Perseus Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Perseus Constellation
Abbreviation: Per
Symbolism: Perseus
R.A. position: 3h
Dec. position: +45°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 438 light-years
Area: 615 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Mirfak (α Per)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −35°
Best viewed: During the month of December at 9.00pm
The Perseus constellation is the 24th largest in the sky. It is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek times. It is associated with a strong, brave warrior who succeeded at many dangerous tasks, including the beheading of the dreaded Gorgon, Medusa.
Perseus can be found in the sky by locating the constellations of Cassiopeia or Andromeda. Perseus is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the spectacular Little Dumbbell Nebula, a favorite amongst stargazers.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
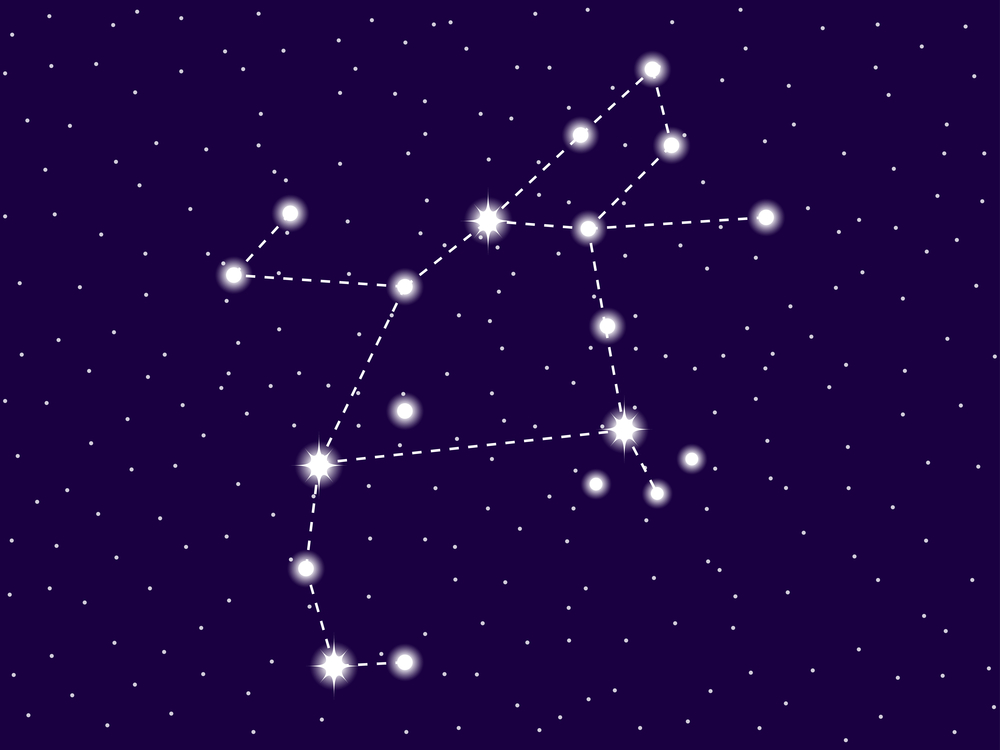
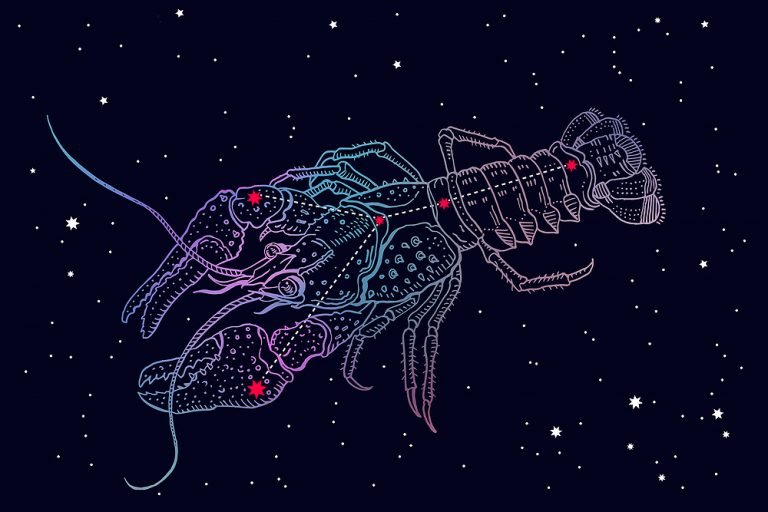
Perseus constellation
The constellation Perseus is a medium-sized constellation located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It has many bright stars with fascinating names like Mirfak, Algol, Menkhib, and Gorgonea Tertia.
