Orion Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Orion Constellation
Abbreviation: Ori
Symbolism: The Hunter
R.A. position: 05h 35m 17.0s
Dec. position: -5° 23′ 27.99”
Distance from Earth: Average distance is 1344 light-years
Brightest star: Rigel
Visible at: Latitudes between +85° and −75°
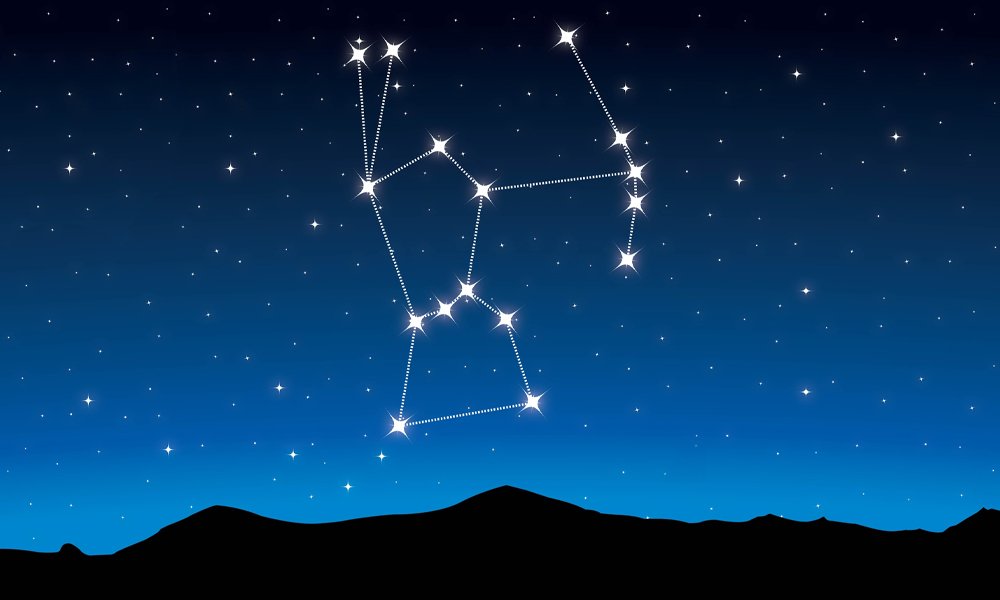
The Orion Constellation is probably one of the most well known and easily recognizable constellations in the night sky, easily spotted even by those who are not star-struck. Also known as the hunter, he stands proudly in the sky with his belt of three stars in a line shining brightly.
Orion has a fascinating story with roots in Greek mythology. You can observe Orion in both the northern and southern hemispheres, even with the naked eye. Orion is a popular constellation for amateur astronomers as it offers one of the brightest stars in the sky – Rigel, a blue-white supergiant (1).
Characteristics
How far is the Orion constellation from earth?
Like most constellations, Orion is made up of numerous stars, nebulae, and deep sky objects.
When observed from planet Earth, the constellation looks as if all the objects lie on the same plane. In fact, each object is at a different distance from the earth.

To give some idea, the brightest star in Orion is Rigel, which is 860 light-years away from Earth. The Orion Nebula is located 1500 light-years away. (2)
The three stars in the Orion belt stars are located at varying distances.
- Alnitak is 1260 light-years from Earth.
- Alnilam is 1975 light-years away.
- Mintaka is around 1200 light-years away.
So, how far is Orion from Earth?
Taking into account the celestial objects and their individual distances, the average distance of Orion from the Earth is 1344 light-years. (3)
What does the Orion constellation look like?
The Constellation Orion is a large bold hunter, standing in the sky with his arm raised, ready to slay any creature that comes close to him!
In the northern hemisphere, the Hunter stands upright.
You can form his body by finding the famous three stars that make up his belt.

- Dangling down from his belt is a sword. The sword is easily seen as it contains the bright Orion Nebula, which looks like a dense, bright spot in the sky.
- The bright star Betelgeuse marks Orion’s left shoulder. Work your way upwards and imagine him holding a large club. Opposite Betelgeuse is a bright star known as Bellatrix.
