Sagittarius Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Sagittarius Constellation
Abbreviation: Sgr
Symbolism: The Archer
R.A. position: 19h
Dec. position: -25°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 1089 light-years
Area: 867 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Kaus Australis (ε Sgr)
Visible at: Latitudes between +55° and −90°
Best viewed: During the month of August at 9.00pm
The Sagittarius constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as the Archer. Sagittarius is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek Mythology.
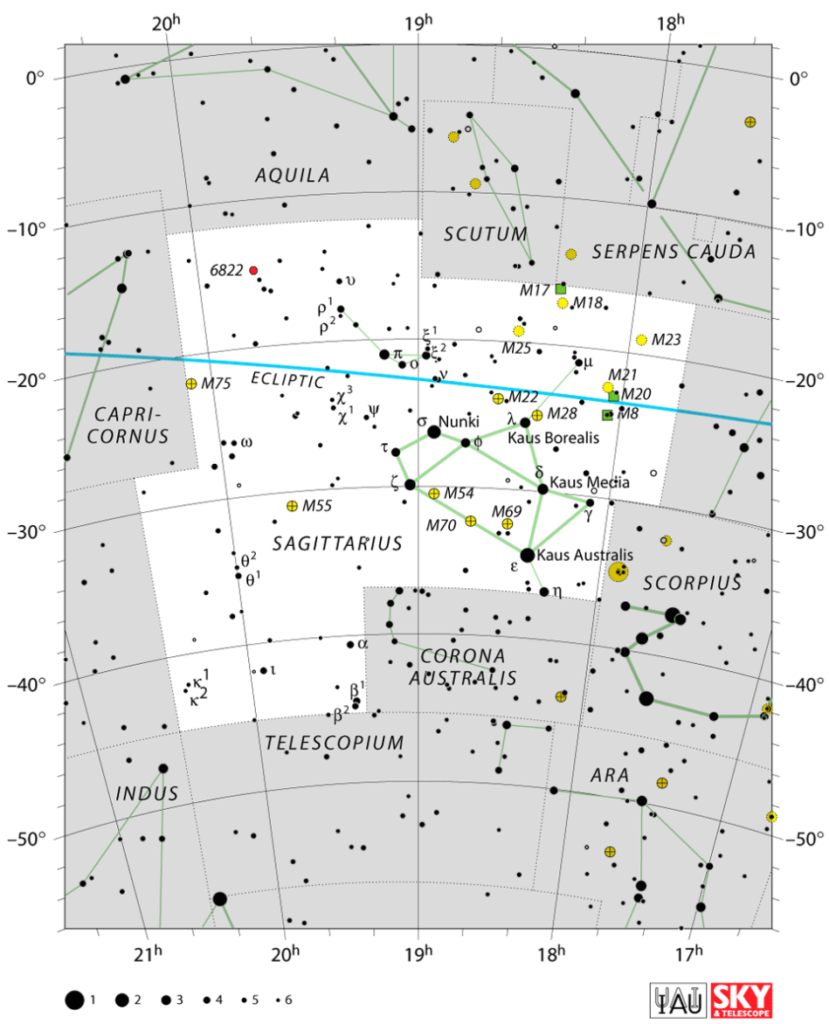
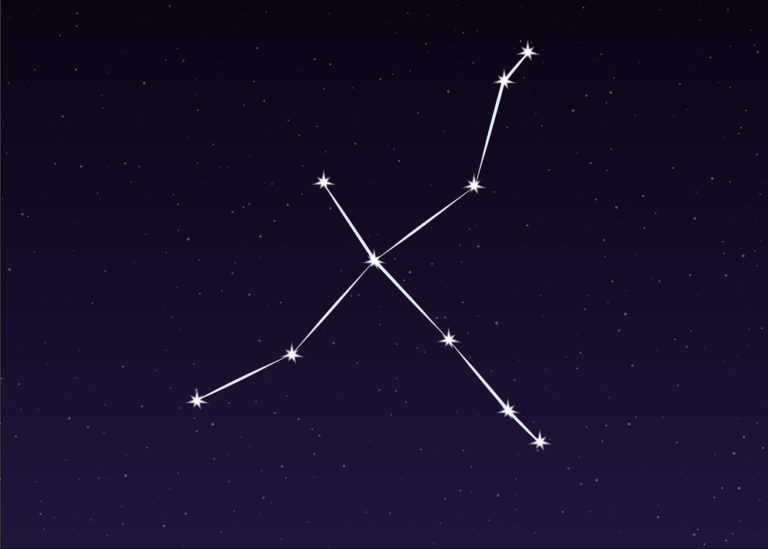
Sagittarius is the largest constellation in the southern sky and the 15th largest constellation overall. A distinct and interesting star pattern known as the Teapot helps you to identify it.
For a more detailed view, a telescope will give home stargazers amazing images. Sagittarius is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the amazing Lagoon Nebula and the Omega Nebula.
