Taurus Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Taurus Constellation
Abbreviation: Tau
Symbolism: The Bull
R.A. position: 4.9h
Dec. position: 19°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 19391 light-years
Area: 797 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Aldebaran – Alpha Tauri (α Tauri)
Messier objects: Messier 1 (Crab Nebula), Messier 45 (the Pleiades)
Meteor Showers: Taurids, Beta Taurids
Bordering Constellations: Aries, Auriga, Gemini, Orion, and Perseus
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −65°
Best viewed: During the month of January at 9.00 pm
The Taurus constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as Bull. Taurus is one of the oldest known constellations and dates as far back as the Bronze Age. In Greek Mythology, Taurus relates to Zeus, King of the Gods, is a fascinating story.
Taurus is easy to find in the sky and has a number of bright stars that home stargazers can see without a telescope. It offers many exciting celestial objects. You can learn about the stars Aldebaran and Elnath, and the variable star T Tauri. You can view the amazing Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters.
Read on to find out more about constellation Taurus and Taurus constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
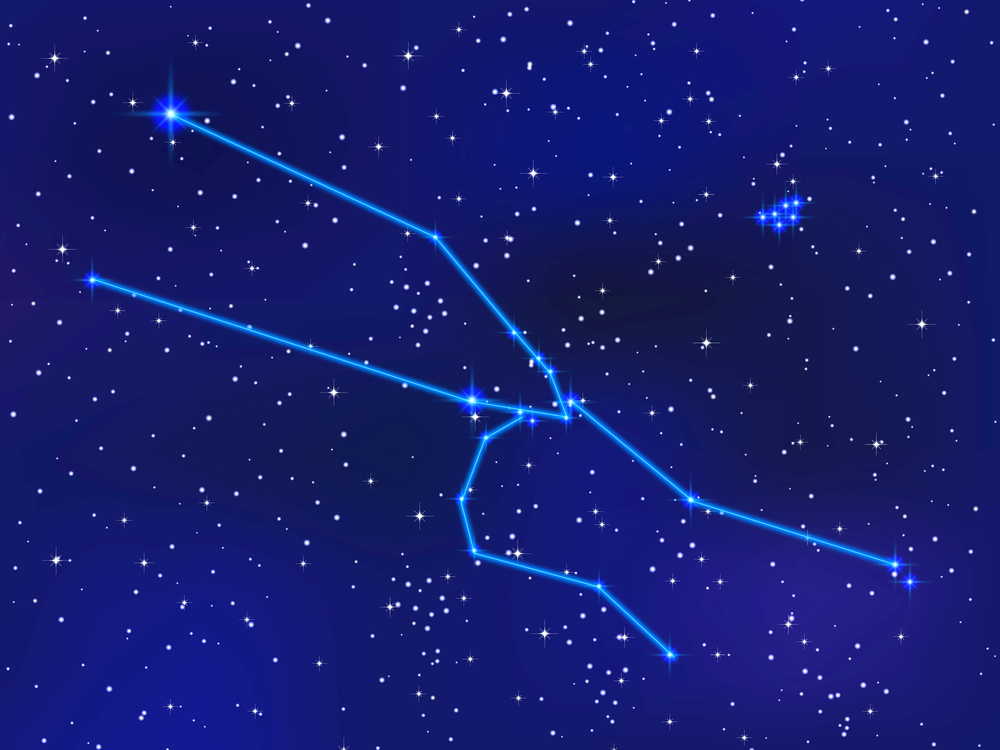
Taurus constellation
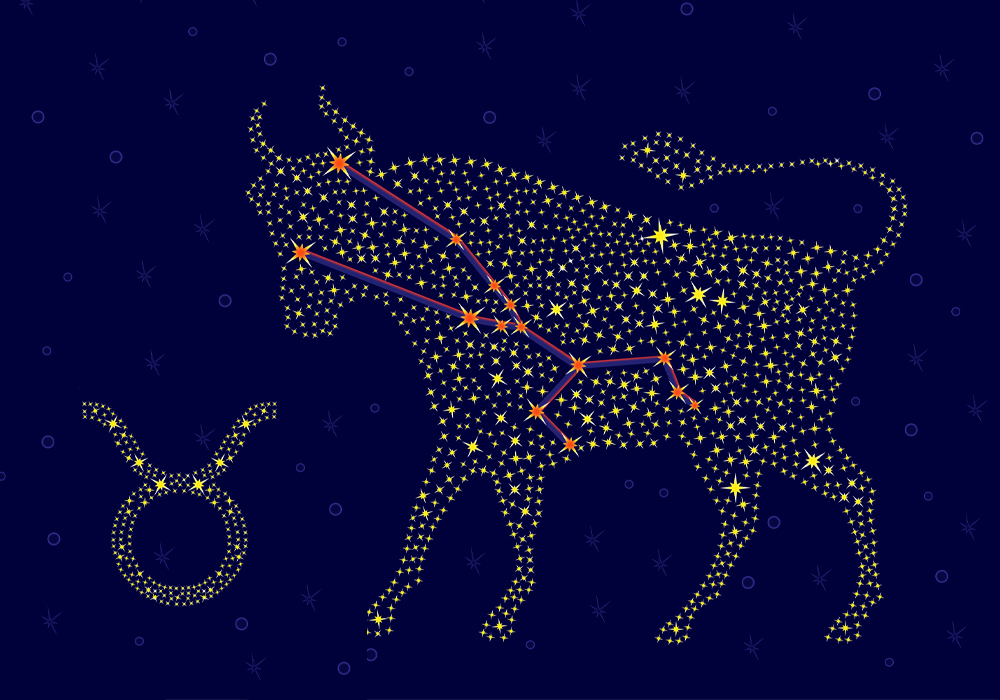
Taurus is a large and distinctive constellation to spot. The raging bull charges across the sky with front legs raised and horns thrust forward. The name comes from the Latin word meaning ‘The Bull.’