- This star marks the shoulder of his right arm, which extends outwards. In his right hand, he holds a shield. Some ancient cultures saw it as animal skin, or a slain lion – you can decide.
- The Hunter’s right leg is raised and the bright star Rigel marks the back of his foot.
Once you locate the belt – the Hunter comes to life. Give it a try. Remember that in the southern hemisphere, the Hunter stands upside-down.
How old is the Orion constellation?
The earliest known history of Orion the Hunter Constellation goes as far back as 38000 years.
The Hunter was documented in a prehistoric Aurignacian ivory carving. The carving was discovered in a cave in the Ach valley in West Germany in 1979.
Babylonian star records, which were created around 1200BC in the Late Bronze Age, also showed the Orion origin as a hunter in the sky.

In ancient Egypt, around 3100BC, astronomers identified the constellation as the God Sah or Sahu, who was swallowed by the underworld.
Scientifically, the constellation contains objects that are millions of years old.
Here are a few Orion facts
- The star Rigel is a relatively young star at only 10 million years old.
- Betelgeuse is also around the same age.
- Bellatrix is older at around 25 million years.
The stars in the dense Orion cluster were thought to have been formed in the last 3 million years (4).
Zodiac family
Orion the Hunter is not one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac.
This is because the constellation does not lie on the ecliptic path of the sun.
This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. Orion lies to the south of the Ecliptic path and is not crossed by the sun.

The Orion constellation story does have an interesting link to Scorpio, the 8th sign of the Zodiac and one of the Zodiac constellations.
- In Greek mythology, the Scorpion was sent by the Goddess of the Earth, Gaea, to kill Orion in a great battle.
- The Scorpion succeeded and Zeus, King of the Gods, placed both Orion and the Scorpion into the skies.
- Because they were enemies, the two constellations are never seen in the sky at the same time (5).
- Orion is also closely connected to Taurus the Bull, the 2nd sign of the Zodiac.
In the sky, he stands facing the Bull, and it appears as if he is about to do battle with this creature.
Features
Stars in Orion constellation
Like most constellations, the constellation of Orion is made up of numerous stars.
Some Orion stars are brighter than others and many are identified for their unique attributes.
How many stars in Orion? Orion has 7 main stars and 10 stars with planets.

Image credit: NASA/Fujii
Here are some names of stars in Orion.
- The brightest Orion star in the constellation is Rigel, a blue supergiant, also known as Beta Orionis.
- Rigel is the 6th brightest star in the sky, with an apparent magnitude of 0.18. It is around 40,000 times brighter than our Sun.
- Rigel is a star system, made up of 3 stars. It marks the position of the left foot of the Hunter. (6)
- Also notable in Orion constellation stars is Betelgeuse, a red supergiant known as Alpha Orionis.
- Betelgeuse is the second brightest star in Orion and the 8th brightest star in the sky. This star is approximately 643 light-years away from the Earth.
- It marks the spot of the armpit of Orion’s raised arm.
The famous belt of Orion is made up of three 3 stars, Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. Mintaka is the western-most star and is a multiple star system about 1200 light-years away.
Alnitak is the eastern-most star and is made up of a star system of 3 blue supergiants. Alnilam is the middle star of the belt; It is a young star, only 5.7 million years old – much younger than our sun, which is around 4.5 billion years old (7).
Deep sky objects in Orion constellation
Orion features a number of interesting deep sky objects.
The first is the Orion Nebula, also known as Messier 42.
A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas thrown out by the explosion of a dying star.
When new stars begin to form, they also throw out the gas, which forms into nebulae (8).

The Orion Nebula lies to the south of the three stars that form Orion’s Belt stars. It is the brightest nebula in the sky and can be seen with the naked eye, appearing to be a blurry star in Orion’s sword.
The Trapezium is a dense open cluster of stars located in the middle of the Orion Nebula. Galileo Galilei discovered it in 1617.
Another deep sky object of interest is the De Mairan’s Nebula, which is also located in the Orion nebula. The French astronomer Jean-Jacques Dortous de Mairan discovered this celestial object in 1731.