Perseus comes from the Greek myth of a strong and fearless warrior, who was born in a dungeon and cast adrift with his mother into the sea. He grew up and became a hero, killing the dreaded Gorgon Medusa and rescuing the beautiful Princess Andromeda.

Perseus is a member of the Perseus family of constellations. They are all connected to the Great Warrior and his adventures. These constellations include Cassiopeia, Andromeda’s Mother, Cetus the Sea Monster, Auriga, Cepheus, Lacerta, Pegasus the Winged Horse, and Triangulum (1).
The Perseus (constellation) occupies an area of 615 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Taurus the Bull and Aries the Ram. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Cassiopeia, Andromeda, Auriga, and Triangulum.
For home astronomers, Perseus has many exciting Perseus constellation facts. It contains the amazing Messier 34 and the beautiful Little Dumbbell Nebula. It also offers the Halloween star, the ghoulish Algol, dripping with the blood of Medusa.
Perseus is not a Zodiac sign, he is a brave warrior from the Greek Myth. The Perseus star system dates back over 3000 years (2).
What does Perseus constellation look like?
Perseus is a brave warrior. He stands in the sky, victorious after his battle with Medusa, the dreaded Gorgon monster, who turned anyone to stone, who looked into her eyes. Near to Perseus is his beautiful wife, Princess Andromeda, and her vain mother, Cassiopeia.
In the sky, the constellation Perseus is depicted by a number of bright stars. It is up to you to imagine a warrior, with one arm raised up brandishing a sword. The other is at the side, holding the head of Medusa. Perseus is depicted as a full figure, unlike some other constellations which are only half-formed.
A prominent star called Mirfak lies in the middle of the body. Imagine the warrior dressed in a flowing robe and a helmet. He has leather sandals on his feet for fast movement.
The red star, Algol, is a ghostly star and indicates the bloody head of Medusa. Imagine her with large snakes, swirling around her face. To complete the image of Perseus, place a large sword into his right, uplifted hand. The Perseus sword is lethal and heavy, and only he can use it to achieve the tasks he has been given.
How far is Perseus constellation from Earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. In reality, this is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some stars may be as close as 40 light-years. Deep-sky objects may be as far as 60 million light-years away.
To give some idea, the star Mirfak is 510 light-years away from Earth. The Demon Star, Algol, is 92 light-years away. Atik is 750 light-years away. Epsilon Persei, the multiple star system, lies about 640 light-years away from the Solar System.

Gamma Persei, a double star system, lies about 243 light-years away from Earth. Delta Persei is also far away, at a distance of 520 light-years. Gorgonea Tertia, also known as Rho Persei, is closer, at a distance of 308 light-years.
The distance from the milky way to the Double Cluster is around 7,600 light-years. The Perseus Cluster is a massive 240 million light-years away and the beautiful Dumbbell Nebula is 2500 light-years away.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the Perseus constellation from Earth is about 438 light-years. If you consider the deep-sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years.
Features
Major stars in Perseus
Mirfak – α Persei (Alpha Persei)
Mirfak is a yellow supergiant star with an apparent visual magnitude of 1.806. It lies about 510 light-years distant. It is the brightest star in Perseus and you can see it with the naked eye. Mirfak circles the Northern Pole and never dips below the horizon, so it is always visible in the northern hemisphere.
Alpha Persei is about 60 times the size of the Sun and 5000 times more luminous. The name comes from Arabic and means “elbow”, “flank” or “side”. The star lies on the right side of the body of Perseus. Mirfak is the only navigational star in Perseus (3).
Algol – β Persei (Beta Persei)
Algol is a triple-star system and is a well-known celestial object. It is the second brightest star in Perseus with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.1. This magnitude varies as the stars orbit and eclipse one another. Algol lies about 92 light-years away from Earth.