Read on to learn more about the constellation Sagittarius and interesting Sagittarius constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
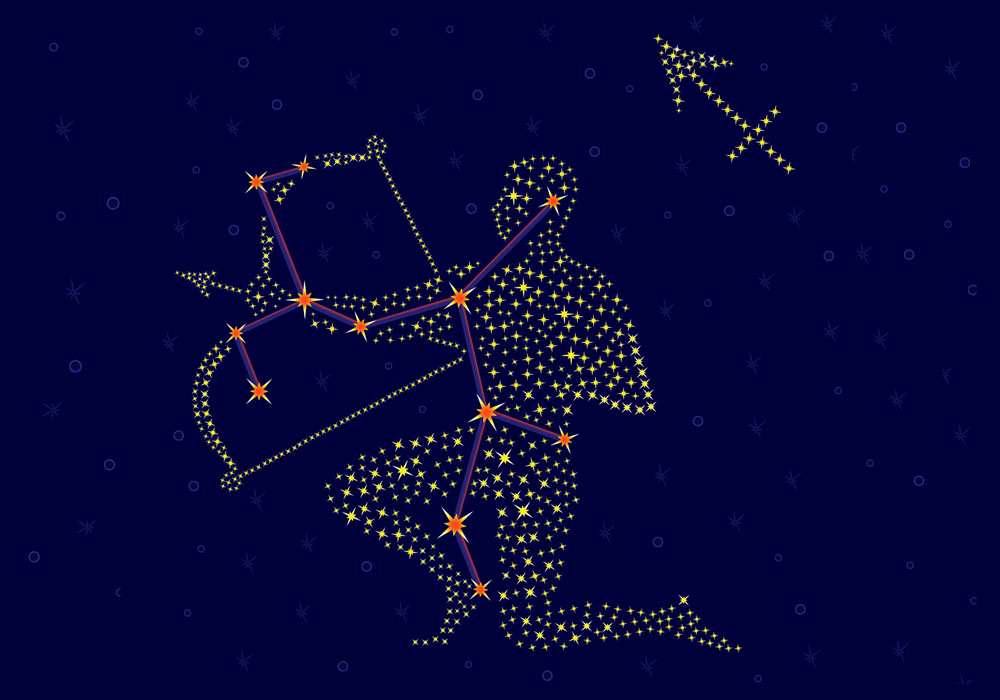
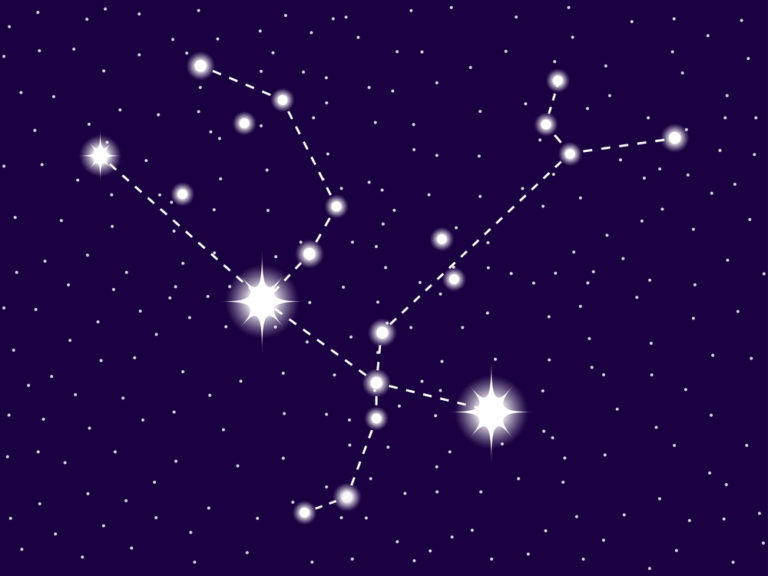
Sagittarius constellation
Sagittarius is a large and exciting constellation that dominates the southern sky. The Archer is a mythical creature known as a Centaur. A Centaur has the head, arms, and torso of a man and the body and legs of a horse. He stands ready to shoot his arrow into the body of the Scorpion.
The Sagittarius (constellation) is the 15 largest constellation in the sky and the 5th largest of the twelve Zodiac constellations. It occupies an area of 867 square degrees.

The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Scorpius and Capricorn. Sagittarius bordering constellations that are not part of the Zodiac are Serpens, Aquila, Telescopium, and Corona Australis (1).
For home astronomers, the constellation of Sagittarius offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains Sagittarius brightest star, a binary-star system called Kaus Australis.
It also offers the amazing Lagoon Nebula and the famous Orion Nebula. For those wanting to try some astrophotography, the star cluster NCG 6530 offers stunning colors and patterns that will thrill.
In the case of Sagittarius, both the constellation archer and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The age of Sagittarius greek mythology dates back over 3000 years (2).
