellation of Libra looks like a classic set of old-fashioned scales. There are two pans of equal size that hang down on two arms.
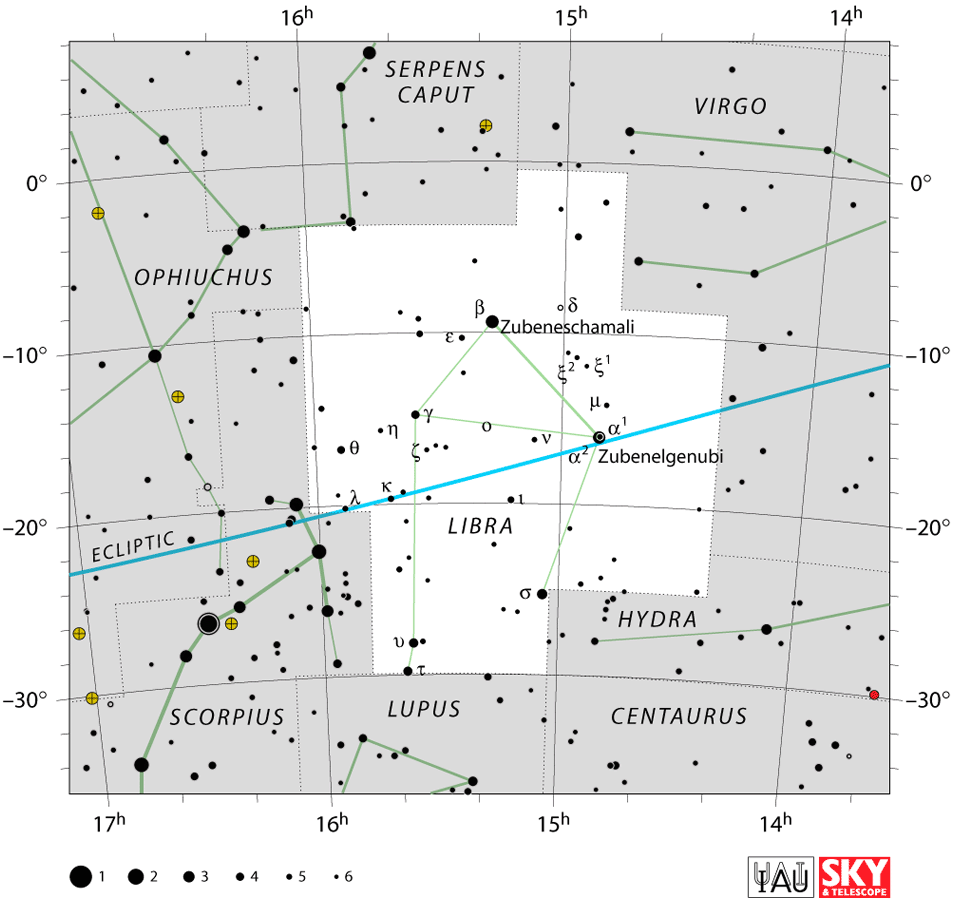
The arms of the Libra scale balance on a horizontal lever that can tilt one way or another, depending on which scale has a greater weight. You need to imagine a set of ornate scales – something like Great Grandma would have had in her kitchen!
In the sky, the constellation scales lie at an angle, as if swinging from the hand of the Goddess who carried them into the heavens.
Libra lies near Virgo and Scorpius. In this story, Virgo is Astraea, Goddess of Justice, who was placed into the sky carrying a torch and a set of Scales. Although Libra lies near the Scorpion, the scales do not link to this creature in any Libra legends.
How far is Libra constellation from Earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it looks as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be as close as 60 light-years, and others as far as millions of light-years.
To give some idea of the stars in Libra constellation – Zubeneschamali, also known as Beta Librae, is the brightest star in Libra and lies about 185 light-years away from the solar system.

Zubenelgenubi is 74.9 light-years from Earth. Sigma Librae is a red giant, 288 light-years away. Methuselah is 190.1 light-years away. Upsilon Librae is an orange giant about 195 light-years away. Tau Librae is 445 light-years away.
The beautiful NGC 5792 barred spiral lies about 83 million light-years away from the Sun. Another galaxy, NGC 5885 is also far away, at about 80 million light-years.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Libra constellation from Earth is about 229 light-years. If you consider the deep-sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years!