Its red hue gives it the nickname ‘demon’ star. Algol passed close to the Earth about 7.3 million years ago – at a distance of only 9.8 light-years. The Perseus stars names come from the Arabic phrase ra’s al-ghul, meaning “the demon’s head”.
Batman fans will certainly recognize this name! In Hebrew, it is the Satan’s Head or Rōsh ha Sāṭān. Algol is thought to be the first variable star discovered. It lies at the head of the dreaded Medusa, which is held in the left hand of Perseus (4).
Atik (Menkhib) – ζ Persei (Zeta Persei)
Atik, also known as Zeta Persei is a blue-white supergiant star. It is 47,000 times more luminous than the Sun. The star has an apparent magnitude of 2.86 and lies about 750 light-years away from our Solar System. Atik has a very dim companion star.
The name comes from the Arabic Al-‘Atiq, which means “The shoulder”. It refers to the Pleiades, which are roughly located near the shoulder of Perseus. In the Perseus constellation stars system, Atik indicates the left sandal of the warrior.
ε Persei (Epsilon Persei)
Epsilon Persei is a multiple-star system. The system has a combined visual magnitude of 2.88 and is about 640 light-years away from the Sun.
The primary star is Epsilon Persei A and is 28,330 times brighter than the Sun. It is also a fast spinner, revolving at a speed of 155km/s. The two main components orbit one another every 14 days (5).
γ Persei (Gamma Persei)
Gamma Persei is a double star system. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.93 and lies about 243 light-years away from Earth. The two stars in the system orbit one another every 14.6 years.
Gamma Persei lies near Mirfak, on the right arm of Perseus. It is the 4th brightest of the Perseus stars. When the two stars eclipse one another, the brightness drops significantly (6).
δ Persei (Delta Persei)
Delta Persei is a binary star with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.01, which is bright and you can see it without a telescope. It lies about 520 light-years away.
The star is about 21 times bigger than our Sun and 3 times as hot, with surface temperatures of around 14,890 K. it is a fast-spinning star, with speeds of around 190km/s. The star lies under Mirfak, on the body of Perseus.
Gorgonea Tertia – ρ Persei (Rho Persei)
Gorgonea Tertia, also known as Rho Persei, gets its name from the Perseus myths of the Gorgon Sisters. There are four Sisters and this star represents the third.
It is a bright star with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.39, which varies up to 4.00. The star lies 308 light-years away from Earth. Gorgonea Tertia is 300 times bigger than our Sun and 2,290 times brighter.
Miram – η Persei (Eta Persei)
Miram, also known as Eta Persei, is a binary star, with its brightest component being part of a triple star system. Miram lies about 780 light-years away. It is a bright star with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.79.
Miram is 268 times bigger than our Sun and is 4,130 times brighter. Miram lies on the right arm of Perseus. In Chinese astronomy, Miram and gamma Persei are known as Tien Chuen, Heaven’s Ship (7).
Deep-sky objects in Perseus
Messier 34 (M34, NGC 1039)
Messier 34 is an open cluster that lies about 1.500 light-years away from Earth. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.5. The cluster is thought to be between 200 and 250 million years old. It is 7 light-years in radius and contains about 400 stars.
To find Messier 34, imagine a line drawn from Algol, the Demon Star, to Almach in Andromeda. The cluster lies just to the north. Discovery was in the mid 17th century by Italian astronomer Giovanni Batista Hodierna (8).
Little Dumbbell Nebula – Messier 76 (M76, NGC 650 & NGC 651)
The Little Dumbbell Nebula is a planetary nebula that lies about 2500 light-years away from our Solar System. It has an apparent 10.1, which is faint and you need a telescope to view it. The name comes from the shape, which resembles keep-fit dumbbells.
It is also known as the Barbell Nebula, the Cork Nebula, and Messier 76. The nebula was discovered by the French astronomer Pierre Méchain in 1780. The Dumbbell Nebula is easy to find – it lies just south of the famous W-Shape asterism in the constellation of Cassiopeia.
Alpha Persei Cluster (Melotte 20, Collinder 39)
The Alpha Persei Cluster is an open star cluster. It contains the well-known star Mirfak also known as Alpha Persei, a white-yellow second magnitude giant. Also in the cluster are Delta, Epsilon, and Psi Persei.