For new astronomers, the Horsehead Nebula is fabulous to view through a telescope.
This nebula is located south of the star Alnitak and has a dark shape that resembles a horse’s head.
Exoplanets in the Orion constellation
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars, other than our star, the sun.
Exoplanets are of great interest as they may very well have similar conditions to our Earth and hence the possibility of life.
Astronomers hunting for exoplanets in the Orion constellation have identified a few.
In 2012, astronomers in Chile noted a star known as CVSO 30, 1200 light-years away. Orbiting this star is a gas giant which they named CVSO 30c.
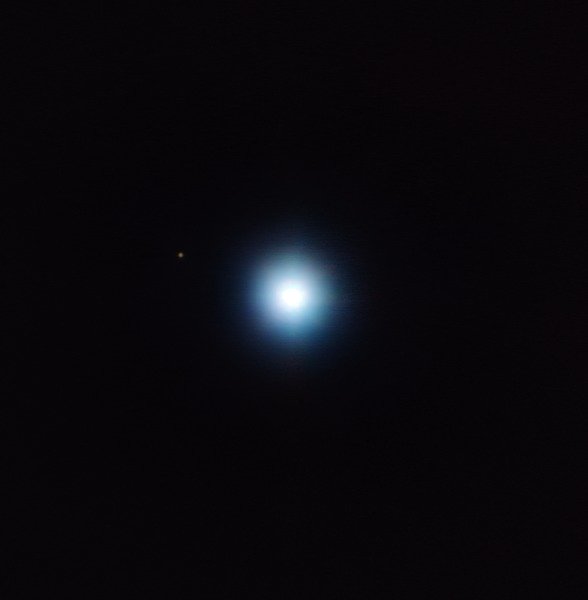

Image credits: VLT image of CVSO 30 and its planet, CVSO 30 c
They also detected a possible another planet, named CVSO 30b, with an orbit close to its star, CVSO 30 (9).