The Taurus (constellation) is the 17th largest constellation. It occupies an area of 797 square degrees. The neighboring constellations are Aries, Auriga, Cetus, Eridanus, Gemini, Orion, and Perseus.
It was officially listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Claudius Ptolemy. For home astronomers, the constellation Taurus offers many interesting celestial objects.

It contains the orange-giant Aldebaran and the binary star Theta Tauri. It offers the sensational Crab Nebula, a favorite to try your hand at astrophotography. Also of interest is Hind’s Variable Nebula, which is illuminated by the star T Tauri, next to it.
In the case of Taurus, both the constellation and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The age of Taurus greek mythology dates back over 3000 years and is also featured in the Bronze Age, 3000BC to 1200BC (1).
The Bull has intrigued ancient civilizations for thousands of years, depicting strength, fertility, and power.
What does Taurus constellation look like?
You may be asking – what does Taurus look like? With many bright stars at strategic points, the bull is a constellation that is easy to spot, even with the naked eye.
The constellation of Taurus looks like a giant bull charging across the sky. His huge head is down for the charge.
Two massive horns are raised upwards in front of him. The bull’s front legs are drawn up in a galloping stance, powering the great beast forwards.
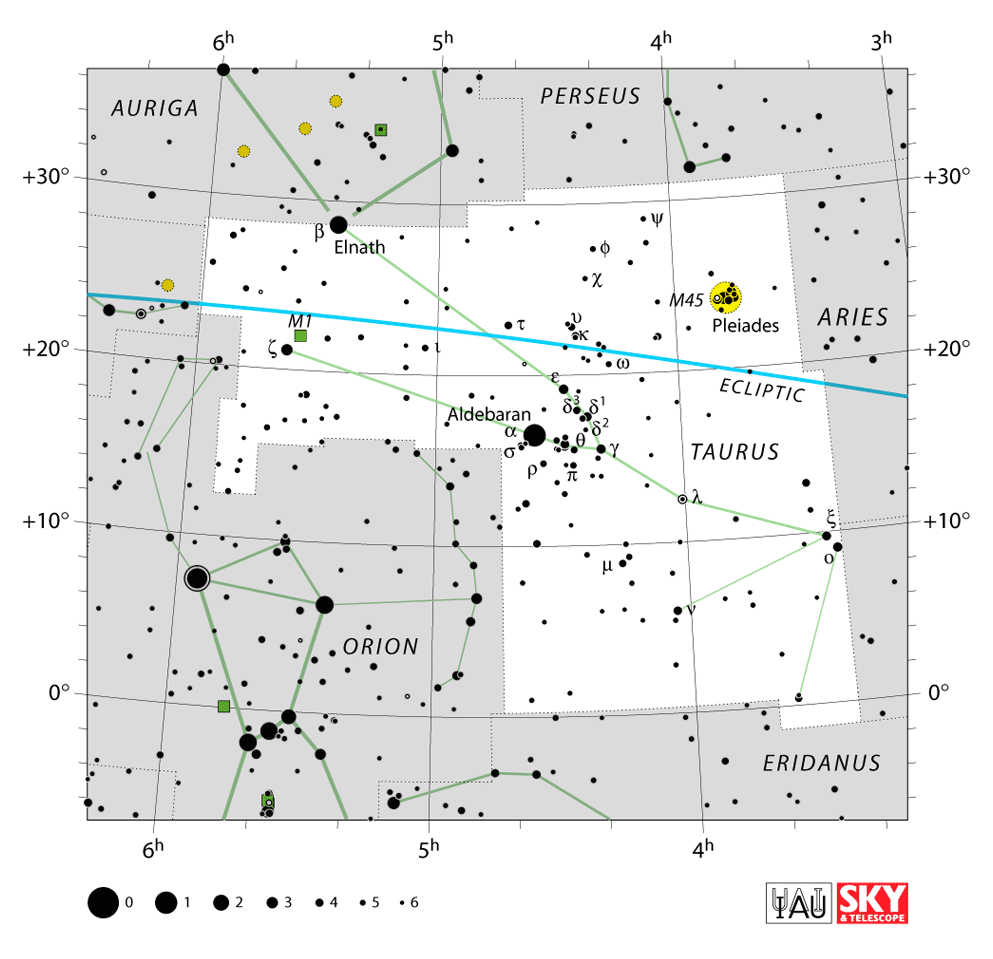
Image credit: IAU and Sky & Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) CC-BY-3.0.