Zodiac family
The Libra symbol is the 7th sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between 22 September and 22 October. It is one of three Air signs, the others being Gemini and Aquarius.
The Libra star constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Virgo stands above the Scales as if she is holding them in her hand. Scorpius the Scorpion lies below the scales but is not connected in any mythological story.

In ancient Greek times, the Libra zodiac constellation was included in the constellation of Scorpius, forming part of the claws. They called the area the Latin word “chelae”, which translates to “the claws” (1).
Like all the Zodiac constellations, the Libra constellation lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. The Sun passes through Libra each year from around 23 September to 23 October.
Libra is a cardinal sign. The cardinal signs indicate a change of season when the sun makes its annual passage through them. Libra represents the start of the autumn season (2).
One of the most interesting Libra facts is that Libra is the only sign in the zodiac family that is an inanimate object. All the other signs are living in the form of gods, goddesses, animals, and mythical creatures.
Features
Major stars in Libra
Here is a list of the major Libra stars.
Zubeneschamali – β Librae (Beta Librae)
Zubeneschamali, also known as Beta Librae, is the brightest star in Libra. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.61 and you can see it without a telescope. It lies about 185 light-years distant from the solar system.
Zubeneschamali is a blue-white dwarf and may be part of a binary star, with a companion. It is 130 times as luminous as our Sun and has a radius of 4.9 times that of the Sun.
The name stems from the Arabic, al-zuban al-šamāliyya, which means “the northern claw”. This star was originally seen by ancient astronomers to be part of the Scorpion. The Latin name is Lanx Borealis, which means “the northern scale” (3).
Zubenelgenubi – α Librae (Alpha Librae)
Alpha Librae is another interesting star of Libra. It is the second brightest star and is a binary star system.
Alpha-1 Librae is the dimmer of the two stars, with an apparent magnitude of 5.153. It lies about 74.9 light-years from Earth. The companion star, Alpha-2 Librae is brighter with an apparent magnitude of 2.741. It is 75.8 light-years away from Earth.
The name Zubenelgenubi comes from the Arabic phrase al-zuban al-janūbiyy, which means “the southern claw”.
This star was originally seen by ancient astronomers to be part of the Scorpion. The Latin name for Zubenelgenubi is Lanx Australis, “the southern scale”. Zubenelgenubi is a favorite of Star Wars fans – the name is very similar to Obi-Wan Kenobi (4).
Brachium – σ Librae (Sigma Librae)
Sigma Librae is one of the red giant stars in Libra with an apparent magnitude of 3.29 and you can see it with the naked eye. It lies about 288 light-years from the Sun. At one time, Brachium was thought to be part of the Scorpius constellation.
It was officially designated part of Libra in 1930 by the International Astronomical Union. It has a surface temperature of below 3.500 K. In comparison, our Sun has a surface temperature of 5,778 K (5).
Methuselah – HD 140283
Methuselah was an ancient biblical figure who lived until the age of 969! HD 140283 is the oldest known star in the Universe and is named after this famous figure. HD 140283 is one of the most exciting stars in the Libra constellation and is around 14.46 billion years old.
The Universe in comparison is 13.77 billion years old, so this star is the ultimate mystery. It is a subgiant star with an apparent magnitude of 7.223 and is 190.1 light-years away from our Solar System. Scientists know that it consists almost entirely of hydrogen and helium (6).
υ Librae (Upsilon Librae)
Upsilon Librae is an orange giant libera star. It is a multiple star with an apparent magnitude of 3.6. The system lies about 195 light-years away from the Sun. The star is also known as Derakrab Borealis which comes from the Arabic “Al-Dhira al-Akrab” meaning “Arm of the Scorpion” and the Latin “borealis” for “northern” (7).
τ Librae (Tau Librae)
Tau Librae is a blue-white dwarf with an apparent magnitude of 3.66. You can see it without a telescope. The star lies about 445 light-years away. It has a radius 3.2 times that of our Sun.
It is also known as Derakrab Australis , which means “That of the south of the arm of the Scorpion”. It comes from the Arabic phrase Al-Dhira al-Akrab meaning “the arm of the Scorpion” and the Latin australis for “from the south” (8).
Deep-sky objects in Libra
NGC 5792
NGC 5792 is a barred spiral galaxy in Libra. Barred galaxies have a well-defined central ‘bar’ made up of stars, from which the arms spiral outwards. NGC 5792 has an apparent magnitude of 12.1 and is about 83 million light-years away from the Sun.
