Pisces Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
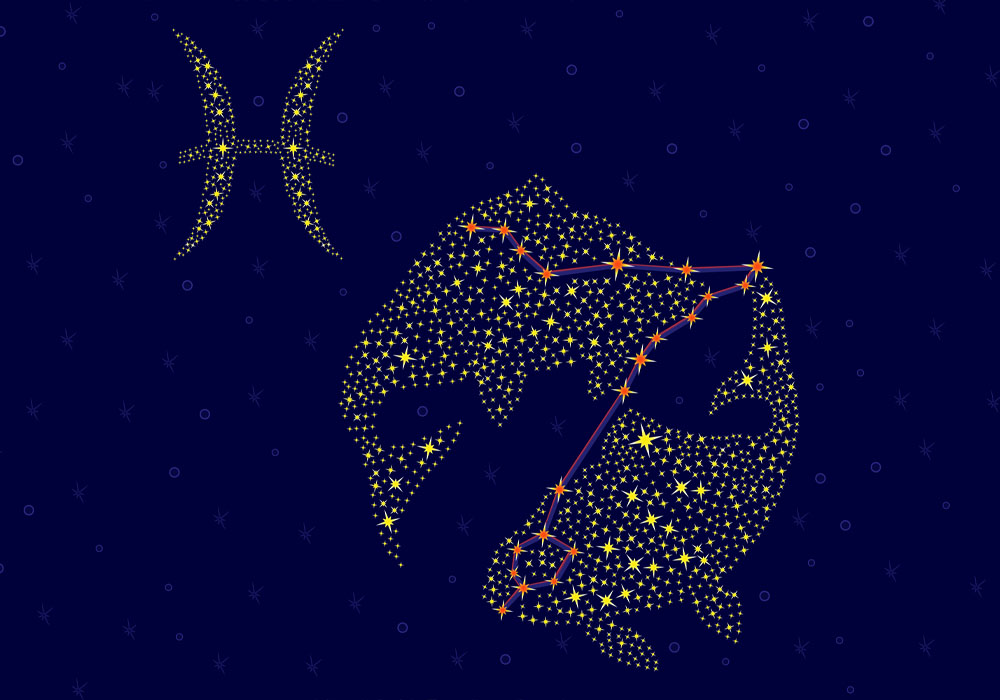
Object name: Pisces Constellation
Abbreviation: Psc
Symbolism: The Fishes
R.A. position: 1h
Dec. position: +15°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 172 light-years
Area: 889 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Alpherg (η Psc)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −65°
Best viewed: During the month of November at 9.00pm
The Pisces constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as The Fishes. Pisces is one of the oldest known constellations and dates back to Greek Mythology where the fish are associated with Aphrodite and her son Eros, who turned into fishes to escape the terrible monster Typhon.
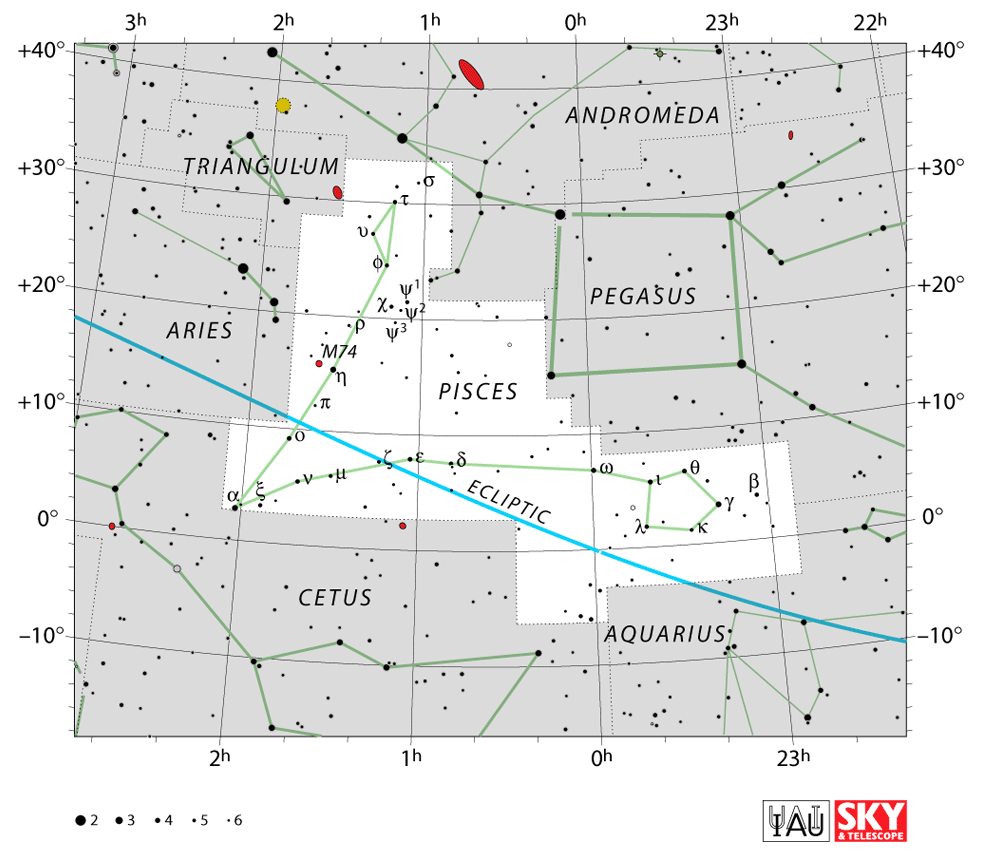
Pisces is the 4th largest of the Zodiac constellations and can be found in the sky by locating the famous Great Square of Pegasus. For home stargazers, Pisces is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the amazing phantom galaxy M74.
Read on to learn more about the constellation Pisces and interesting Pisces facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