The Alpha Persei Cluster lies between 557 and 650 light-years away from our Solar System. Its estimated age is around 50 to 70 million years. It has an apparent magnitude of 1.2.
Perseus molecular cloud
The Perseus molecular cloud is a giant stellar nursery that lies about 600 light-years away from our Solar System. A stellar nursery is an area in the sky in which gas and dust clouds are contracting, forming new stars. The Perseus molecular cloud contains two clusters, IC 348 and NGC 1333. Both clusters are sites of low-mass star formation
(9).
Perseus Cluster – Abell 426
The Perseus Cluster is a cluster of galaxies, one of the largest known in the Universe. It contains thousands of galaxies immersed in a massive cloud of multimillion-degree gas.
The cluster lies about 240 million light-years away and is moving away from us at a speed of 5,366km/s. The brightest member in the cluster is NGC 1275 , also known as the Seyfert Galaxy (10).
3C 83.1B
3C 83.1B is a radio galaxy located in the Perseus Cluster. It lies in the elliptical galaxy NGC 1265. A radio galaxy is a specific type of active galaxy that emits more light at radio wavelengths than at visible wavelengths.
Studies of radio galaxies show that they have radio emissions extending millions of light-years from their nuclei. 3C 83.1B has an apparent visual magnitude of 12.63 (11).
The Double Cluster (Caldwell 14, NGC 869 & NGC 884)
The Double Cluster contains two bright open clusters, NGC 884 and NGC 869. They are relatively young clusters, aged at 3.2 and 5.6 million years respectively. NGC 884 lies about 7.600 light-years away and NGC 869 lies about 6.800 light-years away from our Solar System.
The Double Cluster has a combined apparent magnitude of 4.3 and you can see it with the naked eye in dark skies. There are around 300 supergiant stars in each cluster. Both clusters are moving towards us at speeds of around 21km/s, but will take millions of years to reach us! The beautiful Double Cluster decorates the handle of the Perseus sword.
NGC 1333
NGC 1333 is a reflection nebula in the Perseus constellation. It lies about 967 light-years away from Earth and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.6. The nebula lies in the western part of the Perseus molecular cloud. It is also a young stellar nursery, where new stars are being born (12).
NGC 1260
NGC 1260 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Perseus. It is well-known as the home of supernova SN 2006gy. This supernova event took place in 2006 and was one of the brightest ever seen.
“Of all exploding stars ever observed, this was the king,” said Alex Filippenko, leader of the ground-based observations at the Lick Observatory at Mt. Hamilton, Calif., and the Keck Observatory in Mauna Kea, Hawaii.
“We were astonished to see how bright it got, and how long it lasted” (13). NGC 1260 is about 250 million light-years away and has an apparent visual magnitude of 14.3.
Exoplanets in Perseus
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life.
HAT-P-14
HAT-P-14 is also known as Franz. It is a yellow star with a famous exoplanet called Sissi, or HAT-P-14 b. Exoplanets and stars are given names by the public during the NameExoWorlds campaign for the 100th anniversary of the IAU.
Sissi is a character in the movie Sissi, who is married to Franz. The actress Romy Schneider plays the role of Sissi. HAT-P-14 b is a gas giant exoplanet with a mass of 3.44 Jupiters, it takes 4.6 days to complete one orbit of its star (14).
HD 17092
HD 17092 is an orange-red giant star that lies about 750 light-years away from Earth. It has one exoplanet known as HD 17092 b. The exoplanet is a gas giant with a mass of 10.13 Jupiters. It takes 359.9 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was in 2007.
Sigma Persei
Sigma Persei is an orange-red star that lies about 360 light-years away from Earth. It has one exoplanet known as Sigma Persei b, or sig Per b. The exoplanet has an orbital period of 579.8 days, around its mother star.
HD 22781
HD 22781 is a red star about 107 light-years away from Earth. It has one exoplanet known as HD 22781 b. The exoplanet is a huge gas giant with a mass of 13.65 Jupiters. It takes 1.4 years to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was in 2011. The apparent visual magnitude of the mother star is 6.27, which is faint (15).
Meteor showers in Perseus
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars.