Home stargazers can see this galaxy through a telescope. It has a shallow spiral form and a bright star in the foreground (9).
NGC 5885
NGC 5885 is a beautiful barred spiral Libra galaxy. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.8, which is faint and you cannot see it without using a telescope. The galaxy was discovered by William Herschel in 1784. It lies about 80 million light-years away from our Solar System.
NGC 5890
NGC 5890 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy in Libra. An unbarred galaxy does not have the distinct central bar that is seen in barred galaxies. NGC 5890 is a very faint galaxy that cannot be seen with the naked eye. It has an apparent magnitude of 14. The American astronomer Ormond Stone discovered it in 1785. It lies about 97 million light-years away from our Solar System (10).
NGC 5897
The NGC 5897 galaxy is about 24, 000 light-years away from our Solar System which is relatively close compared to the other galaxies in Libra. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.5 (11).
It is a huge galaxy with a diameter of about 170 light-years. Unlike most globular clusters, NGC 5897 has a mass concentration of XI, which means that the stars are evenly distributed.
They have not yet undergone a process of core-collapse that would collect most of the mass around the core. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784 (12).
Exoplanets in Libra
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life.
Gamma Librae b and c
Gamma Librae, also known as Zubenelhakrabi is a giant orange-red star that lies about 163 light-years away. It has 2 planets that orbit it. The first is Gamma Librae b, a gas giant with a mass of 1.02 Jupiters.
It takes 415.2 days to complete one orbit of its star. It was discovered in 2018. The second planet Gamma Librae c, is much larger at a mass of 4.58 Jupiters. It takes 2.6 years to complete one orbit. (13).
HD 141937 b
HD 141937 b is an exoplanet revolving around its mother star, HD 141937. The star is a yellow sequence star, known to be about 2.5 billion years old.
The exoplanet has a mass of 9.69 that of Jupiter and a radius of 1.11 that of Jupiter. It is 105 light-years away and takes 653 days to complete one orbit of its star (14).
Gliese 581
This star is of great interest to astronomers. It has 6 exoplanets orbiting it. A new one, called Gliese 581 e, was discovered recently in 2011. It is the smallest exoplanet found, with a mass of twice that of our Earth.
Because some of the planets orbit in the habitable zone, scientists thought they may have liquid on their surfaces. This has not yet been proven (15). The farthest Libra planet Gliese d, orbits its mother star in 66.8 days. The nearest exoplanet, Gliese 581 e, takes only 3.15 days (16).
WASP-57
WASP-57 is a yellow G-type star with one exoplanet known as WASP-57 b. The gas-giant exoplanet orbits the mother star every 2.8 days. It has a mass 0.644 that of Jupiter. Discovery was in 2012 (17).
Meteor showers in Libra
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up.
This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars. Libra unfortunately does not offer large meteor showers.
May Librids
This shower takes place between 1 May and 9 May with the peak on 6 May. You can expect to see around 2 to 6 meteors per hour. This is not a significant shower and is seen in the southern hemisphere.
It was first detected on 5 May 5, 1929, by three Texas members of the American Meteor Society. Observations were made by J. E. Morgan, director of the Royal Astronomical Society’s New Zealand meteor section (18).
April Librids
This is a smaller meteor shower that takes place between 13 April to 21 April. It is not a significant shower and not of great interest to home stargazers. Meteors appear at around 2 to 4 per hour.
Location and visibility
Where is Libra constellation located?
Libra is a medium-sized constellation and although it does not have the brightest stars, it is easy to find once you know what to look for. You can find the main stars without the need for a telescope and then you can imagine the two scales swinging on either side of the lever.
Where is Libra in the sky?
Libra is a southern constellation and is the 7th largest zodiac constellation occupying an area of 538 square degrees. It’ss the 49th largest constellation of the 88 named constellations.
Libra lies in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere, SQ3. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the scales constellation at latitudes +65° and −90°.

To find Libra you can locate the two zodiac constellations of Virgo the Virgin and Scorpius the Scorpion. Virgo stands above the scales and the Scorpion is underneath the scales.
Another way to locate Libra is to find the well-known Big Dipper. Follow the handle down to the bright star Arcturus in the nearby constellation Boötes. From there, look down to Virgo. Libra is right next to Virgo. It has a distinct triangle formed by bright star Libra Zubeneschamali, and the stars Zubenelgenubi and Zuben Elakribi.