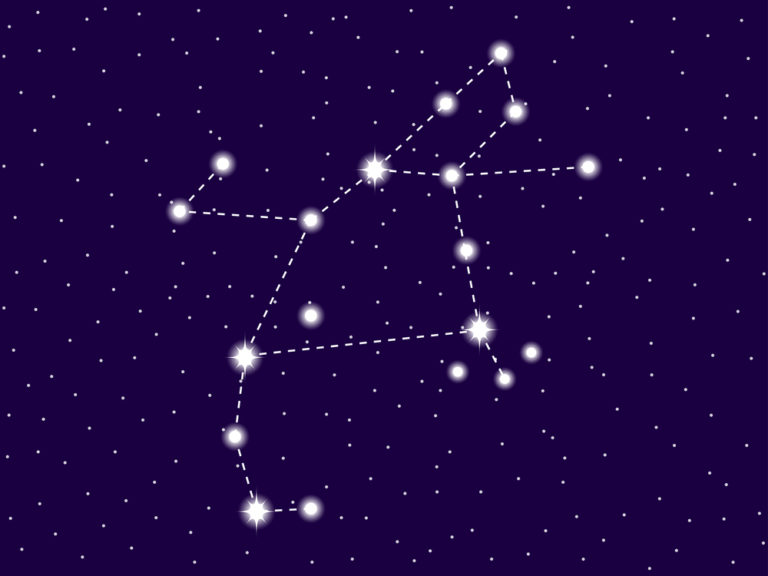
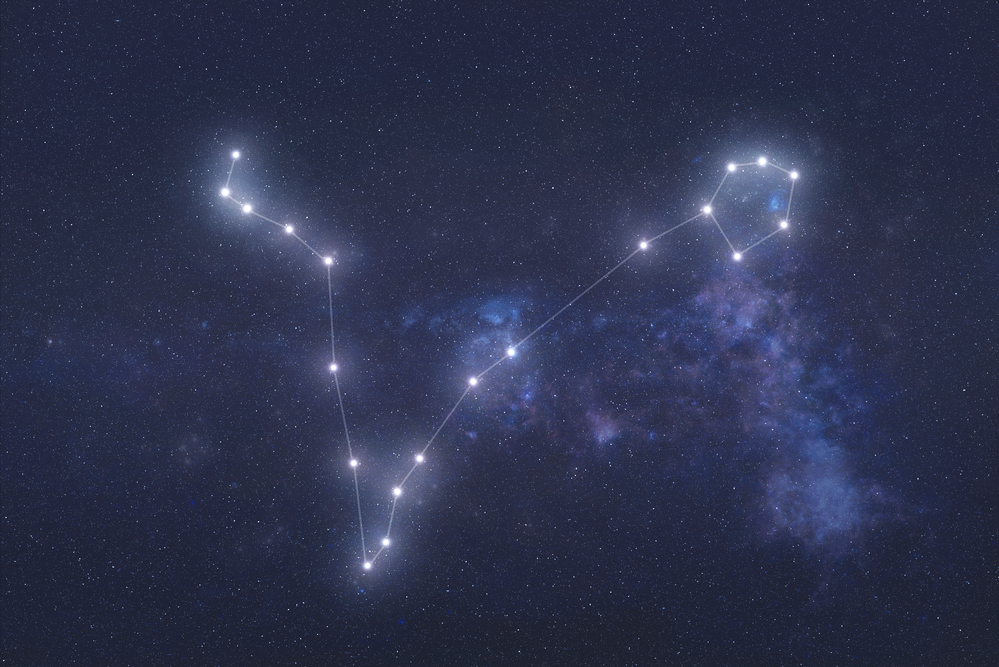
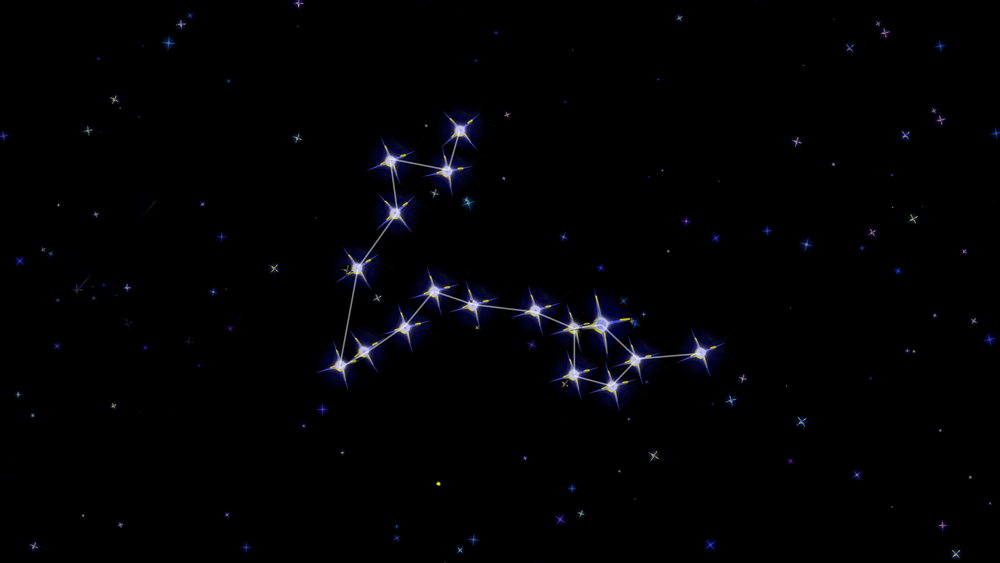
Pisces constellation
Pisces is a large and distinctive constellation that dominates the sky. The Fishes are tied together with two ropes that have a knot at the base. The ropes form a V-shape, with one fish at either end. They are tied together so that they don’t lose one another when swimming in the River Euphrates.
The Pisces (constellation) is the 14th largest constellation. It occupies an area of 889 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Aries and Aquarius. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Triangulum, Pegasus, Andromeda, and Cetus.

For home astronomers, the constellation of Pisces offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains Pisces brightest star, Kullat Nunu, a yellow-giant binary star, also known as Eta Piscium.
Also of great interest to home stargazers is the star Alrescha, or Al Risha, another binary star that forms the knot of the ropes. Pisces also offers the amazing M74 group of galaxies that lie about 32 million light-years away.
In the case of Pisces, both the Pisces constellation and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The age of Pisces greek mythology dates back over 3000 years (1).
What does Pisces constellation look like?
You may be asking – what does Pisces look like? With many bright stars at strategic points, Pisces is a constellation that you can draw with your eye in the sky.
The constellation of Pisces looks like two fish tied together with a rope. They swim in the River Euphrates to escape the wrath of the Monster Typhon. The rope ties at the base with a strong knot to hold the two pieces together. Each rope separates and floats in the river, forming a V-shape.
At the end of each rope is a fish. The fishes are tied at the tail and swim together in the water. Imagine two large fish with round eyes and strong fins along their backs. The western fish swims upwards and has a distinct pattern of stars called the Circlet, near to its head.
This fish is probably Aphrodite, the Goddess of Love. The smaller fish is Eros, her son. Aphrodite leads in the swim, pulling Eros, god of Pisces, along with her to safety.