In your imagination, the bull is looking directly at you – so beware! Some astronomers believe that he is staring down at Orion the Hunter, but Greek mythology has no clear connection between the two.
To complete the picture, imagine a thick mane of curly wooly hair lying flat on his back. The bull in the sky is only half a creature.
His hindquarters and back legs do not form part of the constellation. Despite this, the size of the constellation gives you an awesome idea of the immense power and strength of this mythical creature.
How far is Taurus constellation from earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it looks as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be as close as 60 light-years, and others as far as millions of light-years.
To give some idea, the brightest star in Taurus is Aldebaran and is 65 light-years from Earth. Elnath is the second brightest star in the Taurus constellation and is about 134 light-years from the solar system (2).
The beautiful Crab Nebula lies about 6523 light-years from Earth (3).
The open star system called the Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters, is about 444.2 light-years away. HIP 21533 is the furthest star in the constellation and is 108721.1 light-years away from the Sun. The variable star T Tauri is 460 light-years distant.
Taking into account the objects and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Taurus constellation from Earth is 19391 light-years.
Zodiac family
Taurus is the second sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between April 19 and May 20. It is one of the three earth signs, the others being Virgo and Capricorn.
The Taurus star constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Orion the Hunter stands directly in front of the bull and looks as if he will be seriously hurt if he does not move out of the way. Aries, the Ram, stands behind the bull, facing in the opposite direction.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, Taurus the bull constellation lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the Sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year.