When is Libra constellation visible?
Libra is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
When is Libra visible in the northern hemisphere? Set up your romantic midnight feast to spot Libra at around midnight in April. It will appear low on the southeastern horizon moving across the southern horizon until dawn.
For those who prefer an earlier time, from May to June the constellation is visible from around 10.00pm low in the southeast sky. In July it will appear low in the southern night sky at around 10pm before disappearing below the south-western horizon around 3 hours later.

For those avid stargazers in the southern hemisphere, Libra is seen in April low in the eastern night sky from around 10.00pm, slowly moving higher before reaching overhead at around 3.00am. In May and June, you can spot it earlier, at about 8.00pm getting higher as the night moves on.
At midnight it will begin to descend towards the western horizon. In July and August it appears high in the northern night sky at around 8pm, moving towards the western horizon over the next few hours. In September Libra is visible high in the western night sky from around 8pm, before disappearing below the western horizon around midnight.
Remember – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down. The scale constellation will be balancing on its head! (18)
How to find Libra constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here’s the step-by-step guide on how to find the scales constellation.
- To locate Libra, it is easiest to first find the Big Dipper in Ursa Major, which looks like a plow with a long handle
- Follow the curve of the handle downwards
- You will reach the bright star Arcturus in the nearby constellation of Boötes
- Now look down again to Virgo
- Look for a distinct triangle of 3 bright stars
- Libra is right next to Virgo, with the triangle forming the top of the scale
- You can also locate Libra via the Scorpion – look for the bright star Antares, at the heart of the Scorpion, then find the claws extending upwards
- Libra is directly in front of the claws
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down.
- To locate Libra, it is easiest to first find the Big Dipper in Ursa Major, which looks like a plow with a long handle
- Follow the curve of the handle upwards
- You will reach the bright star Arcturus in the nearby constellation of Boötes
- Now look up again to Virgo
- Look for a distinct triangle of 3 bright stars
- Libra is right next to Virgo, with the triangle forming the top of the scale
- You can also locate Libra via the Scorpion – look for the bright star Antares, at the heart of the Scorpion, then find the claws extending downwards
- Libra is directly in below the claws
How to view Libra Constellation?
Libra is a fairly faint constellation and getting away from city lights and pollution is the best way to see it. You can see the constellation Libra with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make your Libra astronomy experience so much more exciting!
For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Libra in the sky. Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
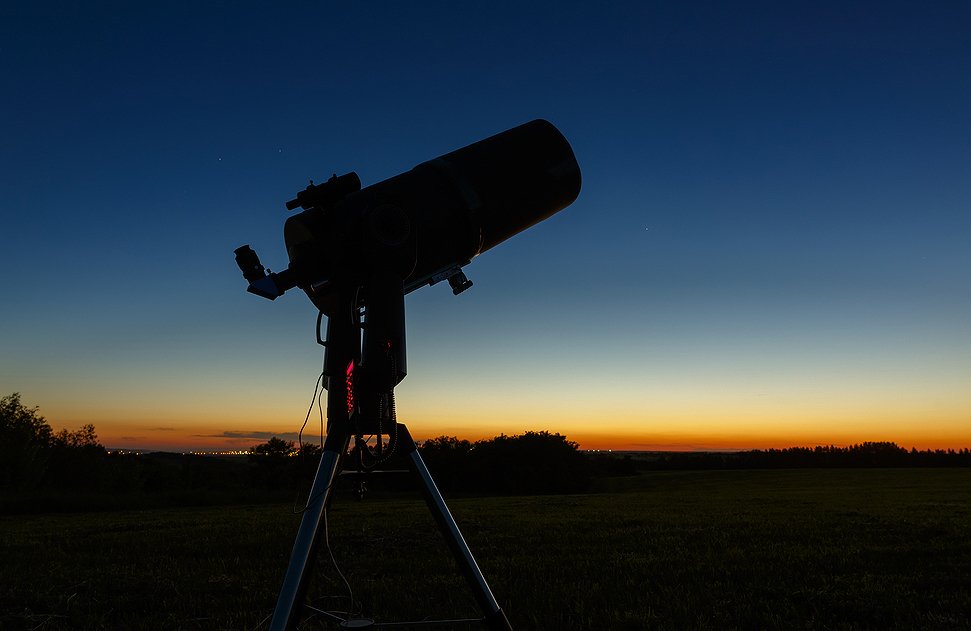

The Celestron NexStar 127SLT Computerized Telescope is a dream – It automatically tracks a celestial object for you, without any intervention needed. At a very acceptable price, this scope is ideal for a family growing from entry to intermediate level.