Another possible exoplanet is PTFO8-8695 b, about 1100 light-years from Earth. It is so close to its star that the outer layers are being burnt away.
Two other gas giants found in the Hunter constellation are known as HD 38529 b and HD 38529 c.
They are of interest to astronomers as they orbit close to the mother star, which could possibly make them habitable planets.
Location and visibility
Where is Orion constellation?
Orion is a great constellation for new astronomers to find in the sky.
It is very bright and can be seen with the naked eye.
Through a telescope, it is spectacular! Orion is the 26th constellation in size, occupying an area of 594 square degrees.
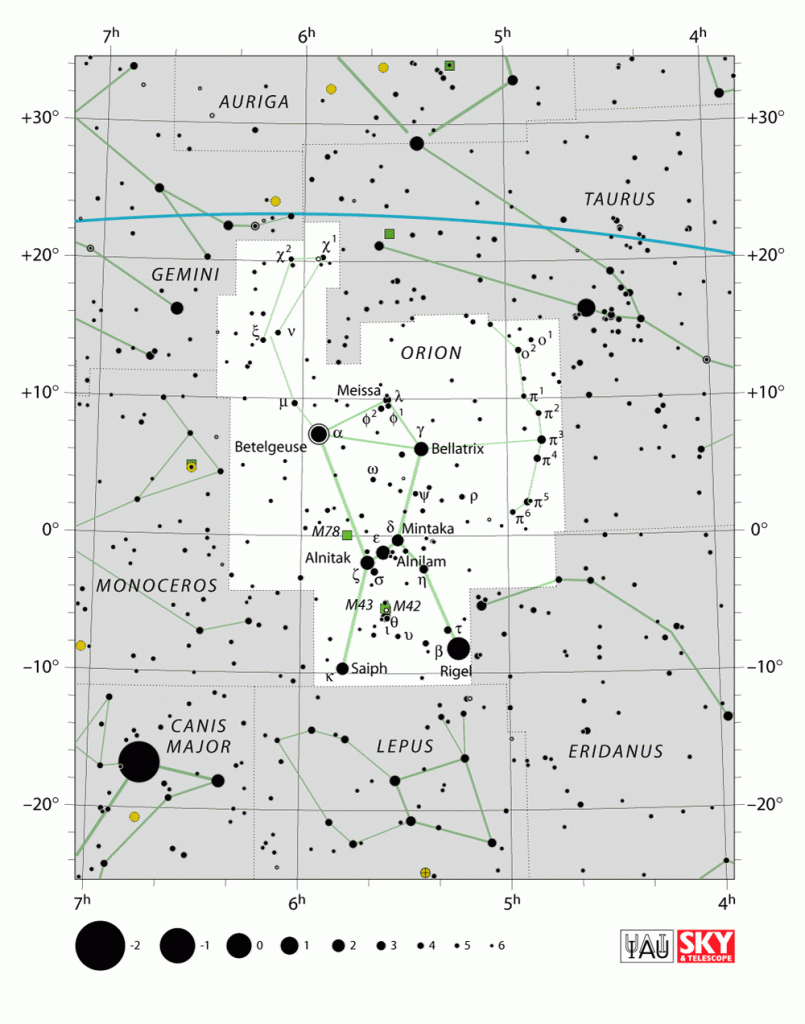
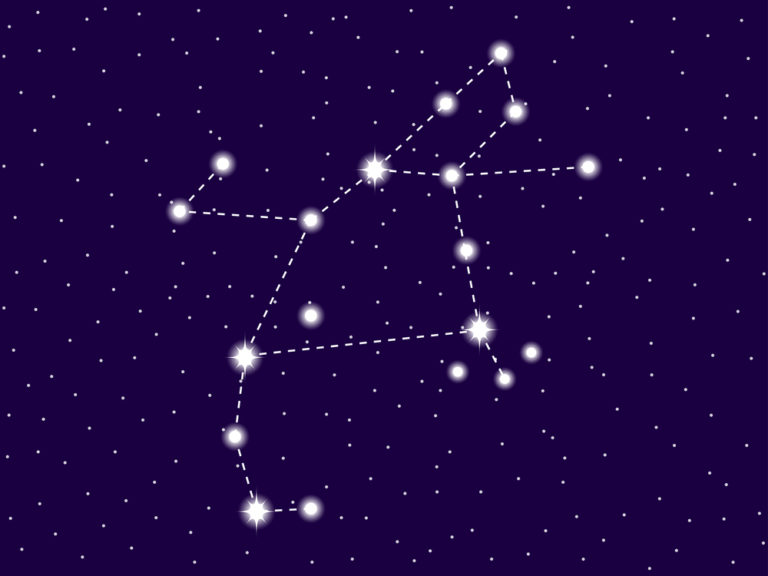
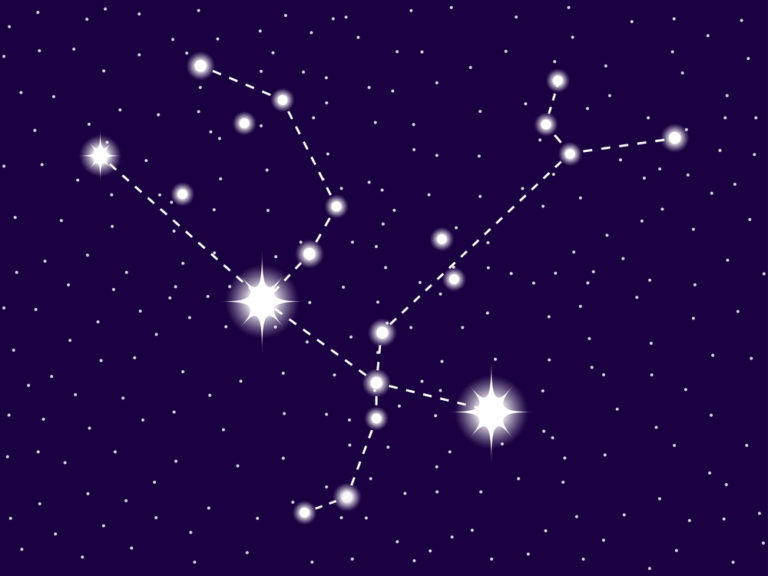
Image credits: Orion Constellation Map, by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine
Where is Orion in the sky? It is located in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere.