What does Sagittarius constellation look like?
With many bright stars at strategic points, the Archer is a constellation that you can draw with your eye in the sky. The constellations Sagittarius looks like a huge centaur standing in the sky.
A centaur is a mythical creature made up of two parts. He has the head, arms, and torso of a man and the body and four legs of a horse.
This centaur is ready for battle! He is holding a large bow and arrow with the strings drawn back, ready to send the arrow flying into the heart of Scorpius the Scorpion.
The centaur has a large flowing beard and a head full of hair. On his shoulders is a flowing cape that billows out behind him.
The body and legs of the Sagittarius creature resemble a horse. He is standing strong and fierce on all four legs. This creature is brave and demands respect.
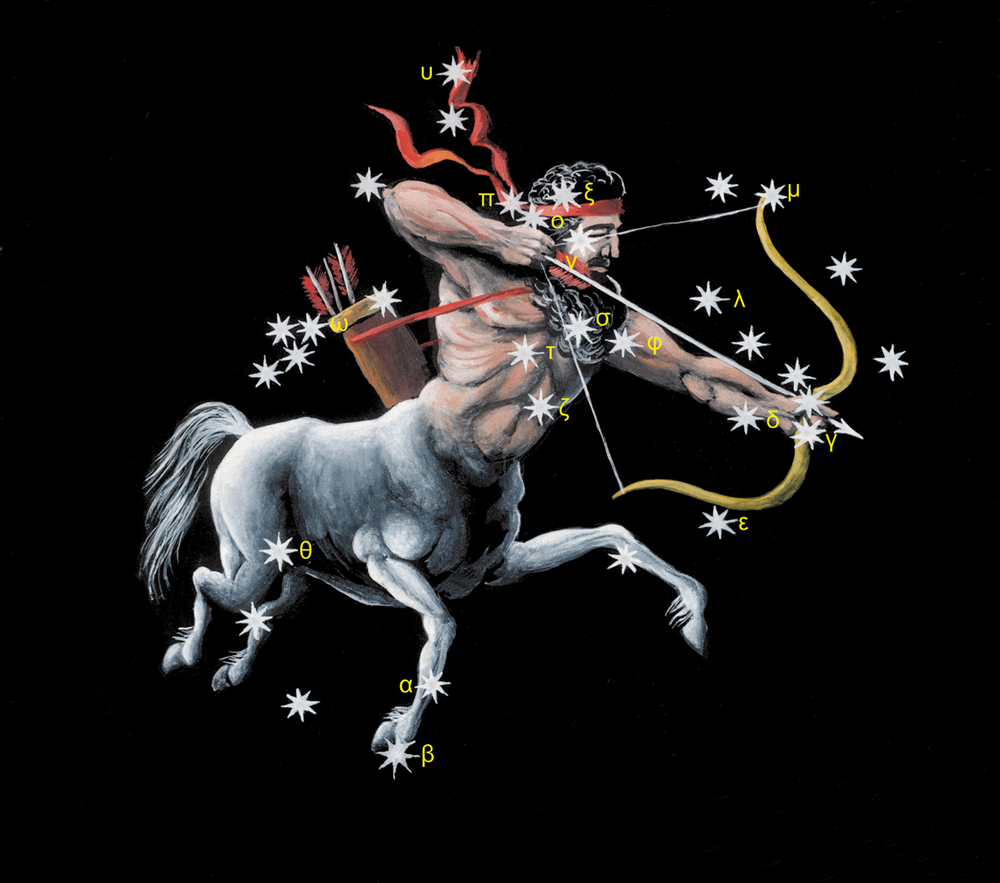
Bright stars are located at strategic points that will help you draw the image in the sky. Kaus Australis lies at the southern bow, Alnasl indicates the arrowhead, and Rukbat is at the archer constellation knee.
In the sky, the archer stands with his arrow pointing to Scorpius the Scorpion, who he has come to kill to try to save Orion the Hunter (3).
How far is Sagittarius constellation from Earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it looks as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be “close’ to Earth at less than 100 light-years distant. Others are millions of light-years away.
To better understand, the brightest star in Sagittarius is Kaus Australis which is around 143 light-years away from Earth. Another important star is Nunki, the second brightest star. It is 228 light-years away. Rubkat is 170 light-years away.

Constellations are not only made up of stars. They also contain deep-sky objects like Messiers and Nebula. In the Sagittarius zodiac constellation, the Orion nebula is about 1344 light-years away. The beautiful Lagoon nebula is further away at 4077 light-years, also known as M18, is 4892 light-years away (4).
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Sagittarius December constellation from Earth is 1089 light-years. If you consider some of the Messier objects, the distance can extend to be millions of light-years.
Zodiac family
Sagittarius is the ninth sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between November 21 to December 21. It is one of three fire signs, the others being Aries and Leo. Fire signs are strong and passionate with a great desire to learn.