In the sky, the Fishes swim between Aries and Aquarius, but there is no mythological connection between these signs in the Pisces story.
How far is Pisces constellation from Earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it looks as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be as close as 60 light-years, and others as far as millions of light-years.
To give some idea, the brightest star in Pisces is Eta Piscium and lies 294 light-years away from Earth. Gamma Piscium is a yellow giant that lies about 138 light-years away.

Another main star is Omega Piscium, a subgiant yellow-white star that is about 104 light-years away. Iota Piscium is relatively close at only 44.73 light-years away. Omicron Piscium is a yellow giant star and lies about 280 light-years away.
The beautiful M74 galaxy is very far away, about 32 million light-years! Also in the Pisces constellation, and far away, is the CL 0024+1654 galaxy at about 5.7 billion light-years. The NGC 7537 spiral galaxy lies about 103.7 million light-years away.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Pisces constellation from Earth is about 172 light-years. If you consider the deep-sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years!
Zodiac family
The Pisces symbol is the 12th sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between February 20 and March 20. It is one of three water signs, the others being Cancer and Scorpio.
Pisces is more connected to water than the other two water signs – in the Pisces myths, Aphrodite and Eros turn into fish and jump into the River Euphrates to escape the Monster Typhon.

The star constellations Pisces has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Aries the Ram is to the right. Aquarius the Water Bearer is below the lower fish.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, the Pisces constellation lies on the ecliptic path.
This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. The Sun passes through Pisces each year from around 12 March to April 18. Pisces is a mutable sign. Mutable signs arrive at the end of each season. Pisces arrives at the end of Winter (27).
One of the most interesting Pisces constellation facts is that Pisces does not connect in any direct way to any other Zodiac creature or symbol. The fish are, however, connected to the King of the Gods, Zeus.
In Greek mythology, Zeus was responsible for placing many Zodiac figures into the night sky, including Pisces.
Features
Major stars in Pisces
Here is a list of the major Pisces stars. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in Pisces? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most interesting Pisces stars names.
Kullat Nunu – η Piscium (Eta Piscium)
Eta Piscium is the brightest star in the constellation Pisces. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.62 and is about 294 light-years away from Earth. Eta Piscium is a binary star and has a faint companion.
The star is a yellow giant and is 316 times more luminous than the Sun, Its size is 26 times larger than the Sun. The star is also called Kullat Nunu which comes from the Babylonian word Nunu for “fish”. Kullat refers to a bucket or the cord used to tie the fish together (2).
γ Piscium (Gamma Piscium)
Gamma Piscium is a yellow giant and is the second brightest star in Pisces. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.699 and you can see it with the naked eye. It lies about 138 light-years away from Earth.
The star is 10 times the size of the Sun and about 61 times more luminous. Scientists put its age at around 5.5 billion years old. Gamma Piscium is part of an asterism, or star pattern called the Circlet of Pisces. The Circlet of Pisces represents the head of the western fish in the Pisces constellations (3).
ω Piscium (Omega Piscium)
Omega Piscium is a subgiant yellow-white star. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.036 and you can see it without using a telescope. It lies about 104 light-years away from the Sun. It has a surface temperature of 6,600 K. In comparison, our Sun has a surface temperature of 5,778 K. Omega Piscium is the first star you find to the east of the Circlet of Stars Pisces.
ι Piscium (Iota Piscium)
Iota Piscium is a yellow-white dwarf. It lies relatively close to us at about 44.73 light-years away and has an apparent magnitude of 4.13. The star is more than 1.5 times the Sun’s diameter and more than three times as luminous. Iota Piscium marks the tail of the lower fish (4).
ο Piscium (Omicron Piscium)
Omicron Piscium is a yellow giant star with an apparent magnitude of 4.26. You can see it without the need for a telescope. It lies about 280 light-years away. Omicron Piscium is also known as Torcularis, or Torcularis septentrionalis. In the fish constellation, you will find it just above the knot of the rope that ties the two fish together (5).
Alrescha – α Piscium (Alpha Piscium)
Alpha Piscium is an important star in the Pisces star constellation as it marks the knot of the rope. It is a binary star with 2 close components. The primary star has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.33.
The companion is fainter, with an apparent magnitude of 5.23. The stars orbit each other for a period of over 700 years. The primary star is 2.3 times the mass of our Sun and 31 times brighter.