The Perseids
The Perseids are one of the most famous meteor showers, radiating outwards from between the constellations of Perseus and Cassiopeia. Perseus mythology tells that the shower comes from the fiery battle that took place when Perseus beheaded the dreaded Gorgon monster, Medusa.
The shower occurs between 17 July to 24 August, with the peak on 13 August. Expect to see over 50 per hour, traveling at speeds of up to 60km/s.
The comet of origin that creates this amazing show is 09P/Swift-Tuttle. This comet got its name from two astronomers who discovered it. Comets are usually named after their discoverer, or the name of the observatory or telescope used. The two people, in this case, are Lewis Swift and Horace Tuttle.
The letter “P” indicates that Swift-Tuttle is a periodic comet. Periodic comets have an orbital period of under 200 years. Comet 109P/Swift-Tuttle orbits the Sun every 133 years. It appeared in 1992 and will return in 2125. It is a large comet with a nucleus size of 16 miles (16).
The September Epsilon Perseids
This smaller shower occurs between 5 September and 21 September with the peak on 9 September. Meteors occur at a rate of 5 per hour, traveling at speeds of 64km/s.
Location and visibility
Where is Perseus constellation located?
Perseus is a medium-sized constellation with many bright stars and you can easily spot it once you know what to look for. In dark skies, you can see the main stars without a telescope.
Then, you can imagine the strong, brave warrior standing in the sky, with a sword in one hand and the head of the slain Gorgon Medusa in the other hand.
Where is Perseus constellation?
Perseus is a northern constellation and is the 24th largest constellation of the 88 named constellation. It occupies an area of 615 square degrees. Perseus lies in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ1.
A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes between +90° and −35°.

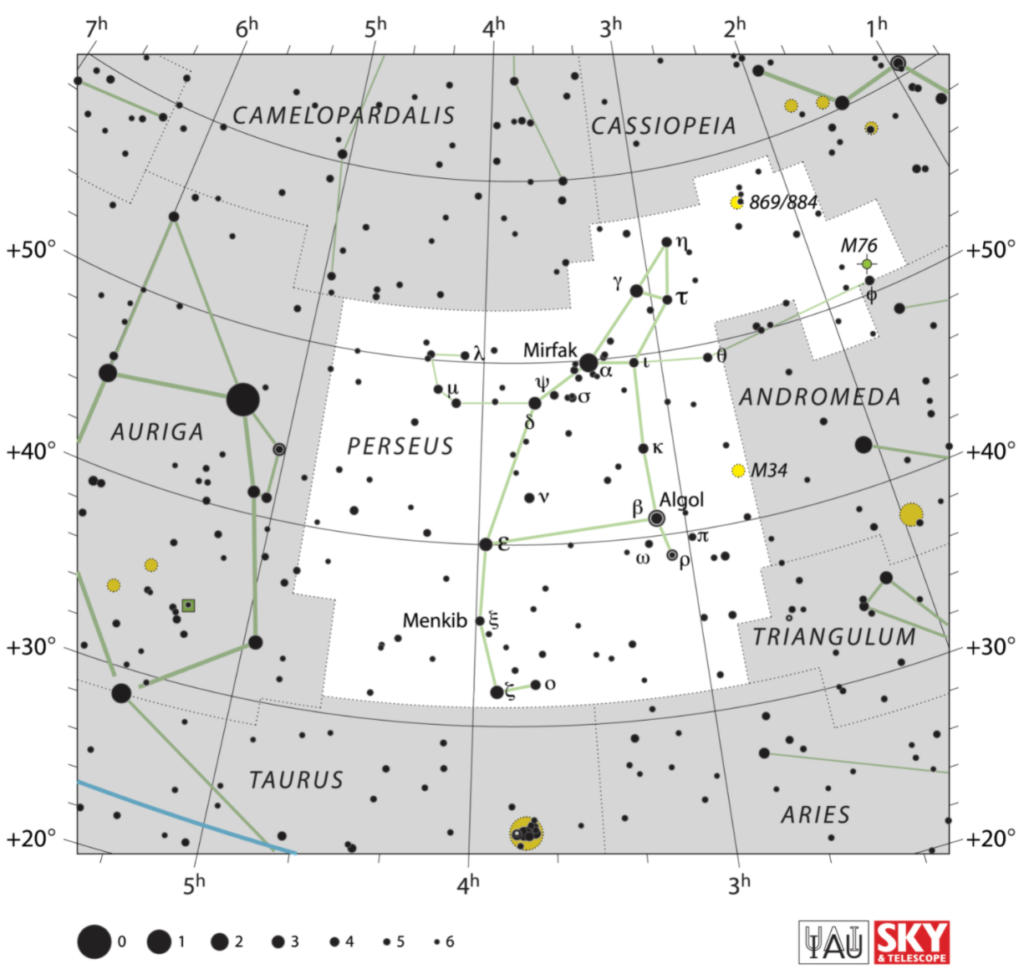
To find the Perseus constellation location, you can find the distinctive W-shape, or M-shape pattern of Cassiopeia, the Queen. You can also look for the bright star Alpheratz which indicates the head of Andromeda.