The Sun passes through Taurus each year from around mid-May to Mid June.
Many stargazers believe that the bull is charging Orion the Hunter. In Greek Mythology, this is not the case. But, there is a connection. In another myth, Orion the Hunter was pursuing the seven daughters of Atlas after he was forced to hold up the heavens.
To protect them, Zeus turned them into doves and then into stars and placed them into the sky. They lie in a cluster called the Seven Sisters, inside the constellation of Taurus.
In the Sumerian myth of Gilgamesh, Orion represented a hero who did fight a raging bull. The Bull was Taurus and in this myth, they connect as we see them in the sky.
Features
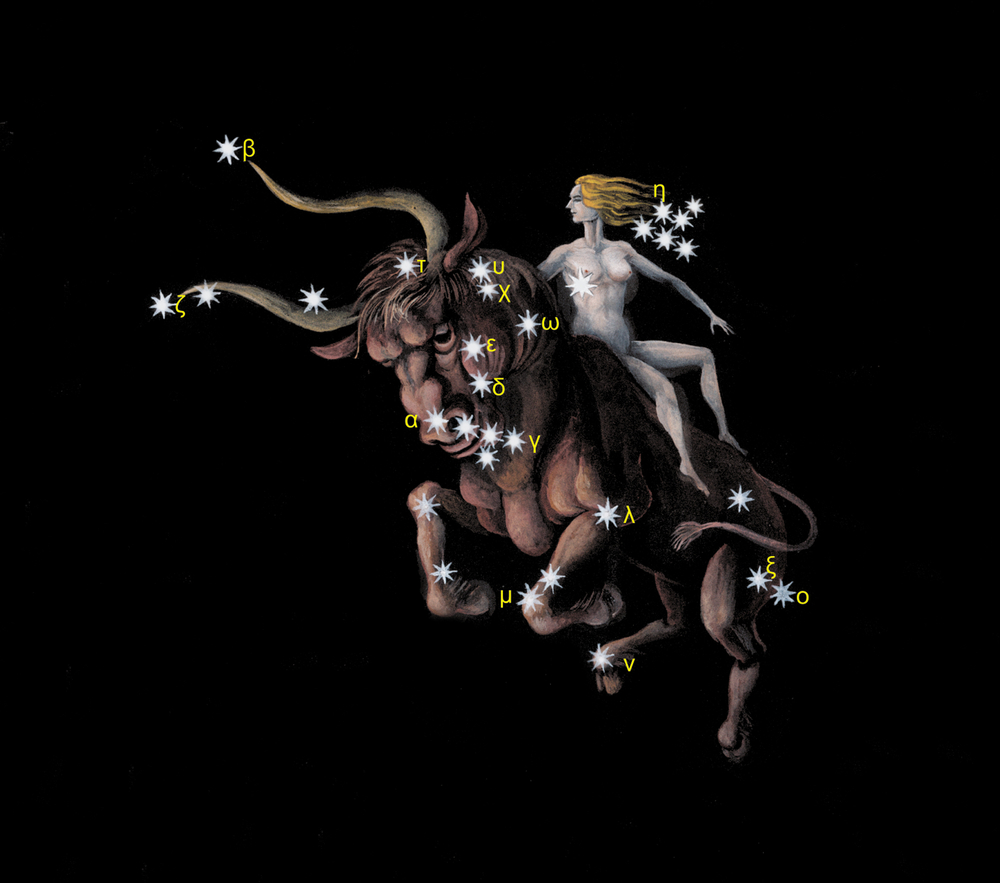
Major stars in Taurus
Here is a list of the major Taurus stars. Astronomers ask – how many stars does Taurus have? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most interesting stars for home stargazers to look at.
Aldebaran – Alpha Tauri (α Tauri)
You may ask – what is the brightest star in Taurus? It is Aldebaran, also known as Alpha Tauri. Aldebaran is an orange giant that indicates the eye of the Bull. Its name comes from the Arabic, al-dabarān, which means ‘The Follower.’ This relates to the eye that appears to follow the Pleiades across the sky.
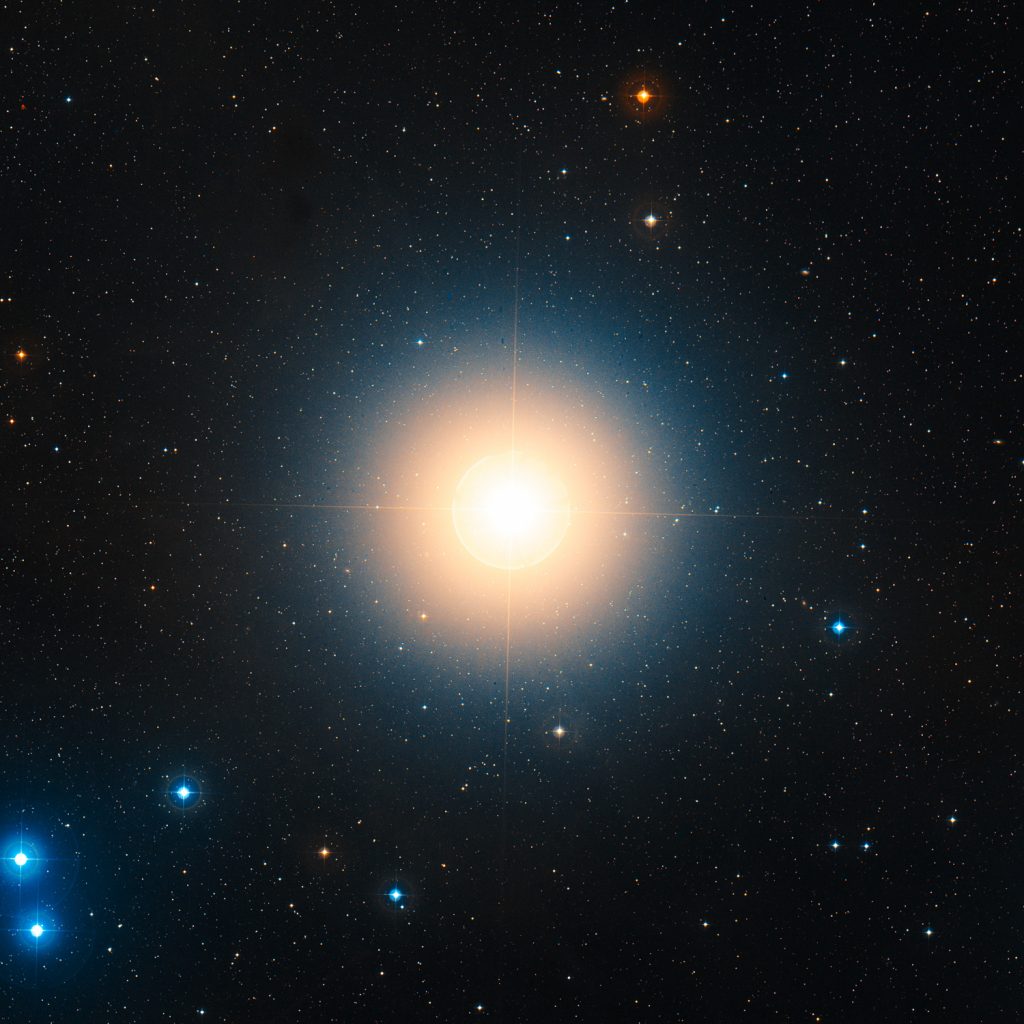

Image credit: ESA/Hubble (full image)
Aldebaran has an apparent magnitude of around 0.85. It is the 14th brightest star in the sky. The star is 425 times brighter than the sun and lies about 65.1 light-years from Earth. To find Aldebaran, locate the 3 stars of Orions’s belt and extend the line upwards to the first bright star (4).