These Pisces constellation stars lie about 139 light-years from the Solar System. The Pisces constellation stars names Alrescha (also Al Rescha, Alrischa, or Al Risha) come from the Arabic phrase al-rišā, which means “the good rope”.
Van Maanen’s Star
Van Maanen’s star is one of the most fascinating stars in Pisces as it lies only 14.4 light-years from our Sun. it is a white dwarf star with an apparent magnitude of 12.37.
This means that it is very dim and you need a telescope to see it. It lies in the center of the constellation, west of Delta Piscium and east of Omega Piscium. Adriaan van Maanen from the Mount Wilson Observatory discovered these stars in Pisces constellation in 1917 (6).
Deep-sky objects in Pisces
Messier 74 (M74, NGC 628)
This stunning spiral Pisces galaxy, also known as the Phantom Galaxy, was discovered in 1780 by Charles Messier’s assistant, the French astronomer Pierre Méchain. M74 lies about 32 million light-years away from Earth.
It has a high apparent magnitude of around 10, which means that it appears only as a faint patch of light through a small telescope. M74 is a classic spiral galaxy with perfectly symmetrical arms that spiral out from the center.
Clusters of young blue stars are on the arms of the spiral. In the picture, the pink areas are where the ultraviolet light from these stars has ionized clouds of hydrogen, causing them to glow (7).
M74 Group
M74 Group is a small group of galaxies and includes the famous M74 spiral galaxy. It is also known as the NGC 628 Group.
Included in this group is the beautiful polar ring galaxy NGC 660. It lies about 40 million light-years away from the Solar System.
For those new to Pisces astronomy, polar ring galaxies are rare and have a substantial population of stars, gas, and dust that orbits in rings that are strongly tilted from the plane of the galactic disk (8).
CL 0024+1654
CL 0024+1654 is a large galaxy cluster composed mainly of yellow elliptical and spiral galaxies. The closest cluster lies about 3.6 billion light-years away and the galaxy behind it is around 5.7 billion light-years away. In this image, the blue images are of single blue, ring-like galaxies that line up behind a giant cluster of galaxies (9).
NGC 7537
NGC 7537 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Pisces. It has an apparent magnitude of 13.9 which means that you cannot see it even with a small telescope!
It was first documented by German-born astronomer William Herschel in 1785. This object forms a pair with the close-by barred spiral galaxy NGC 7541. NGC 7537 lies about 103.7 million light-years away (10).
3C 31 (NGC 383)
The 3C 31 galaxy has an apparent magnitude of 13.4 and lies about 240 million light-years away from our Sun. It is an active galaxy with a supermassive black hole at its center.
The black hole causes the galaxy’s jets to extend for millions of light-years in both directions. It is a powerful emitter of radio waves. Blasting away from one side of the galaxy is a large jet, which astronomy Pisces scientists call NGC 383. Other galaxies close by are NGC 379, NGC 380, NGC 385, and NGC 384 (11).
CGCG 436-030 (PGC 4798)
CGCG 436-030 is a spiral galaxy in Pisces. It has an apparent magnitude of 14.9 which is very faint and will only appear as a dim light in a small telescope. It lies about 400 million light-years away from our Solar System.
The companion galaxy at the bottom-right of the image has an intricate structure with trailing tails that extend far out from its core (12).
Exoplanets in Pisces
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life.
HD 217107 b and c
HD 217107 is a yellow subgiant star that lies about 64.77 light-years away. It has 2 known exoplanets revolving around it. The first is HD 217107 b which has an apparent magnitude of 4.7. Its orbit period is 7.12 days. The second planet is HD 217107 c and has an orbital period of 4210 days (13).
HD 5891 b
Hd 5891 is a yellow star with 1 exoplanet called HD 5891 b. The main star has an apparent magnitude of 2.2 and lies about 819 light-years away. Its exoplanet orbits the Mother star every 177 days. It was discovered in 2011 (14).
WASP-118 b
WASP-118 b is a giant hot Jupiter planet composed mainly of gas. It orbits its F-type star once every 4 days. WASP-118 b has a mass of 0.514 Jupiters but is larger with a radius of 1.44 Jupiters. Discovery was in 2016. The mother star and planet lie about 250 light-years away. (15).