The Sagittarius zodiac constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Scorpius the Scorpion, is directly in the line of flight of the Archer’s arrow. He is part of the myth, as the Archer was possibly sent to kill the Scorpion to save Orion.

Behind the archer Sagittarius we find Capricornus the Horned Goat. The goat is not part of the mythology of Sagittarius. The Archer enjoys roaming and exploring, and when he has achieved his mission, he will continue on his journey across the sky.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, Sagittarius the archer constellation lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year.
The Sun passes through Sagittarius each year from around 18 December to 20 January. This differs from the astrological sun dates – November 21 to December 21 (5).
Features
Major stars in Sagittarius
Here is a list of Sagittarius major stars. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in Sagittarius? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most interesting stars in Sagittarius to look for.
Kaus Australis – ε Sagittarii (Epsilon Sagittarii)
Kaus Australis is the brightest Sagittarius star. It is a binary star system that lies about 143 light-years away. This blue giant has an apparent magnitude of 1.79 and you can see it without a telescope.
The star’s name comes from the Arabic word for bow – qaws, and the Latin word for southern – australis. The star is one of the bow stars and lies at the base of the Sagittarius bow (6).
Nunki – σ Sagittarii (Sigma Sagittarii)
Nunki is the second brightest star in the bow and arrow constellation and lies about 228 light-years away. It is one of the interesting Sagittarius constellation stars, in that its name is of Assyrian or Babylonian origin, but the meaning is unknown.
Nunki is a hydrogen dwarf with an apparent magnitude of 2.1. It rotates extremely fast at a speed of more than 200km/s. That is about 100 faster than the Sun. The star is around 31.4 million years old, quite young in comparison to our Sun, which is 4603 billion years old (7).
Kaus Media – δ Sagittarii (Delta Sagittarii)
Kaus Media, also known as delta sagittarii, is a multiple star system that lies about 306 light-years away from Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.72 and you can see it without a telescope. It has a radius 62 times that of the sun and is 1180 times brighter.
The name means the “middle bow”. Delta Sagittari is a Sagittarius star surrounded by a circumstellar disk of dust. It has a close companion star called Epsilon Sagitarri B, which is covered by the dust cloud (8).
Kaus Borealis – λ Sagittarii (Lambda Sagittarii)
Lambda Sagittarii is an orange giant star marking the top of the archer’s bow. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.82 and is about 77.3 light-years away from Earth.
Kaus Borealis has a radius 11 times that of the Sun and is 52 times brighter. The traditional name means “northern bow”.
This star Sagittarius is important for stargazers to locate as it also marks the handle of the Teapot asterism and points to the beautiful Lagoon Nebula (9).
Rukbat – α Sagittarii (Alpha Sagittarii)
Rukbat is one of the fascinating stars in Sagittarius. Its name comes from the Arabic word rukbah, which means “knee”. It is a blue dwarf and lies about 170 light-years away. The star has an apparent magnitude of 3.97.
This means that you can see it without the need for a telescope. Rukbat is also written as Rucba, Rucbah, Rukbah, and Rucbar. The star is thought to have a debris disk around it, consisting of asteroids, dust, and other gas emissions (10).
Arkab – β Sagittarii (Beta Sagittarii)
In Sagittarius astronomy, Beta Sagittarii, also known as Arkab, gets its name from the Arabic carqūb, which means “hamstring”. It is also known to come from Al ‘Urkub, translated by Ideler as the “Tendon uniting the calf of the leg to the heel.
It is a double star system that lies about 378 light-years away from our Solar System. The system contains two stars, Beta-1 Sagittarii and Beta-2 Sagittarii. Beta Sagittarii has an apparent magnitude of 3.96. Arkab lies at the ankle of the left front leg of the Archer (11).
Ascella – ζ Sagittarii (Zeta Sagittarii)
Zeta Sagittarii is part of a triple-star system that lies at the armpit of the Archer. It is one of Sagittarius major stars.
The name comes from the Latin word Ascella, which means “armpit”. Zeta Sagittarii is a binary star system and is the third brightest star in Sagittarius constellation.
The star has an apparent magnitude of 3.26. Its companion has a magnitude of 3.37. Ascella lies about 89.1 light-years away from Earth. Ascella also forms part of the teapot asterism. You can see Ascella in the night sky without a telescope.
Deep-sky objects in Sagittarius
Sagittarius A
Sagittarius A is a massive black hole that emits large amounts of radio waves. It lies at the center of the Milky Way and consists of large cosmic dust clouds from the spiral arms of the galaxy.
Sagittarius A is made up of a supernova remnant Sagittarius A East, the spiral structure Sagittarius A West, and a radio source. Sagittarius A lies about 25 640 light-years away and has a diameter of about 44 million kilometers (12).