It is extremely portable for packing into a car for a weekend away from the city lights. The scope features a Maksutov-Cassegrain Optical Design with a 127mm (5”) aperture.
The large-high-quality lens gathers enough light to give stunning views of the Libra constellation. This telescope is easy to use with the Celeston Skyalign functionality.
Simply center any three bright objects in the eyepiece and the NexStar SLT aligns to the night sky. It comes with a Red Dot StarPointer finderscope and 2 eyepieces, a 25mm, and a 9mm.
History of observation
Who discovered Libra constellation?
The Libra origin goes back to ancient civilizations including the Greeks, Romans, and Babylonians. It was documented in stories, folklore, and myths over thousands of years.
Most civilizations associated the constellation with the Libra goddess of Justice. During the time of the Roman Empire, 27BC to 476AD, the constellation represented the scales held by Astraea, the Goddess of Justice (19).

She was a figure similar to that of the Greek Goddess, Virgo in Greek mythology, dating back to 3000BC. Originally, the Greeks saw the scales of Libra as part of the Scorpius constellation. In this story, the Scorpion was sent to kill Orion the Hunter. At some stage, thousands of years ago in the Libra story, the two constellations became separated.
In Libra constellation history, the Babylonian astronomers also knew of the Scales as far back as 2000BC. The scales were sacred to the God Shamash. Shamash was the Sun God and also the God of Justice. As a Libra god of the sun, he was able to see all that was going on in the world during the day.
This also meant that he was able to see through deception and deceit. As such, he was worshipped as the God of Truth and Justice (20). In ancient Egypt around 3000BC, the three brightest stars of Libra were seen as a constellation that formed a boat that sailed on the Celestial River (21).
In traditional Chinese uranography, around 750BC, the modern constellation Libra is located within the eastern quadrant of the sky, symbolized as the Azure Dragon of the East (22).
In more recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially included Libra in his 48 asterisms. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD (23).
How old is Libra constellation?
Libra is an ancient constellation, and Libra history dates back to the era of the Roman Empire around 27BC to 476AD,. The constellation represented the scales held by the Astraea, the Goddess of Justice (24).
Long before that, around 3000BC, the Greeks associated the Scales with the Goddess Virgo who was also known as Astraea.

When she ascended into the sky, she carried a torch and a set of scales with her. Before this, Greek astronomers saw Libra as part of the Scorpius constellation. The main stars forming parts of the two claws extending outwards from the head.
Libra is also an old Chinese constellation. In traditional Chinese uranography, around 750BC, it is located within the eastern quadrant of the sky, symbolized as the Azure Dragon of the East (25).
The Babylonian astronomers knew about Libra as far back as 3000BC. The name was MUL Zibanu, meaning the “scales” or “balance”. The scales were held by the God Shamash, who was the God of the Sun and the God of Justice. The Sumerians knew this area as ZIB-BA AN-NA, the ‘balance of heaven’ in 2000BC (26).
How did the Libra constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, what does Libra mean?
Libra etymology shows that most ancient cultures saw the constellation as a representation of justice, fairness, and balance. The constellation resembles a set of scales, and is named from the Latin word Libra, meaning ‘The weighing scales’.
The scales are the only inanimate object in the zodiac constellations. Unlike the other mythical creatures, animals, Gods, and Goddesses, Zeus did not put Libra into the sky. The Goddess Astraea carried them into the heavens when she was banished from Earth.