The warrior links to both constellations in the Perseus constellation story. Perseus saved the beautiful princess Andromeda from the Sea Monster, Cetus. Cassiopeia is the vain mother of Andromeda, who caused her to be sacrificed to protect her husband’s lands from destruction.
Perseus belongs to the Perseus family of constellations. They are all connected to the Great Warrior and his adventures. These constellations include Cassiopeia, Andromeda’s Mother, Cetus the Sea Monster, Auriga, Cepheus, Lacerta, Pegasus the Winged Horse, and Triangulum (17).
When is Perseus constellation visible?
In the northern hemisphere, Perseus is visible from August to March. In the southern hemisphere, constellation Perseus is visible in northerly areas from November to January.

Northern Hemisphere
If you are in the northern hemisphere – In August and September, the constellation Perseus appears low on the north-eastern horizon at about 11pm, and slowly moves higher in the sky. In October and November, Perseus is visible low on the horizon in the northeast around 8pm.
By 3am the constellation is directly overhead. In December and January it will be visible in the eastern night sky at around 6pm. This is a great time to take the kids out for some stargazing and to learn about Perseus astronomy.
In February and March, the constellation appears overhead around 7pm, and moves northwest as the night progresses.
Southern Hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere – In November the constellation of Perseus appears low on the north-eastern horizon at around 10pm. It moves westwards. But always remains low on the horizon.
In December and January, Perseus is visible around 10pm. He appears low in the north-eastern or northern horizon and moves westwards before dipping below the north-western horizon.
Remember – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down (18).
How to find Perseus constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here are 7 steps on how to find Perseus constellation.
- To find the Perseus location, it is easiest to first locate Cassiopeia, a well-defined star pattern that forms a W-shape
- Look below Cassiopeia to the left and locate two bright stars
- The first is Mirfak, a yellow star that lies in the center of the warrior’s body
- The next is Algol, the ghoulish star that defines the head of Medusa
- If you are having difficulty with this, locate the Great Square of Pegasus
- Then move downwards to find Andromeda, who shares the star Alpheratz at her head
- Andromeda’s feet point towards Perseus
Southern Hemisphere
- To find the Perseus constellation location, it is easiest to first locate Cassiopeia, a well-defined star pattern that forms an M-shape
- Look above Cassiopeia to the right and locate two bright stars
- The first is Mirfak, a yellow star that lies in the center of the warrior’s body
- The next is Algol, the ghoulish star that defines the head of Medusa
- If you are having difficulty with this, locate the Great Square of Pegasus
- Then move upwards to find Andromeda, who shares the star Alpheratz at her head
- Andromeda’s feet point towards Perseus
Do you want to know some more interesting Perseus facts? In the Southern hemisphere, constellations appear upside down. So Perseus is standing on his head!
How to view Perseus Constellation?
Perseus is the 24th largest constellation in the sky. It has many well-defined stars that you can see with the naked eye. By locating these stars, you can imagine the brave warrior, sword in one hand, and the head of the terrible Gorgon monster Medusa in the other.
Perseus lies in a region of the sky known as the Perseus Family of Constellations. They are all related to the story of Perseus and include Andromeda, Cassiopeia, Cetus, and Cepheus.
Getting away from city lights and pollution is the best way to see constellations and deep-sky objects. You can see Perseus the hero constellation with the naked eye or with a pair of binoculars, but using a telescope will make it so much more exciting.