Sagittarius B2
Sagittarius B2 is a massive molecular cloud of dust and gas that lies about 26,000 light-years away from Earth. It is also part of the center of the Milky way and has a mass 3 million times that of our Sun.
Sagittarius B spans an area of 150 light-years across. If these numbers are difficult to understand, here is another one!
Astronomers have found that there are 10 billion, billion, billion (see 27 zeros in this number) liters of methanol and ethanol molecules in the cloud. Scientists study Sagittarius B2 in search of amino acids, which are vital compounds for life (13).
Lagoon Nebula – Messier 8 (M8, NGC 6523)
The beautiful Lagoon Nebula is a large interstellar cloud known as an emission nebula. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.0 and is approximately 4,100 light-years away from Earth. Also known as Messier 8, it is a star-forming region in the Universe.
If you are away from city lights, you can see it with the naked eye. It was discovered in 1747 by French astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil. Also exciting to astronomers is the Hourglass Nebula which lies at the center of the Lagoon Nebula (14).
NGC 6530
Within the Lagoon Nebula is the amazing open cluster called NGC 6530. The cluster has an apparent magnitude of 4.6 and is about 4,300 light-years away. The cluster is known for its complex morphology and star-formation history.
It was discovered by Italian astronomer Giovanni Battista Hodierna in 1654. Scientists believe that the cluster contains about 2720 stars (15).
Omega Nebula – Messier 17 (M17, NGC 6618, Swan, Horseshoe or Lobster Nebula)
Another fabulous emission nebula in Sagittarius is the Omega Nebula. It is also known as the Horseshoe Nebula, the Lobster Nebula, the Swan Nebula, and Sharpless 45. Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys De Chéseaux discovered it in 1745.
The Omega Nebula has an apparent magnitude of 6.0 and is about 5,500 light-years away.
This is one of the largest star-forming regions in the Milky Way Galaxy. Messier 17 also contains one of the galaxy’s youngest star clusters, only 1 million years old. On a dark night, you can see the nebula using powerful binoculars (16).
Messier 18 (M18, NGC 6613)
Messier 18 is a fairly dim open star Sagittarius cluster with an apparent magnitude of 7.5. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. The cluster lies about 4,900 light-years away from Earth and is about 32 million years old.
With a powerful telescope, you can locate it between the Sagittarius Star Cloud and the Omega Nebula. Scientists speculate that Messier 18 may form a binary star cluster with the nearby NGC 6618. Because of their close proximity, they may have formed at the same time (17).
Trifid Nebula – Messier 20 (M20, NGC 6514)
Another stunning nebula to view is the Trifid Nebula, It offers bright, colorful emissions that will delight home stargazers. Messier 20 is also a star-forming region. It lies about 5,200 light-years away and has an apparent magnitude of 6.3.
This Messier is a combination of an emission nebula at the lower section and a reflection nebula at the upper section. This phenomenon makes it glow with spectacular colors. The name Trifid means ‘divided into 3 sections. At only 300,000 years old, it is a young nebula (18).
Exoplanets in Sagittarius
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to Earth, and hence the possibility of life.
Caleuche
Caleuche is an exoplanet revolving around its mother star called HD 164604. It has a magnitude of 6.72 and takes 641 days to orbit its star.
The name comes from a ghost ship in southern Chilean mythology which sails the seas around the island of Chiloé at night. The main star is also known as Pincoya, a female “water spirit” of the Chilotan Seas (19).
Mastika
Mastika revolves around its mother star, called Gumala or HD 179949. Mastika is also known as HD 179949 b. Mastika is a hot Jupiter about 88 light-years away. It takes only 3 days to orbit its mother star. Mastika is a Malay word that means a gem, precious stone, jewel, or the most beautiful (20).
Toge
Toge, also known as HD 181720 b revolves around a mother star HD 181720. The mother star is also known as Sika. Toge has an apparent magnitude of 7.84 and takes 956 days to orbit its star. Toge is 183 light-years away from Earth.
The ‘NameExoWorlds campaign’ allows members of the public to name stars and exoplanets. Andrews Mawuli Dzodzomenyo from Ghana named HD 181720 and its planet. Toge means earrings in the Ewe language. Sika means gold, and gold is one of Ghana’s main exports (21).
OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb
In 2005, astronomers discovered an interesting exoplanet in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is about 5.5 times the mass of Earth. This is one of the smallest exoplanets known and has the name OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb. The exoplanet takes 9 years to complete one orbit of its star (22).
Meteor showers in Sagittarius
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as Falling Stars.
Sagittariids Meteor Shower
The teapot constellation has fewer well-defined meteor showers than other zodiac constellations. Meteor showers get their names from the constellation from where they appear to radiate. Although it is known as the Sagittariids meteor shower, this shower radiates closer to the neighboring Scorpius constellation.
The showers light up the sky between 1 June and 15 July, with the peak being on 19 June. You can expect to see around 5 meteors per hour traveling at a speed of 23km/s.