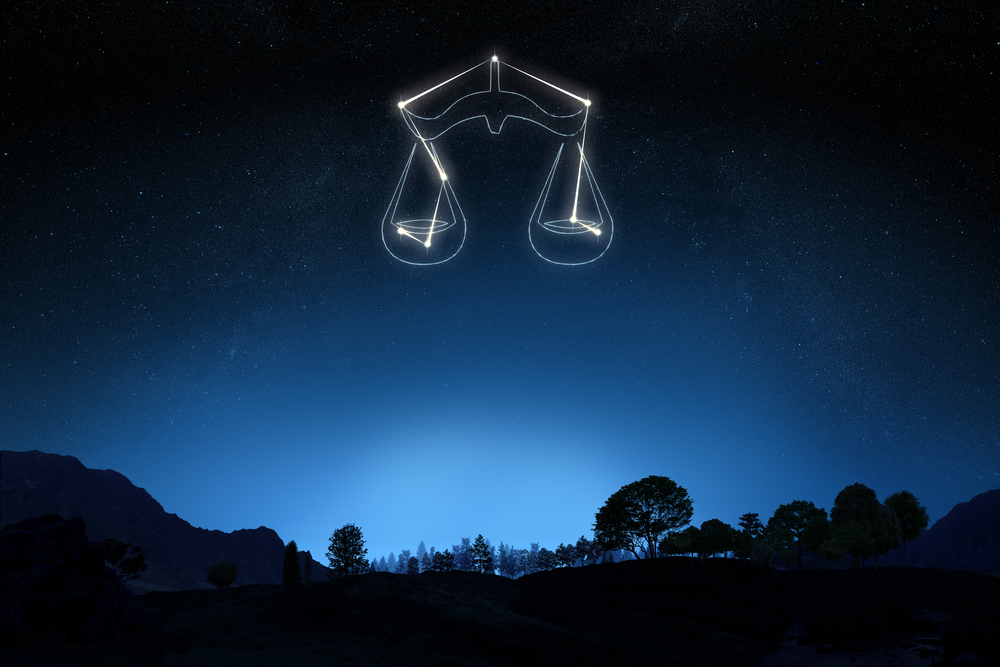

The word Libra has a plural form Librae. In Greek, the Libra name comes from the word ‘lithra’, which means weighing scale. In ancient times, Libra was part of Scorpius the Scorpion, forming the scales. Or, according to another story, held the scales in his claws.
The main stars of Libra start with the word ‘Zuben’ which comes from the Arabic word meaning ‘claw’. Zubenelgenubi is the “southern claw of the Scorpion” and Zubeneschamali is the “northern claw of the Scorpion”.
The Sumerians knew this area as ZIB-BA AN-NA. In this Libra name meaning, it represents the balance of heaven in 2000BC.
There is also another interesting Libra meaning – the word Libra also means pound’, as in a measure of weight. In the Libra constellation meaning, this also relates to scales, an apparatus used to measure weights (27).
Mythology and meaning
Libra myth
Like many of the constellations, there are different Libra mythology stories. Unlike the other Zodiac constellations, Libra does not only have its roots in Libra greek mythology.
The first mythology of Libra dates back to around 2,000BC in Babylon. Babylonian astronomers associated the constellation with scales or a balance. They called it ZIB.BA.AN.NA, which means “the balance of heaven”.
The name possible came from the fact that the Sun at the autumn equinox shone in front of the stars of Libra at that time. The Equinox indicates the balance of natural forces in the world when day and night are of equal lengths.

The ancient Greeks also knew of the constellation, although it did not form part of any story of gods and goddesses in Libra constellation greek mythology. In this Libra constellation myth, the stars were part of Scorpius the Scorpion.
The two brightest stars indicate the outstretched claws. Zubenelgenubi was the “the southern claw of the Scorpion” and Zubeneschamali was the “the northern claw of the Scorpion.”
Another myth of Libra speaks of Astraea, the Goddess of Justice. She was a celestial virgin and the last of the immortals to live with humans during the Golden Age. When she ascended into the skies she became Virgo, carrying a torch in one hand and the Libra scales of Justice in the other (28).
What does Libra symbolize?
As you see in the above picture, the scales are the symbol for Libra. What does Libra represent? In all ancient stories and myths, Libra represents balance, harmony, and justice. The Libra symbolism is a set of scales.
The Libra symbol meaning represents the inherent nature of people born under this sign to be peacemakers. They always strive to create balance and equilibrium in all areas of life. This applies to work, home, leisure, family, friends, and any situation that they find themselves in!
The Libra modality is cardinal. The cardinal modality represents beginnings, initiation, and action. The Libra sign meaning cardinal signs form the main axis on the zodiac wheel.

People born under cardinal signs are usually more traditional or conservative than others. Libras are diplomatic and fair. They listen and understand both sides of a story. Libras are extremely intelligent, good-natured, and pleasant.