For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of pegasus rising in the sky. Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Explore Scientific FirstLight AR102 TN Refractor Telescope has a cool white tube that is ultra-modern and stylish. It features a 102mm aperture and a 600mm focal length. It comes with a Plossl 25mm eyepiece and a 1.25″ 90-degree Diagonal.
Mounted on a Twilight Nano Alt/Az mount, the telescope is stable and it is very easy to locate any stars in Perseus. The legs adjust up and down, a great perk if you have smaller children. The altazimuth mount allows movement both horizontally and vertically, making it very precise to operate.
It also has an HD132 Red-dot Finder and a Smartphone Camera adapter. The included Sky Software program is a helpful tool for beginner stargazers to discover the story of Perseus. This is well-priced scope at under $300.
History of observation
Who discovered Perseus constellation?
Perseus constellation history dates back to ancient civilizations of the Greeks, Chinese, and Polynesia, and was documented in stories, folklore, and myths.
Perseus holds up Medusa’s head so Andromeda may safely see its reflection in the pool below (fresco, 1st century AD, Pompeii)
The Perseus story dates as far back as 3000BC. It associates with the Perseus greek mythology character, a bold and fearless warrior who was tasked with impossible missions. He never gave up and always showed great strength of character and braveness to fight for those he loved (19).

The mythology of Perseus was also known to the Chinese astronomers. It is an old Chinese constellation that dates back as far as 750BC. Four Chinese constellations are in the area of the sky identified with Perseus. One is Tiānchuán, the Celestial Boat. Perseus lies within the western quadrant of the sky, which is symbolized as the White Tiger of the West, Xī Fāng Bái Hǔ. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is yīng xiān zuò – “the brave god constellation”.
Around the 7th and 8th centuries, Babylonian astronomers wrote about the story of Perseus. The constellation of Perseus was the Old Man constellation (SU.GI). It features in the MUL.APIN, an astronomical text (20).
Persian astronomers around 830AD also knew of the Perseus constellation. The Etymologies of Isidore of Seville from the 7th century AD referred to the Persian peach as Persicus from the name Perseus. In Persia, this tree produced a deadly fruit, but in the western world, it is delicious and sweet (21).
In more recent times, Perseus was one of the original 48 constellations formulated by Ptolemy in his 2nd-century work, the Almagest. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Perseus constellation?
Perseus is an ancient constellation that dates back to the era of Greek mythology around 3000BC. The constellation depicts the myth of Perseus, son of Zeus and Danaë, who was tasked with many difficult missions.
This brave warrior killed the terrible Gorgon Medusa, who had snakes in place of hair. He then used her head to turn the Sea Monster Cetus to stone to save the beautiful Andromeda (22).

Here are some more interesting facts about Perseus.
Perseus is also an old Chinese constellation known as far back as 750BC. Perseus is located within the western quadrant of the sky, which is symbolized as the White Tiger of the West, Xī Fāng Bái Hǔ.
The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is yīng xiān zuò, which means “the brave god constellation”.
Around the 7th and 8th centuries, Babylonian astronomers wrote about the story of Perseus. The constellation Perseus is known as the Old Man constellation, SU.GI (23).
In Biblical times, around 1200BC and 165BC, the Hebrews wrote about Perseus. The constellation is Peretz or Parats. The Hebrew means “Breaker” or “Deliverer” or “the One who Breaks Open the Way” as in Micah 2:12, 13. The Messiah gathers the remnant of Israel and breaks open the way as their Lord (24).
How did the Perseus constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, what is the Perseus name meaning?
The name Perseus is possibly derived from the Greek word πέρθω, pertho. meaning “to destroy”. In Perseus mythology, he is a great hero who faced many impossible challenges.
The terrible Gorgon Monster, Medusa, a creature with snakes for hair, was destroyed by Perseus. Anyone who looked at her in the eye turned to stone. Using the head, he killed the Sea Monster, Cetus, to save the beautiful Princess Andromeda.
Another derivative could be from the ancient Greek verb, perthein. This means to “waste, ravage, destroy, sack” from the Greek verb perth-. Again, this fits in with the story of Perseus who destroyed many foes on his missions.