WASP-151 b
Another Pisces star known to have an exoplanet revolving around it is WASP-151. This star is a yellow star about 1565 light-years away. The exoplanet is a gas giant known as WASP-151 b. Its mass is 0.31 Jupiters and it takes 4.5 days to complete one orbit of its star. Discovery was in 2017 (16).
Meteor showers in Pisces
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up.
This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars. The Pisces zodiac constellation has one main meteor shower known as the Piscids which are identified by different names.
The Piscids
Also known as the April Piscids, this meteor shower occurs between 8 April and 29 April with a peak around 20 April. This is a small shower that is not very spectacular to watch.
The Omega Piscids
The Omega Piscids have a peak of activity around 17 September. The source of the meteor shower comes from the Asteroid 2001 HA4. Meteors travel at speeds of around 21lm/s and appear at a rate of about 5 per hour (17).
The Delta Piscids
This meteor shower occurs between 20 June and 26 June with the peak occurring on 23 June. The closest star to the radiant point of the meteor shower is Linteum. The speed of the meteor shower particles is around 69km/s.
The phi Piscids
This shower was discovered by Dr. Peter Brown and associates using data from the Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar (CMOR) installation. The shower is active from 8 June to 2 August with a peak on 4 July. This is not a spectacular show, with only 1 meteor per hour traveling at a speed of 67km/s (18).
Location and visibility
Where is Pisces constellation located?
Pisces is a large constellation and although it does not have the brightest stars, it is easy to find once you know what to look for. The main stars can be seen without the need for a telescope and then you can imagine the two fish tied together with a rope in the sky.
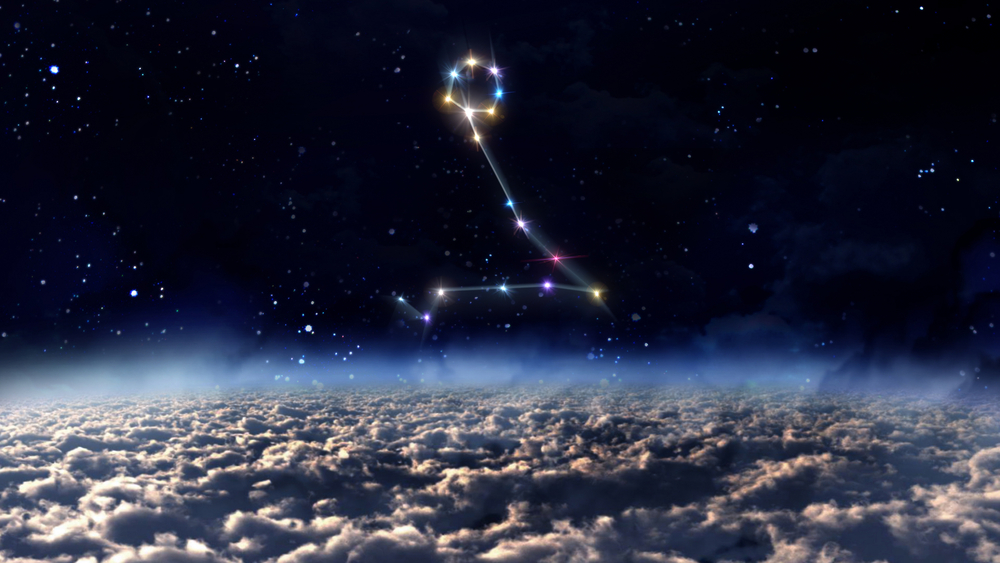

Where is Pisces in the sky? Pisces is a northern constellation and is the 4th largest zodiac constellation occupying an area of 889 square degrees.
It’s the 14th largest constellation of the 88 named constellations. Pisces lies in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ1. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the fish constellation at latitudes +90° and −65°.
To find Pisces in the north sky, you can locate the two zodiac constellations of Aries the Ram and Aquarius the Water Bearer. Aries stands to the west of the fish. Aquarius is underneath and to the right of the lower fish.
Another easy way to locate Pisces is to find the famous Great Square of Pegasus which lies between the two fish. The Great Square of Pegasus consists of 4 stars of nearly equal brightness, Scheat, Alpheratz, Markab, and Algenib.
When is Pisces constellation visible?
Pisces the fish constellation is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.

Northern Hemisphere
When is Pisces visible in the northern hemisphere? In August and September look low on the eastern horizon around 11pm. In October it will appear low in the eastern horizon around 8pm and then continue towards the western horizon until daybreak.