On the negative side, what do the Libra scales mean? They don’t react kindly to taking orders. Like Grandma’s old scale that tipped from side to side until perfectly balanced, Libras can often be off-balance. They then become restless, sullen, self-pitying and confused (29).
Many people ask – what is the Libra planet? Venus is the planet that rules the sign of the scales. You may also ask – what is the Libra animal? Libra is neither an animal nor a mythical creature!
The age of Libra occurred around 17,000BCE to 15,000BCE. We are currently in the age of Pisces and at the dawn of the age of Aquarius.
Here are some famous Libra personalities – Mahatma Gandhi, Horatio Nelson, John Lennon, Margaret Thatcher, Serena Williams, and Vladimir Putin (30).
Do you want to know how to spot a Libra? It is easy – look for the person who is trying to keep the peace, resolve an argument, or turn enemies into friends!
Future of Libra constellation
Libra is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study.
The most current and exciting info surrounds the star Gliese 581. This star has numerous exoplanets that orbit it. A recently discovered exoplanet is the closest one yet found to the size of our Earth.
It is the smallest exoplanet known with a mass of only twice that of our planet. Because some of the planets orbit in the habitable zone, scientists thought they may have liquid on their surfaces. This has not yet been proven, but as telescopes and analytical processes become more advanced, who knows what we may find! (31).
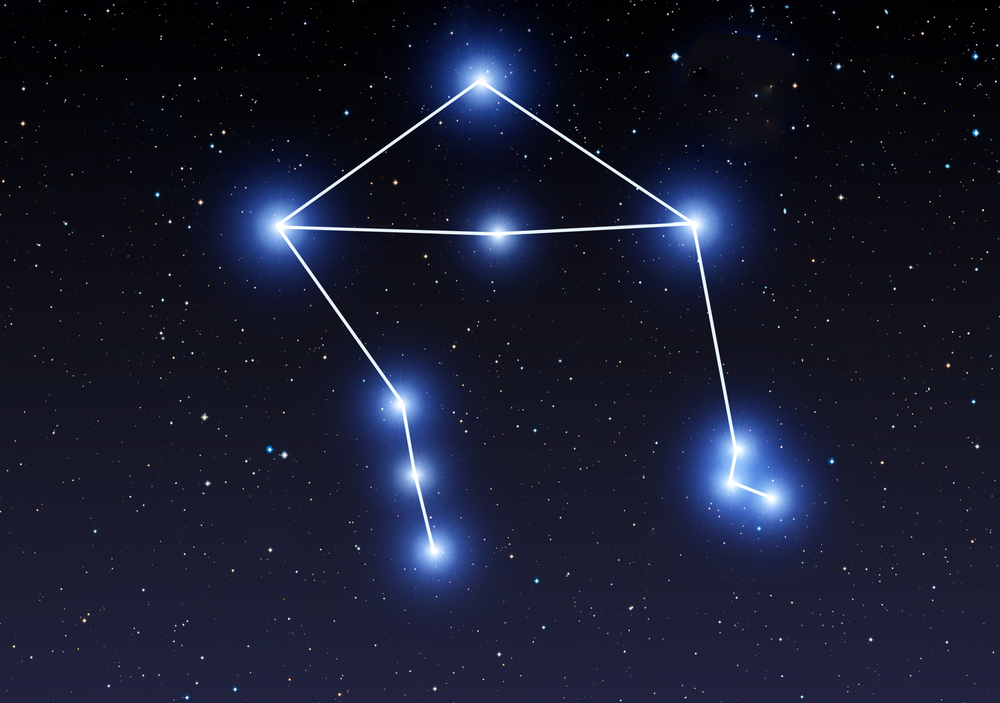

NGC 5897 is an 8.5 magnitude globular cluster in Libra, that lies about 24,000 light-years away. This cluster is of great interest as it has stars that are evenly distributed.
Most galaxies that we know have stars gathered around the core. That is because they have collapsed and clustered together. The stars in NGC 5897 still have to collapse and scientists may be able to monitor this process (32). The star Sigma Librae in Libra is a red giant.
Red giants are in a phase of shedding their outer layers and becoming a small, dense body called a white dwarf. If they are part of a binary star system, they may attract excess matter from their companion stars and eventually explode – turning into a bright nova. Unfortunately, we will not be around long enough to see this, but future generations may! (33).