The origin of perth- may derive from the Indo-European root *bher-, (*bh- descends to Greek as ph-) from which Latin ferio, ‘strike’ derives. The constellation could also relate to the Perseus latin word “ferio”, which has roots in “to strike, to interfere, or to strike a bargain” (25).
So what does Perseus mean? In Perseus etymology, he is a bold and honorable warrior, who fought to protect those he cared for and loved.
The Perseus constellation nickname is Per (26).
Mythology and meaning
Perseus myth
The Perseus constellation myth comes from the Greek mythology story that starts with the beautiful Danaë, daughter of King Acrisius, ruler of Argos. An oracle warned him that one of his grandsons would kill him. He methodically killed Perseus siblings. The King locked Danaë in a dungeon.
Zeus, King of the Gods fell in love with her and turned himself into golden rain so he could enter the dungeon. When the rain fell into her lap, she fell pregnant. Acrisius put Danaë and the child into a wooden chest and cast them out to sea.
They were saved by a fisherman, Dictys, who raised Perseus as his own son. Perseus parents are Danaë, a mortal, and Zeus, a God. In the Greek myth Perseus is a demi-god.

Perseus god became a great warrior and fulfilled many missions. One was to kill the dreaded Gorgon Medusa, a creature with snakes in place of hair, who turned anyone who looked at her into stone.
Using the famous Perseus sword, he beheaded the dreaded Gorgon. After achieving his mission, the greek Perseus used the head to turn the sea monster Cetus into stone. Cetus was about to kill Andromeda, who was sacrificed to the monster for her Mother’s vanity and chained to a rock in the ocean.
In Greek mythology Perseus, after saving her, two married, and Andromeda bore him 7 sons and 2 daughters. After Perseus death, Zeus placed him into the sky. The Goddess Athena placed Andromeda among the stars near to her husband. Also in the sky is Cassiopeia her mother, and Cetus the Sea Monster (27).
What does Perseus symbolize?
In Perseus greek mythology, the Perseus symbol is a strong and fearless warrior, born to the beautiful Danaë, daughter of King Acrisius. Danaë bore the child after Golden Rain fell into her lap. The rain was Zeus in disguise, who visited her when she was locked away by King Acrisius. Perseus father is Zeus, King of the Gods and he is a demi-god.
After being cast into the ocean, mother and child were rescued by the fisherman Dictys. The legend of Perseus shows great courage and perseverance in the face of little hope. When Perseus grew up, he faced many very difficult challenges but never gave up hope. He focused his energy and succeeded against all odds. The love of his parents sustained him and drove him to great success.
The Perseus greek god represents a warrior and a fighter with a pure nature. In the Perseus and medusa story, he fought those who were a threat and saved those in need. He rescued the beautiful Andromeda from the Sea Monster Cetus. With great dignity and honor, he married her and in the story of Perseus and andromeda, she bore him many children.
The Perseus myth shows that no matter how hard or difficult your beginnings are, anyone can achieve success by believing. Remember that Perseus birthplace was a dungeon!
The Perseus character represents perseverance, bravery, honesty and dignity. He is a young man who inspires others to greatness and shows the lengths one can go to protect those you love (28).
Future of Perseus constellation
Perseus is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study. It contains many active stellar galaxies, which are star-forming regions. Studying these galaxies gives astronomers more insight into the formation of the Universe.
Gorgonea Tertia, also known as Rho Persei, is an interesting Perseus star. It represents the 3rd Gorgon sister in the quartet of four. The star belongs to the spectral type M4 II. This means that it has reached the asymptotic giant branch stage of evolution.

It is near to the tip of the red giant branch. A red giant is a star in a late stage of stellar evolution and is also known as a dying star. Gorgonea Tertia is moving into this phase and astronomers observe this change, even though it may take millions of years (29).
The Little Dumbbell Nebula is also undergoing an interesting transformation. It formed when a Sun-like star ran out of fuel in a late stage of its life. It expelled its outer layers which were heated by the radiation of the remains of the star.
This produces the beautiful glowing clouds that stargazers enjoy viewing. Over the next few thousand years, the clouds will disperse. The central white dwarf in the nebula will cool down and eventually fade away (30).