In November, December, and January, Pisces is visible much earlier, at around 6pm to 8pm. A good time to take the children out for some stargazing. If you stay up later and track the Pisces constellation with a telescope, you will watch it dip below the western horizon at around midnight.
Southern Hemisphere
When can you see Pisces in the southern hemisphere? In October you can spot Pisces at around 9pm low on the eastern horizon. In November the constellation will appear in the north-eastern night sky at around 10pm. In December it appears for a short time in the northwest between 11pm and 2am.
Here is an interesting Pisces constellation fact – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down. The mythological fish will be swimming in the opposite direction (19).
How to find Pisces constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here are 6 steps on how to find constellations Pisces.
- To locate Pisces, it is easiest to first find the Great Square of Pegasus in the northern sky
- Locate the four bright stars that make up the square, Scheat, Alpheratz, Markab, and Algenib
- Extend a line from the lowest pieces star, Algenid, down and slightly to the left to find the bright star Alrischa at the knot to the rope
- Now imagine a V-shape rising up to follow the sides of the square. At the top of each arm of the V-shape, is a fish
- The western fish lies near to the famous Circlet, a star pattern that forms a distinct circle
- One fish swims upwards at the top and the second swims downwards at the bottom
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down.
- To locate Pisces, it is easiest to first find the Great Square of Pegasus
- Locate the four bright stars that make up the square, Scheat, Alpheratz, Markab, and Algenib
- Extend a line from the top-most star, Algenid, up and slightly to the right to find the bright star Alrischa at the knot to the rope
- Now imagine a V-shape with arms pointing downwards, following the sides of the square. At the base of each arm of the V-shape is a fish
- The eastern fish lies near to the famous Circlet, a star pattern that forms a distinct circle
- One fish swims downwards and the second swims upwards
How to view Pisces Constellation?
Pisces is not the brightest constellation and getting away from city lights and pollution is the best way to see it.
You can see the fish constellation with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make your Pisces astronomy experience so much more exciting! For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Pisces in the sky.

Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Sky-Watcher Virtuoso is well priced at under $300. It is great for a family wanting a telescope with advanced features at a very affordable price. The scope stands on an Altazimuth table mount which is very easy to use.
It also has a mounting bracket if you prefer to attach it to a tripod. The scope has a 90mm lens and a 5×24 finder scope. It features a bracket for DSLR (Digital Single Lens Reflex) cameras.
As a motorized telescope, it will automatically track objects across the sky for you. For safe viewing of the sun, there is a Solar filter and Solar finder. It comes with two eyepieces, a 10mm and 20mm 1.25″.
History of observation
Who discovered Pisces constellation?
The Pisces origin was documented by many ancient cultures in stories, folklore, and myths over thousands of years.
Greek history of Pisces constellation dates back to 3000BC. It tells the story of Aphrodite and Pisces god Eros, who became fish to escape the wrath of the Monster Typhon.
The Egyptian astronomers also knew of the Fish as far back as 2300BC. Many ancient coffins found in archaeological sites depict fish engraved as part of the designs.
The stars of Pisces also featured in Chinese astronomy dating back to 750BC. The northern fish of Pisces is part of the House of the Sandal.
During biblical times, the age of Pisces began in AD1 and coincided with the birth of Christ. It will end around AD2150, after which we move into the age of Aquarius.
Biblical history has very strong connections with Pisces symbolism and fish are part of the narrative. Many Christian symbols for Christ use the sign of the fish and the astrological symbol for Pisces. The twelve apostles are also known as the “fishers of men” (20).
In recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Pisces constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Pisces constellation?
Pisces is an ancient constellation that dates back to the age of Greek Mythology around 3000BC. The myth tells of Aphrodite and Eros, who turned into fish to escape from the Monster Typhon. In Egypt, as far back as 2300BC the symbol of the fish was depicted on coffins.
In Chinese astronomy, around 750BC, some stars that form part of the modern Pisces constellation were included in the House of the Sandal.

The Persians also knew of the Pisces constellation. The fourth Mughal Emperor, known as Jahangir, ruled from 1605 until 1627. He minted gold coins with the image of the two fish.
In Pisces history, the age of Pisces began in AD1 and will continue until AD2150. This coincided with the birth of Christ. The constellation was important during biblical times and there are many references to fish in the Bible. The 12 apostles were known as the ‘fishers of men’ (21).