Capricornids-Sagittariids Meteor Shower
This is a daytime meteor shower and as such, you cannot see it. The source of the meteor shower is the Asteroid 2001 ME1. The peak activity is around 4 February, and the speed of the meteors is around 29km/s (23).
The shower has a shared name as it radiates from a region between the constellation of Capricorn and the constellation of Sagittarius.
Location and visibility
Where is Sagittarius constellation located?
Sagittarius is easy to find once you know what to look for. You can see the bright stars without a telescope. Then you can imagine the imposing centaur archer in the sky, standing with his bow and arrow pointing towards the Scorpion.
The Sagittarius archer constellation is the largest in the southern sky and fifth-largest of the twelve Zodiac constellations. It occupies an area of 867 square degrees.
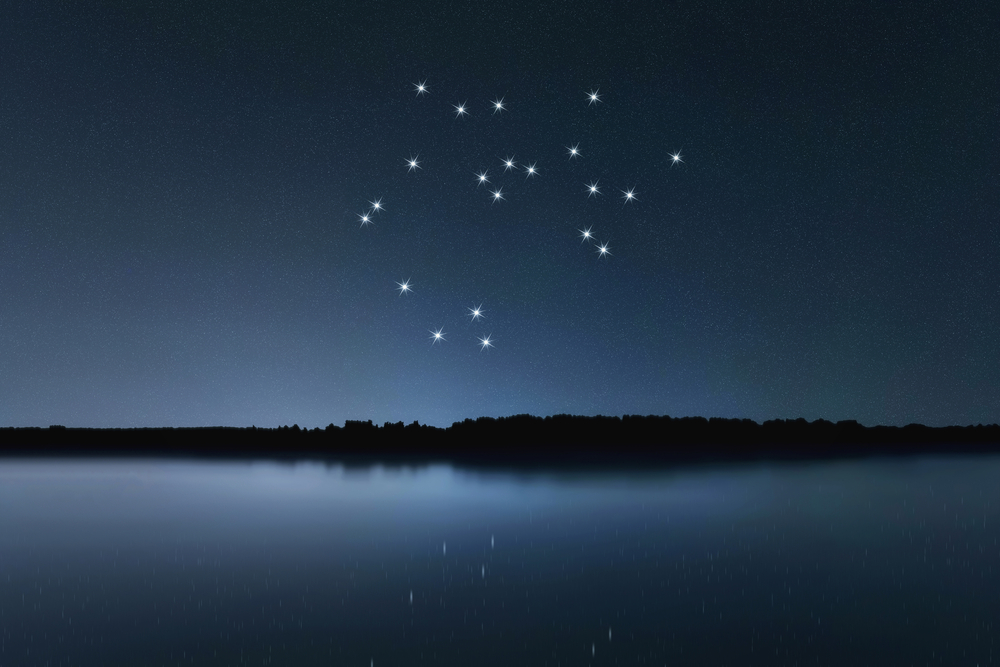

The Sagittarius star constellation is in the fourth quadrant of the southern hemisphere, SQ4. A quadrant is a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the archer constellation at latitudes +55° and −90°.
To find Sagittarius the archer constellation, you can locate the two neighboring zodiac constellations. Look for Capricornus the Goat and Scorpius the Scorpion. The Scorpion is directly in front of the Sagittarius arrow. Capricornus stands behind the archer’s back legs.
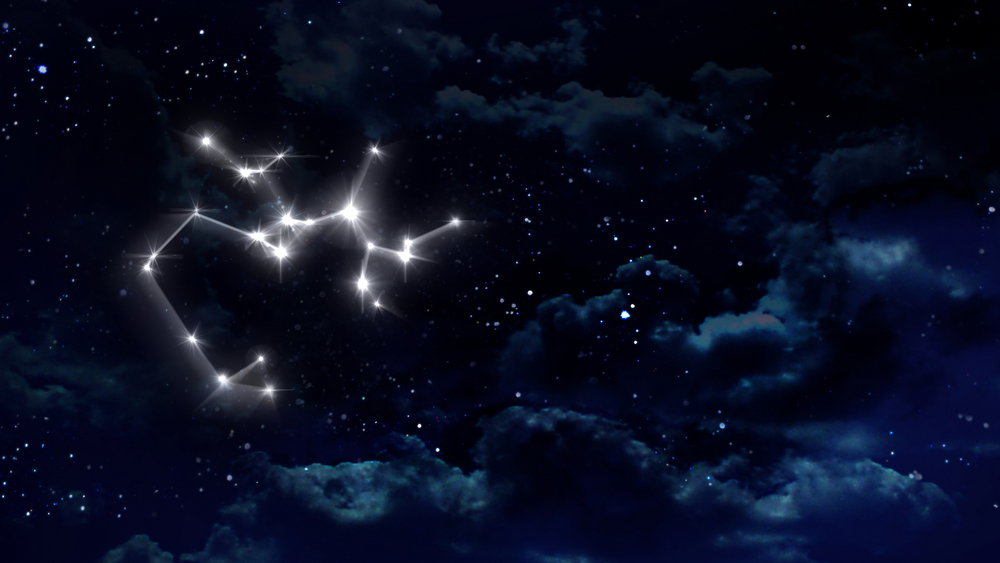
Another famous section of the Sagittarius constellation is the Teapot Asterism. This is a star pattern in the middle of the archer, resembling a teapot with a handle and spout (24).