Elnath – Beta Tauri (β Tauri)
Elnath, as one of the Taurus constellation stars, is interesting in that it is 700 times brighter than our Sun. This blue-white giant has a visual magnitude of 1.68 and is the second brightest star in Taurus.
Elnath gets its name from the Arabic an-naţħ, which means “the butting,” referring to the bull’s horns. It is also known as Alnath, El Nath, and Beta Tauri. Elnath lies about 131 light-years away.
Hyadum I – Gamma Tauri (γ Tauri)
Gamma Tauri, also known as Prima Hyadum, is a yellow-giant about 154 light-years away from Earth. It lies near the center of the spectacular Hyades cluster. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.654 and you can see it without using a telescope. The age of the bull star is around 430 to 530 million years. Gamma Tauri is 85 times more luminous than the Sun. The name comes from the Latin word meaning “First Hyad” (5).
Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri)
Zeta Tauri is also known as Tianguan. Tianguan comes from Chinese astronomy and means Celestial Gate, which lies with the asterism called the Net. Zeta Tauri is a binary star with a visual magnitude of 3.010. It lies about 440 light-years away from Earth. The main component is about 6 times greater than the Sun. The companion is slightly smaller than the Sun (6).
Theta Tauri (θ Tauri)
Theta Tauri is a binary star in the bull constellation that lies in the Hyades open cluster. The primary star is 154.4 light-years away and the secondary is 150.4 light-years away. Theta-1 Tauri is an orange-giant with a visual magnitude of 3.84 and you can see it with the naked eye. In the mythology of the Maya peoples, Theta Tauri has a name from the Yucatec Maya language, Chamukuy, which means a small bird.
T Tauri
T Tauri is an interesting Taurus star system that consists of 3 stars. In the Taurus star map, they lie next to the nebula NGC 1555 and illuminate it, causing the nebula to shine with varying degrees of brightness. John Russell Hind discovered the star system in October 1852.
It has an apparent visual magnitude of around 10.27 and is approximately 600 light-years away from Earth. Looking through a telescope, T Tauri lies near Epsilon Tauri in the Hyades cluster. In reality, it lies about 420 light-years behind it.
New stargazers ask – how many stars are in Taurus? There are thousands, but only some major stars can be easily observed with a home telescope.
Deep sky objects in Taurus
Pleiades (Seven Sisters)
This beautiful Taurus cluster lies inside the constellation near the eye of the Bull. It is also known as Messier 45. This cluster is a favorite of beginner astronomers as it is very bright with an apparent magnitude of 1.6 and is easy to see. The Pleiades Taurus consists of very hot, luminous stars that are around 390 to 460 light-years away.