A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon.
Orion is seen at latitudes between +85° and -75°.
The neighboring constellations are Eridanus, Gemini, Lepus, Monoceros, and Taurus.
Taurus lies just above the shield as if he about to be slain by the great Hunter.
Also read: Leo Constellation & Cancer Constellation
How to find Orion constellation?
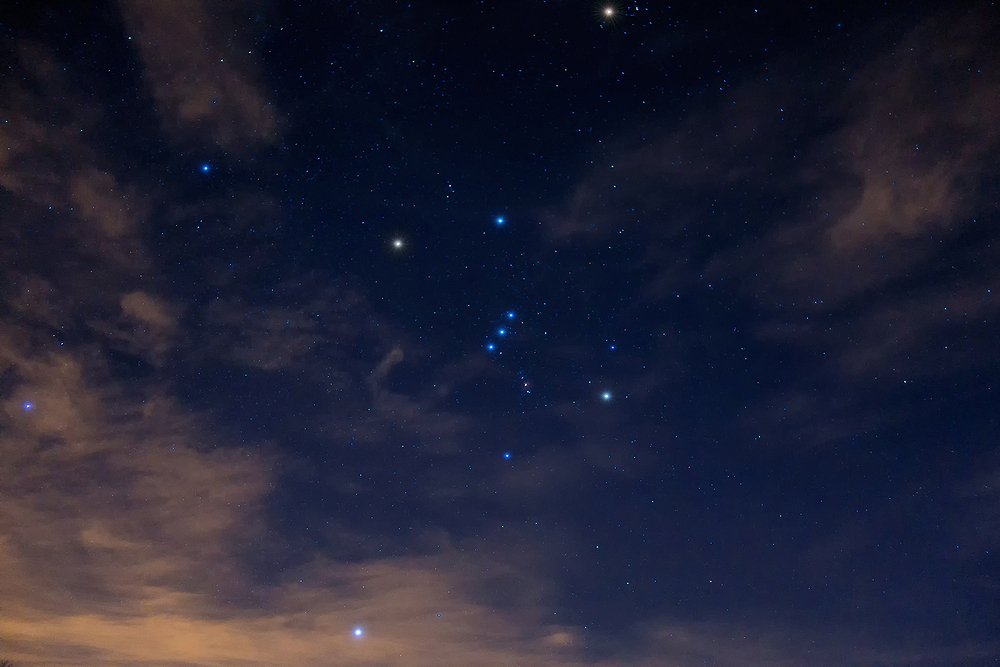
The Orion (constellation) is easy to find in the night sky, both in the northern and southern hemispheres. The easiest starting point is to locate the 3 stars that make up the Hunter’s belt.
How to find Orion belt – look for three bright stars in a straight line, they cannot be missed.
- Underneath the belt is a bright, dense collection of millions of stars known as the Orion nebula.
- The nebula lies in the sword and can be seen on a clear night with the naked eye.
- Look diagonally down to the right and find the bright star, Rigel. This is the foot of the Hunter.
- Diagonally upwards is Betelgeuse, the star that indicates the shoulder of his raised arm.
- Taurus the Bull lies above Orion’s shield. Gemini, the twins, are on his left, and Canis Major, the large dog, is located at his left foot.
When is the Orion constellation visible?
Orion in the sky can be seen in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
Orion northern hemisphere, rises in the east and sets in the west. In December the constellation appears in the night sky at around 8 pm and moves slowly westwards until around 6 am.
From January to March it first appears in the south-east at around 6 pm and slowly moves out of view at around 2 am.
In April, look out for Orion at around 9pm in the south-west and watch it dip below the horizon at midnight.
When is Orion visible in the southern hemisphere?
Orion appears in December low on the horizon in the eastern night sky at around 10 pm. It moves slowly westwards until around 6am.