Archaeological excavations from Old Jaffa show that this seaport existed 4000 years ago. The constellation was known to astronomers at the time. Here, you can see it on a carving on a ‘wishing bridge’.
How did the Pisces constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, what does Pisces mean?
Most ancient cultures see Pisces as a Pisces greek god and Goddess who became fish to escape danger. They swim in the River Euphrates tied together by a rope.
The word Pisces comes from the Latin plural word meaning ‘fishes, or more than one fish. In the singular, the Latin word for one fish is ‘piscis’. Because the story of Pisces involves two fish, it has the Pisces Latin name in the plural form.
The word Pisces also derives from the Indo-European root *peisk- ‘Fish’, and has the derivatives piscary and piscatorial. The code word for Jesus was the Greek word for fish, “Ikhthus”.
The ichthys or ichthus, is a symbol from ancient Greece consisting of two intersecting arcs. The ends of the right side extend beyond the meeting point to resemble the profile of a fish (22).
Mythology and meaning
Pisces myth
Like many of the constellations, there are different Pisces mythology stories. The most well-known is the Pisces constellation story of Aphrodite, the Goddess of Love, and her son Eros.
Greek Mythology speaks of a terrifying and immortal giant called Typhon. He was sent by Mother Earth, Gaia, to punish the Gods for defeating their predecessors, the Titans. Aphrodite and her son Eros were walking along the banks of the Euphrates River while on a visit to Syria.

The monster Typhon suddenly descends upon Mount Olympus and threatens all the Gods and Goddesses. In great fear, Aphrodite called on Zeus to turn her and her son into fish so they could jump into the river and swim to safety.
Some versions say that two fish rescued the pair. Either way, the two Pisces fish, joined by a rope were placed into the sky.
The Roman Pisces constellation myth tells of Venus and Cupid who were carried from the Typhon’s threats on the backs of two fish.
Here is yet another version of Pisces constellation mythology, this time from Persia. Venus and Cupid, also Gods of Love, tied themselves together with a cord in order not to lose each other in the Euphrates. The knot of the rope is marked by the Pisces star Alpha Piscium.
What does Pisces symbolize?
What does the Pisces sign symbol represent? Pisces represents the duality within the nature of people born under the Piscean sign. Because they swim in opposite directions, in the Pisces meaning, there is a constant division in the psyche.
The Pisces modality is mutable. Mutable signs are flexible, adaptable, and open to change. They can see life from many perspectives and are great observers, They are often quiet and shy, gentle and wise, never rushing head-first into situations. Pisces love music and anything to do with water.

What is the Pisces symbol on the negative side? Pisces can be too trusting. They often have a desire to escape from reality. This is part of the Pisces description in the myth, in which the God and Goddess escaped reality by turning into fish.
Many people ask – what is the Pisces planet? Neptune is the planet that rules the sign of Pisces the fish.
Because we live in the Age of Pisces, the Pisces symbol meaning is closely connected to Christ, the Apostles, and many stories in the Bible.
Here are some famous Pisces personalities – George Washington, Michelangelo, Albert Einstein, Elizabeth Taylor, John Steinbeck, Rihanna, and Justine Bieber (23).
Future of Pisces constellation
Pisces is a constellation that is very exciting for astronomers to study. It contains galaxies that are changing and forming new stars as we watch.
Parts of the CL0024+1654 galaxy are still forming. This can be seen by the bright blue images of a beaded, ring-like galaxy that lies behind a giant cluster of galaxies. In the photo, 11 separate background galaxies are discernible, and more are forming (24).

Astronomers have more exciting Pisces information – A new galaxy known as UCG 477, has been found as recently as 2016. It is a low surface brightness (LSB) galaxy and lies 110 million light-years away.
Unlike normal spiral galaxies, the centers of LSB galaxies do not contain large numbers of stars. This could be because they are found in regions that have fewer galactic interactions.
LSB galaxies have large neutral hydrogen reservoirs. This allows them to slowly form stars that astronomers can study in years to come (25).
Van Maanen’s star is a white dwarf. This star is interesting because it is in the process of cooling down. When a white dwarf cools down it becomes a black dwarf that emits no energy at all. At this stage, there are no black dwarfs in the universe, but there may be in a few billion years!
Scientists use white dwarfs to determine how long they have been cooling and learn more about the age of the universe. Because Van Maanen’ star is only 14 light-years away, it is a perfect candidate for research (26).