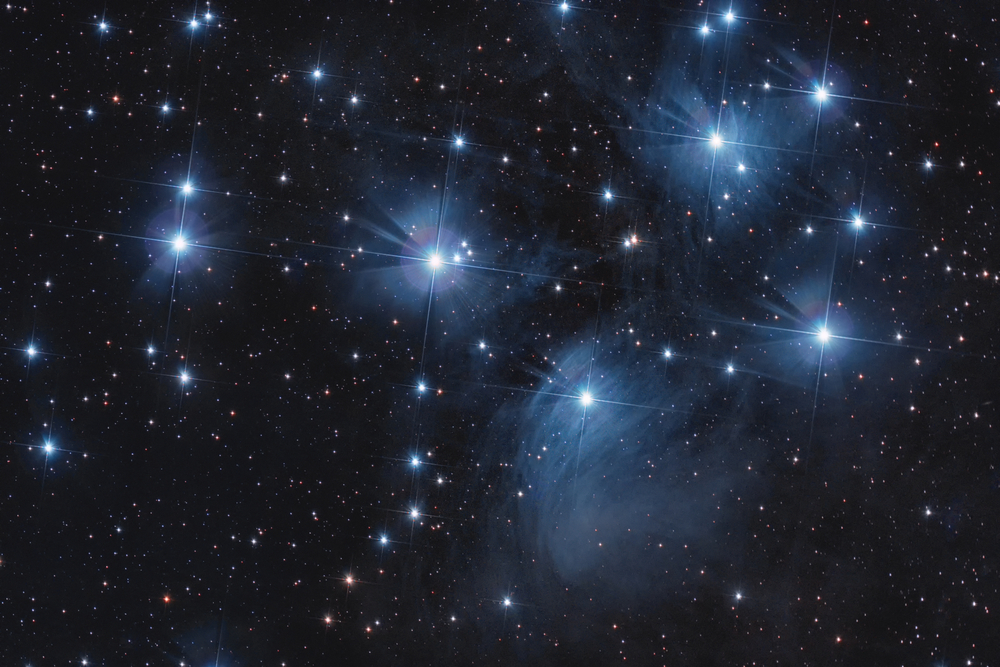

The name ‘Seven Sisters’ comes from the Greek myth. They are the daughters of the sea-nymph Pleione and the titan Atlas. When Atlas was forced to forever hold up the heavens, Orion pursued his daughters. Zeus transformed them doves and then into a cluster of stars in Taurus.
Crab Nebula
The spectacular Crab Nebula, also known as Messier 1, is a fascinating celestial body in Taurus astronomy. It is a plerion, or pulsar wind nebula. This body is a rare supernova emitting radiation from the central region as well as from the expanding shell. This creates an amazing show of light and color. Astronomer John Bevis discovered it in 1731. It was the first astronomical object entered in Messier’s catalog in 1758, and that is why it is called Messier 1. The Crab Nebula has an apparent 8.4 and is about 6,500 light-years away. (7)
Hyades
The Hyades is a Taurus star cluster containing stars that form the V, marking the head of the Bull. It is also known as Melotte 25. The cluster has an apparent magnitude of 0.5. At 153 light-years from Earth, it is the nearest famous Taurus cluster of stars to our solar system. There are hundreds of stars in the cluster, believed to be around 625 million years old. The name comes from the Greek Taurus myth, in which a sisterhood of nymphs that bring rain was changed into a cluster of stars.
Exoplanets in Taurus
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars, other than our star, the sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to our solar system, with the possibility of life.
Gliese 176 b
Gliese 176 b is a red dwarf located in the constellation Taurus, revolving around its star Gliese 176. Its size is about half the mass of our Sun. The planet is made up mostly of rock. Astronomers believe that it has a thick gas atmosphere. Discovery was in 2007 and it lies about 31 light-years away.
Epsilon Tauri b
Epsilon Tauri b is a super-Jupiter exoplanet orbiting its star Epsilon Tauri. It lies about 55 light-years away. Epsilon Tauri is one of the four major stars in the Hyades cluster. It has a mass of 7.6 that of Jupiters. The planet takes 1.6 years to complete one orbit of its star. Scientists announced its discovery in 2006.
K2-25b
Astronomers have recently discovered a new exoplanet, named K2-25b, orbiting a star in the Hyades cluster. Using NSF’s NOIRLab facilities, they reveal that this exoplanet is unusually dense for its size and age. It is a little smaller than Neptune and 25 times the mass of Earth. K2-25b orbits its M-Dwarf star every 3.5 days. It lies 150 light-years away and the star system is thought to be around 600 million years old.
DH Tauri b
DH Tauri b is another interesting exoplanet in the Taurus constellation. It orbits its star, Dh Tauri and takes 10441.5 years to complete one orbit. This gas giant, discovered in 2004, has a mass size of 11 times that of Jupiter and a radius of 2.7 times the size of Jupiter. It is about 457 light-years away.
Meteor showers in Taurus
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as Falling Stars.
The Taurids
Here are some Taurus constellation fun facts. Halloween is a time of celebration and superstition, with eerie pumpkin-face creatures roaming the streets. Add to this a meteor shower in the night skies and the scene is complete! The common name for the Taurids is the Halloween Fireballs, and the shower originates from the Comet Encke.
This shower is very large and spread out and is visible over an extended period of time. It also features a distinct North and South stream. The North stream is best seen between 12 October 1 to 2 December, with the peak being the night of 11 November.
The South stream lasts from 25 September to 25 November, with the peak on 5 November. Expect to see about 5 to 7 meteors per hour. This may not sound like a lot, but because the particles are large, they are exceptionally bright and often have trails of smoke behind them. Meteors travel at speeds of 27km/s.