From January to March look north-east at around 10pm. It will move slowly down to the horizon by 4am.
In April it first appears in the north-west at around 8pm and dips below the horizon around midnight.
What is the best way to view it?
If you live in the city, there is a good chance that you will see the three famous stars of Orion’s belt constellation, even with the city lights.
However, getting into the countryside away from the city lights gives a glorious view of Orion.
The Hunter can be seen with the naked eye and is fairly easy to make out his large body, raised hand, and shield by locating the bright stars.

Using a powerful pair of binos will give you an even better view of the constellation. The best way to view Orion is through a telescope.
For beginners, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that give fabulous views, even if you live in the city.
Dobsonian telescopes are versatile and easy to transport if you want to get away from bright lights.
Depending on your budget, plan to spend around $250 to $900 on a telescope.
The Zhumell Z8 Deluxe Dobsonian Reflector Telescope offers the best price/value ratio in a middle-of-the-range telescope. Priced at around $500, it has a 200mm (8”) parabolic primary mirror lens that produces crisp, bright images.
It also comes with two eyepieces, a 30mm (2”) eyepiece for wide-field views and a 9mm (1.25”) eyepiece, which gives higher magnification.
The scope easily dismantles into pieces for transporting – great to take with on the weekend away for some star-gazing!.
History
Who discovered Orion constellation?
Orion has a rich history in almost every ancient civilization from Greek to Roman, Chinese, and Aztec.
Fascinating prehistoric Aurignacian ivory carvings, dating as far back as 38000 years, show images of the Orion Constellation.
Archaeologists found the carving in a cave in the Ach valley in West Germany in 1979 (10).
Babylonian astronomical records dating back to 1200BC in the Late Bronze Age also showed a hunter in the sky.
In ancient Egypt, around 3100BC, astronomers identified the constellation as the God Sah or Sahu. Sahu was swallowed by the underworld every day at dawn and then reappeared at night.
The Aztecs celebrated a ritual known as the Fire Ceremony, which was carried out when Orion rose in the sky. This ancient tradition took place as long ago as 1300AD.
When was it first recorded?
Orion has an ancient history and was known to civilizations like the Greeks, Chinese, and Aztecs.
Records dating back as far as 38000 years have been found on prehistoric Aurignacian ivory carvings.
Babylonian astronomical records dating back to 1200BC in the Late Bronze Age also showed a hunter in the sky.
In ancient Egypt, around 3100BC, astronomers identified the constellation as the God Sah.
In more recent times – around 1300AD, the Aztecs knew of Orion and celebrated a ritual known as the Fire Ceremony when the constellation arose in the sky.
How did the Orion constellation get its name?
The name Orion stems from the ancient Greek Mythology of Orion, the Hunter. In this story, Orion was the son of God Poseidon and the daughter of King Minos of Crete, Euryale.
After being blinded and having his sight restored, he became a strong and fearless Hunter.
He stands in the sky, facing the raging bull Taurus. The constellation is also known as the Hunter.
Other ancient civilizations named the constellation according to their folklore and beliefs.
For avid historians, here are some Orion the Hunter facts – The Egyptians knew him as the God Sah or Sahu.
Sahu was swallowed by the underworld every day at dawn and then reappeared at night.
Ancient Chinese astronomers knew Orion as Shen, a great hunter or warrior. Orion is interesting in that so many ancient civilizations viewed it in the same way.
Shen was set in the sky in the middle of a hunting scene, with Three Stars that depicted his belt.
Mythology
Orion constellation in mythology
The most famous Orion mythology story tells of the hunter, who was
the son of the God Poseidon and the daughter of King Minos of Crete, Euryale. Having immense powers of the sea, Poseidon gave Orion the ability to walk on water. Using this power, he crossed the ocean and arrived at the island of Chios.
After partying and drinking too much, he tried to force himself upon Merope, the daughter of the local King Oenopion.

In a rage, the King had him blinded and banished from the island. Orion eventually had his sight restored by the sun God Helios.