When is Sagittarius constellation visible?
Star constellations Sagittarius is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
The best viewing of Sagittarius is in the southern hemisphere during the months of June to November.
In the northern hemisphere the constellation can be viewed low on the horizon from August to October.

Northern hemisphere
In the northern hemisphere, you can spot the Sagittarius star pattern
August, September and October. Look very low in the southern skies from about 8.00pm to 2.00am, depending on the month.
Southern Hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere, in June and July Sagittarius (constellation) will appear in the southeastern sky at about 9.00pm. In August and September, the Sagittarius constellation location is visible earlier at around 8.00pm.
From October to November it appears high in the western sky at 10.00pm. Set up a blanket and chair in a dark spot and watch as it slowly dips below the horizon by around 1.00am.
Remember that in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so Sagittarius in the sky will be standing on his head! (25).
How to find Sagittarius constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here’s the 5 step guide on how to find Sagittarius constellation.
- To locate archer Sagittarius, it is easiest to look for the teapot shape
- Extend a line from the spout to the right and you will reach the bright star Alnasl, the tip of the arrow
- Behind Alnasl are two bright stars, Kaus Media and Kaus Borealis, forming the triangular shape of the bow
- Extending a line down and backward from the teapot, you can locate Rubkat, the Archers knee, and Arkab Prior, at the ankle
- Once you have these pinpoints complete the image a large imposing centaur Sagittarius with bow drawn back and arrow ready to pierce the heart of the Scorpion
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down.
- To locate Sagittarius, it is easiest to look for the teapot shape
- Extend a line from the spout to the left and you will reach the bright star Alnasl, the tip of the arrow
- In front of Alnasl are two bright stars, Kaus Media and Kaus Borealis, forming the triangular shape of the bow
- Extending a line upwards and forwards from the teapot, you can locate Rubkat, the Archers knee, and Arkab Prior, at the ankle
- Once you have these pinpoints complete the image a large imposing centaur with bow drawn back and arrow ready to pierce the heart of the Scorpion
How to view Sagittarius Constellation?
Getting away from city lights and pollution is the best way to see the archer and bow constellation. Many of the main stars are visible to the naked eye.
Using a telescope will make the experience so much more exciting! For home stargazers, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that give you fabulous images of Sagittarius the constellation.

Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Explore Scientific FirstLight AR102 TN Refractor Telescope is a refractor scope with a super-cool stylish white tube. It features a 102mm aperture and a 600mm focal length. It comes with a Plossl 25mm eyepiece and a 1.25″ 90-degree Diagonal.
The scope has a Twilight Nano Alt/Az mount that is very stable, By easily moving the mount horizontally and vertically it is easy to locate any Sagittarius nebula or Sagittarius stars that you want to explore.
The legs adjust to give you the height you want, a great perk if you have children with you. It has an HD132 Red-dot Finder, a Smartphone Camera adapter, and comes with a Sky Software program.
This scope is easy to set up and does not require time to learn how to use it. Simply point and be amazed!
History of observation
Who discovered Sagittarius constellation?
The Sagittarius origin was documented by many ancient cultures in stories, folklore, and Sagittarius history myths over thousands of years.
Sagittarius constellation mythology was written in stories of Greek mythology dating back to 3000BC. There are a few different stories. One identifies the Archer as the satyr Crotus, son of Pan, who invented archery.
According to the myth, Crotus hunted on horseback and lived among the Muses. They requested that the Sagittarius greek god, Zeus placed him in the sky, where he shows off his archery skills.

The Babylonian astronomers around 2300BC knew Sagittarius the archer as the god Nergal, a centaur creature firing an arrow from a bow.
The Chinese astronomers around 70BC knew of the horseman. Sagittarius lies across two of the quadrants symbolized by the Azure Dragon of the East and Black Tortoise of the North.
The name of the constellation in Chinese is rén mǎ zuò, meaning “the horse-man constellation” (26).
The famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Sagittarius constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
More recent discoveries of deep-sky objects in the Sagittarius constellation can be attributed to Charles Messier, an astronomer who lived between 1730 and 1817.
He named many of the famous objects including the Lagoon Nebula (Messier 8), the Omega Nebula (Messier 17), and the Trifid Nebula (Messier 20) (27).
How old is Sagittarius constellation?