The Beta Taurids
This is a less spectacular shower that occurs in the daytime from 5 June and to 18 July. The peak is around the end of June. Home stargazers cannot see the meteors because the radiant lies close to the Sun.
The Tunguska event was a massive explosion in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, that happened near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River. It took place on 30 June 1908. The scientific theory is that a meteor from the Beta Taurids hit the Earth.
Location and visibility
Where is Taurus constellation located?
Taurus is one of the more easily identified constellations. You can see many of the bright stars that define the outline of Taurus in the sky with the naked eye.
The bull constellation alpha is the 17th largest constellation occupying an area of 797 square degrees. The Taurus constellation location is in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ1.
A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the Taurus location at latitudes +90° and −65°.
To find where Taurus is located in the sky, you can look for the neighboring Zodiac constellations of Aries the ram, Gemini the twins, and Orion the Hunter. Orion stands in front of the bull Taurus, directly in line with its horns.
Aries stands behind the Bull, facing in the opposite direction. Gemini, the Twins, lies a bit farther away. They stand with their feet facing the horns of the Bull. See the Taurus constellation map to find your way around.
When is Taurus constellation visible?
When is Taurus visible? The Taurus zodiac constellation is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
In the northern hemisphere, Taurus rises in the east and sets in the west. From October to November, it appears low in the sky at around 10.00 pm. From December to January it rises in the north-eastern sky at about 6.00 pm.
From February to March, it appears almost directly overhead at around 7.00 pm, a great time to get the family outdoors for some stargazing.

In the southern hemisphere, you can look for Taurus the bull in December and January lying low on the northeast horizon at about 10.00 pm.
From February to March, it appears in a more northerly direction between 9.00 pm and 10.00 pm and slowly dips below the horizon after 2.00 am.
Remember that in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so the bull constellation will be standing on his head!
How to find Taurus constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
- To locate Taurus, it is easiest to first find the three stars that make up the belt of Orion
- Draw a line through them and extend it upwards to the brightest star in Taurus, Aldebaran, at the eye of the Bull
- Now imagine a V-shape to the left forming the Taurus horns
- There are two bright stars, one at the tip of each horn, Elnath and Zeta Tauri
- Extending a line away from the horns to the right, you get to the bright stars in the Taurus constellation, known as Hyades, on the back of the Bull
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so where is Taurus located?
- To locate the Aldebaran Taurus constellation, it is easiest to first find the three stars that make up the belt of Orion
- Draw a line through them and extend it downwards to the brightest star, Aldebaran, at the eye of the Bull
- Now imagine a V-shape to the right forming the horns
- There are two bright stars, one at the tip of each horn, Elnath and Zeta Tauri
- Extending a line away from the horns to the left, you get to the bright star cluster Hyades, on the back of the Bull
How to view Taurus Constellation?
If you are away from very bright city lights and pollution, you can see the bright stars in Taurus with the naked eye.
Using a powerful pair of binos will give you a better view of the Bull. If you really want to enjoy this constellation, you will need a telescope.
For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous Taurus galaxy images.
Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will last for many years.

The Meade Infinity 102mm Altazimuth Refractor Telescope is ideal for a family who wants to start stargazing as a hobby. It is a well-priced refractor telescope with a 102mm (4″) lens and a focal length of 600mm. The precision Altazimuth mount has slow motion controls allowing you to easily keep your celestial object in view as it moves across the sky.
The telescope comes with 3 eyepieces for low, medium, and high magnification. It has a Red Dot Viewfinder that helps to pinpoint objects. Also included is an Autostar Suite Astronomy planetarium DVD with over 10,000 celestial objects.
History of observation
Who discovered Taurus constellation?
Astronomers often ask – who named Taurus? Taurus is one of the oldest constellations known to skywatchers. It was discovered and documented by many astronomers and stargazers over thousands of years.
The first known records of the Taurus constellation history date back over 15,000 years. Ancient cave drawings on the walls of underground rooms at Lascaux, France, show images of a charging bull.
In ancient Babylonia, around 2300BC, astronomers had identified the Bull and called it “MUL.APIN,” meaning “The Heavenly Bull.” Ancient Taurus history exists in the Greek myths that date back 3000 years.
The Greeks wrote about the Bull in the story of Zeus. Zeus, King of the Gods, turned himself into a white bull to capture his Love, Europa. So that answers the question – why is Taurus a bull!
Taurus was also known to the Persians. The Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi wrote about it in the Book of Fixed Stars in the year 964AD.
So who named Taurus? Many ancient civilizations. In recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Taurus constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Taurus constellation?
Here are some more fascinating Taurus facts.