He became an enthusiastic hunter but unfortunately had a bad attitude. When he declared that he would kill every animal in the world, the Goddess of the Earth, Gaea, became angry and sent a giant scorpion to do battle with him.
The Scorpion succeeded in killing Orion. His fellow hunters, Artemis and Leto, asked the great God Zeus to put Orion into the skies. Zeus turned both Orion and the Scorpion into constellations.
As they were enemies, the two can never be seen in the sky at the same time.
What does Orion symbolize?
Are you fascinated by the Orion name meaning and the Orion symbol?
In ancient mythology, the Hunter symbolized a force that was strong and powerful. He was feared by his enemies and admired by his friends.
The Hunter has strength, speed, and agility.
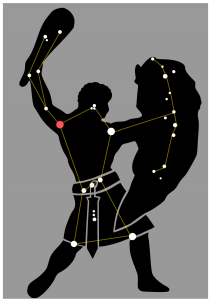
Image credit: Sanu N.
He has huge amounts of perseverance, endurance, and stamina, stalking his prey, sometimes for many miles before the kill.
The Egyptians were also known to have discovered Orion. They recognized the cosmic power of Orion and built the three pyramids accurately aligned with the main stars on Orion’s Belt.
Orion Starseeds personify Cosmic Wisdom and Spiritual Knowledge. Starseeds are highly evolved souls who have great powers of wisdom.
The Starseeds in Orion’s belt meaning are known to have great powers of spiritual teaching.
Related: Taurus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Future
Astronomers are fascinated by the myriad of stars in the Orion nebulae.
They believe that closer observations with more powerful telescopes will reveal many more exoplanets.
Exoplanets are exciting in that they revolve around the main star and could offer similar conditions to our solar system.
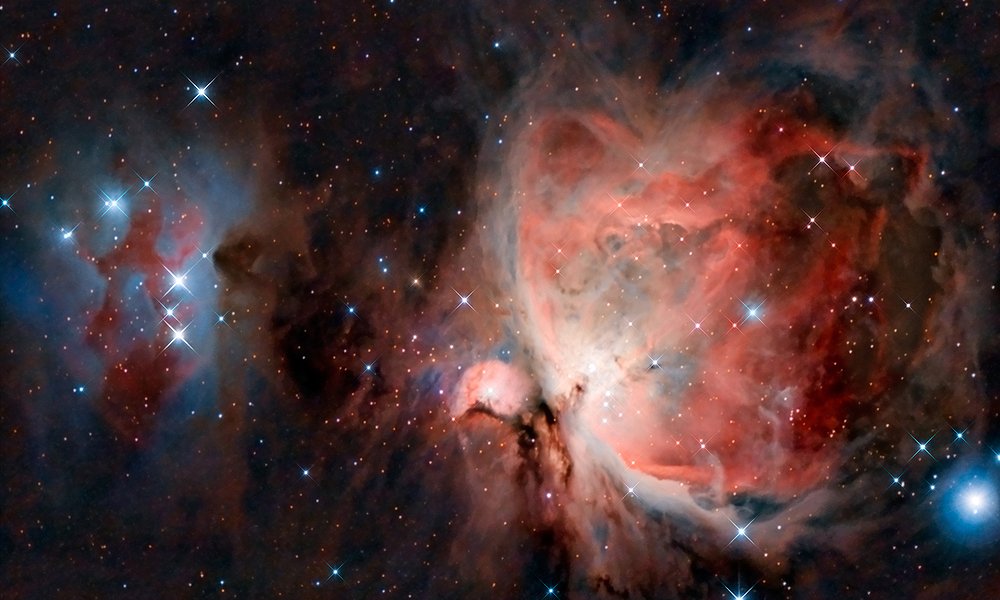

Great Orion Nebula
Meteor showers make awesome viewing if you are lucky enough to be in an area where they are visible. The Orionids is a shower that stems from the club that Orion holds aloft in his hand.
These showers will be seen around October 21, 2020, before dawn. You will see around 10 to 20 meteors per hour, leaving long trains in the sky.
This year, there will be no moon to detract from the sight – grab your telescope and get ready!