Sagittarius is an ancient constellation that dates back to the age of Greek Mythology around 3000BC. The mythology of Sagittarius tells of Crotus, son of Pan, who invented archery.
According to the myth, Crotus hunted on horseback and lived among the Muses, who requested that Zeus place him in the sky, where he is seen demonstrating archery.

Sagittarius constellation history was also documented by the Babylonian astronomers around 2300BC. They knew Sagittarius as the god Nergal, a centaur creature firing an arrow from a bow.
Sagittarius is also a constellation of Sumerian origin, dating back to around 2300BC. Sumerian astronomers identified it as PA.BIL.SAG, a god of war and hunting (28).
In the 8th and 9th centuries, Centaurs featured on Pictish carved stones from northeast Scotland. They appear to have origins in the Roman Empire from around 27BC to 476AD (29).
How did the Sagittarius constellation get its name?
You may ask – how did Sagittarius get its name? Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. The word Sagittarius is Latin and translates to Archer.
In ancient history, the archer is a half-horse, half-man figure called a centaur. This creature was powerful and strong and could fire arrows with deadly accuracy.
Sagittarius in greek comes from the word centaur, κένταυρος, kéntauros. Centaurs feature in many Greek myths as wild as untamed horses. They lived in the region of Mount Pelion in Thessaly.
The Greeks also called this constellation Toxeutes, the Archer, from the word Toxon, meaning bow. The word Archer also has roots in the Indo-European *arku- meaning ‘bow and arrow ‘
In some myths, the archer was not a centaur, He was Crotus, son of Pan, Crotus would ride in the forest on horseback with his bow and arrow, becoming a mystical figure of a man on a horse (30).
Mythology and meaning
Sagittarius myth
The Sagittarius constellation myth has many different stories, each one fascinating and you can choose which you prefer! So, what is the myth behind Sagittarius?
In one Sagittarius myth, the creature is not a centaur. He is the satyr Crotus, son of Pan, who Greeks credited with the invention of archery. Crotus would ride in the forests practicing his archery and hunting skills. He lived amongst the Muses, who asked Zeus to place him into the sky.

Another Sagittarius story tells of Chiron, a centaur, son of Philyra and Cronus. Chiron lived at the base of Mount Pelion. Unlike other Centaurs, who were savage and violent, he was known as a wise creature with a great knowledge of medicine.
He also taught many heroes, such as Jason, Heracles, and Achilles. One day, Hercules accidentally shot a poisoned arrow and struck Chiron, As he was immortal, he could not die.
He gave up his immortality and was placed among the stars. As there are two centaurs in the sky, Sagittarius and Centaurus, it is a mystery in Sagittarius mythology as to which one he is (31).
Why is Sagittarius aiming at scorpio? A common story linking the zodiac myths is that Sagittarius stands ready to fire his arrow into the heart of a scorpion. When Orion the Hunter grew arrogant, boasting that he would kill all the creatures of the Earth, Gaia, the Goddess of Earth, sent the Scorpion to destroy Orion and a massive battle followed.
Did Sagittarius win? No, the Scorpion killed Orion and both were placed into the sky!
What does Sagittarius symbolize?
Sagittarius symbolizes a centaur, a half-horse, half-man who is a knowledgeable healer of great intelligence. The Sagittarius centaur forms a bridge between Earth and Heaven. Unlike other centaurs, he is not violent but is nurturing and wise.
The Sagittarius modality is mutable. Sagittarius is also associated with the Sagittarius god, Zeus.
People born under this sign tend to be optimistic, fun, fair-minded, intellectual, and honest. They are lovers of freedom and enjoy engaging in conversation. Sagittarius people usually have many friends.
Like the Archer, they know their own minds and don’t like to be contained, ignored, or bossed around. With a Sagittarius background, the weakness is to promise more than they can deliver. They can also be very impatient.
Here are some famous Sagittarius personalities – Winston Churchill, Joseph Stalon, Jane Austin, Taylor Swift, Brad Pitt, and Bruce Lee (32).
Future of Sagittarius constellation
Over millions of years, stars and deep-sky objects change the form, move or even explode. Sagittarius is of great interest to scientists and astronomers as it contains nebulas that are active star-forming regions.
This means that even now, new stars are being born. The Lagoon Nebula, also known as Messier 8 is one of the most active star-forming regions in the universe (33).
Also known for its star-forming history is the amazing NGC 6530 cluster. Scientists study its complex morphology and star-formation history.
Nasa scientists are studying the supermassive black hole in the middle of the Milky Way galaxy, known as Sagittarius A*. By observing this relatively close celestial object, they will better understand the flow of matter in star clusters and galaxies.
But, it goes even further than that – this phenomenon in Sagittarius will also help scientists to better understand the universe (34).
Scientists believe that black holes may be the last remaining matter in the universe. Sagittarius A* is demonstrating in a scary way how that can happen. Don’t worry – it will only occur in many millions of years from now.