Taurus star constellations are the oldest of the twelve Zodiac signs. The first images of the bull, found by archaeologists, are drawn by cavemen in underground caves discovered in Lascaux, France.
This cave system dates back over 15,000 years.
Ancient Babylonian astronomers also knew of the bull constellation. They identified it around 2300BC and named it “MUL.APIN,” meaning “The Heavenly Bull.” Greek mythology is the most well known Taurus the bull myth.

The stories date back around 3000 years and tell the story of Zeus, King of the Gods. Zeus turned himself into a white bull to capture his Love, Europa.
Taurus was also known to the Persians. The Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi wrote about it in the Book of Fixed Stars in the year 964AD.
In Chinese astronomy, the age of Taurus goes back to 488CE. The Pleiades star cluster in the constellation was known as Mao and was said to represent a hairy head.
How did Taurus constellation get its name?
Stargazers often ask – how did Taurus get its name? Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology.
The bull is an imposing constellation and is easy to recognize. It closely resembles the head, horns, and front legs of the huge animal charging across the skies.
The Latin word for bull is “Taurus,” and that is the most common derivative of the name. It also has an Indo-European root, “Tauro,” also meaning bull.

Ancient Babylonian astronomers knew of the bull constellation and “MUL.APIN,” meaning “The Heavenly Bull.” Many other cultures have worshipped the bull throughout history.
In the Sumerian religion, the “Bull of Utu” has the name Marduk. In Hinduism, the Taurus origin of the bull is Nandi, a huge Bull ridden by Shiva. The Greek word for bull reads as “távros,” and in Greek, you write it as ταύρος.
Mythology and meaning
Taurus myth
Like many of the constellations, there are many different Taurus mythology stories. In the stories of Greek Gods, the Taurus constellation myth tells the story of Zeus, King of the Gods. When he set his eyes upon the beautiful Europa, he was smitten and made a plan to capture her.
A master of disguise, this time, he chose to transform himself into a bull. He became a magnificent white bull and mingled with her father’s herd. Europa spotted the animal and fell in love.

She climbed onto its back and Zeus charged off, leaping into the sea and taking her to the Island of Crete.
Zeus then revealed himself and proclaimed that she should become his mistress. The story has a happy ending and Europa bore him three sons. Zeus placed the bull in the sky to commemorate his conquest and his happiness.
In the Sumerian myth of Gilgamesh, Orion the Hunter represented a hero who fought a raging bull. They were both placed into the sky, with the bull facing the hunter, ready to charge.
What does Taurus symbolize?
In ancient Greek mythology, the Bull is Zeus, King of the Gods. The Taurus greek god disguised himself as a magnificent white bull in a quest to capture the Love of his life.
Ancient cultures worshipped the bull as a creature of stature, pride, power, and reliability. The bull is brave, fearless, and intelligent. He is dedicated to his plans and won’t give up until he has achieved his goals.
Bulls strive for perfection and become very disappointed in you if you don’t live up to their demanding standards. The bull is also stubborn – beware if you are planning to have a bull as a life partner!

Taurus symbolizes hard work, and people born under this sign make great employees.
The Taurus modality is fixed. This Taurus meaning indicates that people born under this sign tend to be reliable, stable, and persistent.
Another one of the characteristics of Taurus is that they find comfort in stability and prefer to remain in one place that they can call home. The planet Venus rules Taurus and the Taurus god is Sri Mahalakshmi.
Here are some famous Taurus personalities – Queen Elizabeth II, William Shakespeare, David Beckham, Adele, Andy Murray, and Billy Joel.
Future of Taurus constellation
Over millions of years, stars and deep-sky objects change the form, move or even explode. Here is some interesting Taurus information.
Aldebaran, the star at the Taurus eyes, is a star that will explode in the future. It is a red giant, which means that it has depleted most of the hydrogen in its core. At this stage, it is in its second phase of death. It will continue to expand and eventually explode.
After the explosion, the star becomes a white dwarf. A white dwarf has expelled most of its outer shell, creating a planetary nebula. Over millions of years, it will cool down and become smaller. Astronomers are always on the hunt for exoplanets and the existence of possible life.
Recently, scientists using a WIYN 0.9-meter Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory found a new exoplanet named K2-25b.
It orbits its star K2-25 every 3.5 days. This exciting discovery will lead to more knowledge about exoplanets in Taurus, their formation, and whether there are life-sustaining properties on its surface.
Also, with a “limited” lifespan in Taurus, the bull constellations are the stars in the Pleiades star cluster. They were born from a gigantic cloud of gas and dust and are extremely hot. These stars will burn out quickly in astronomy terms, within a few hundred million years. Compare this to our Sun, which will burn for billions of years.