Virgo Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Virgo Constellation
Abbreviation: Vir
Symbolism: The Virgin
R.A. position: 13h
Dec. position: -4°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 117 light-years
Area: 1294 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Spica (α Vir)
Messier objects: Virgo Cluster, Messier 49 (NGC 4472), Messier 58 (NGC 4579)
Meteor Showers: Virginids, Mu Virginids
Bordering Constellations: Leo, Crater, Corvus, Hydra, Libra
Visible at: Latitudes between +80° and −80°
Best viewed: During the month of May at 9.00pm
The Virgo constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as the Virgin. Virgo is one of the oldest known constellations and dates back to Greek Mythology where she is associated with Persephone, the daughter of Demeter, the Harvest Goddess.
Virgo is the largest of the Zodiac constellations and the 2nd largest of all the constellations in the sky. Virgo can be found in the sky by locating the bright star Spica, For a more detailed view, a telescope will give amazing images. For home stargazers, Virgo is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the amazing Virgo Galaxy Cluster and a host of Messier deep-sky objects.
Read on to learn more about the constellation Virgo and interesting Virgo constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
Virgo constellation
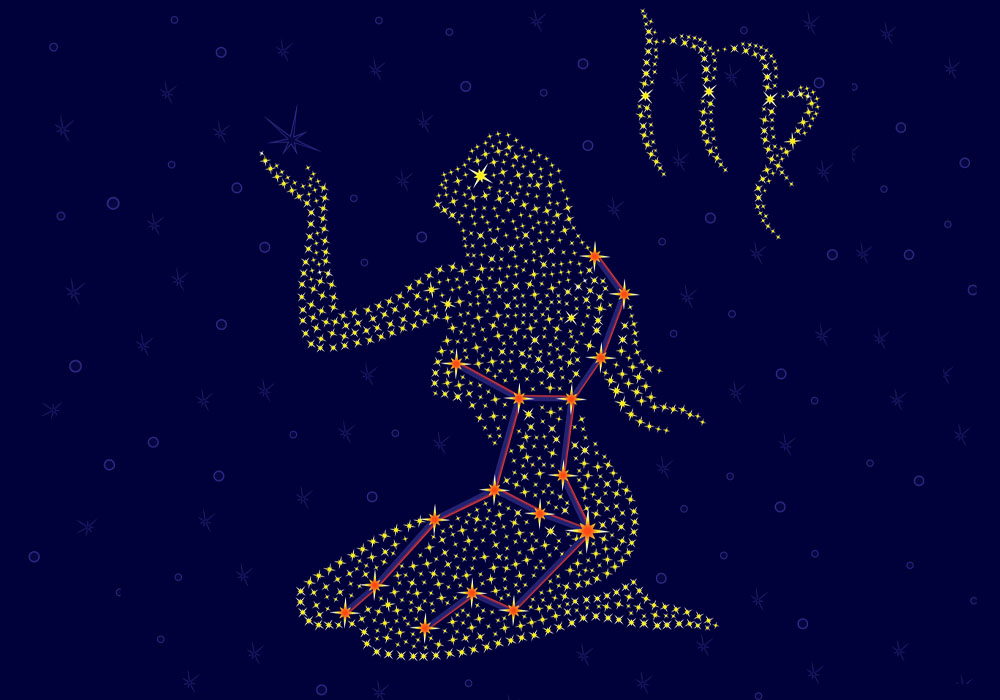
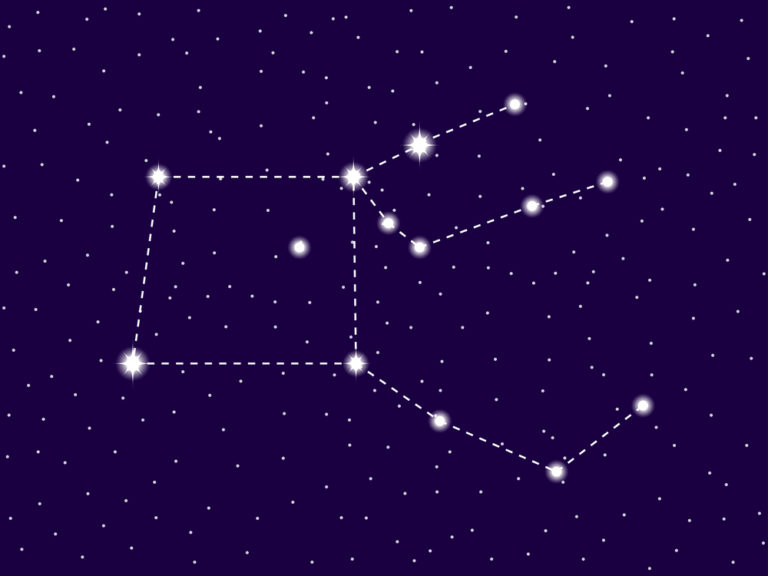
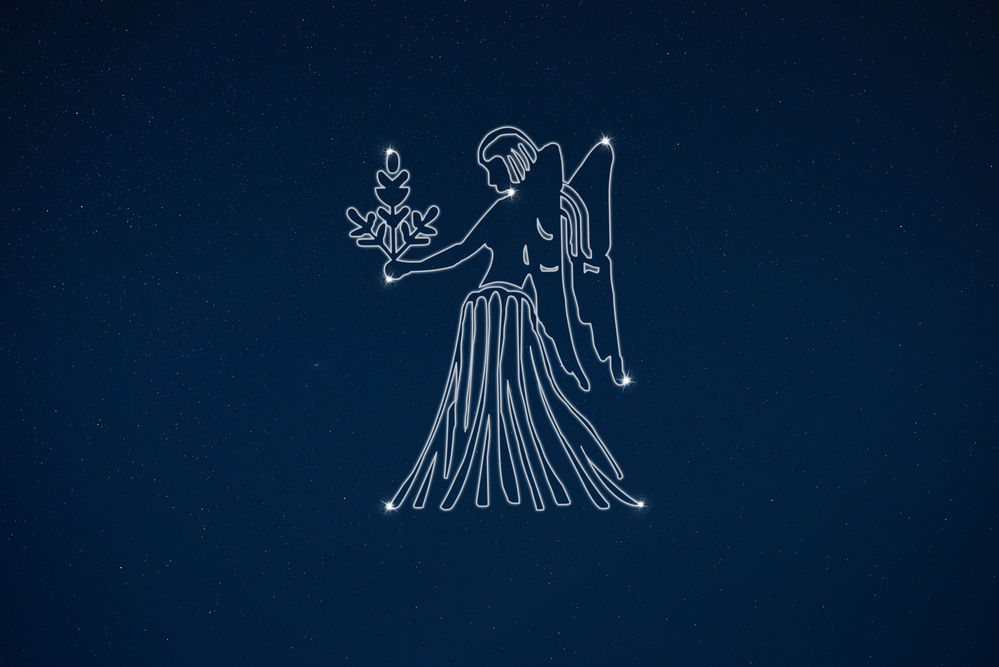
Virgo is a large and distinctive constellation that dominates the sky. The Virgin is a lovely Goddess of Wheat and Agriculture, standing upright with arms slightly outstretched. She holds a long ear of corn in her hand. Perhaps you can even imagine angel wings spread out behind her.
The Virgo (constellation) is the 2nd largest constellation. It occupies an area of 1294 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Leo and Libra. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Boötes, Coma Berenices, Crater, Corvus, Hydra, and Serpens Caput.

For home astronomers, the constellation of Virgo offers many interesting celestial objects. It contains Virgo brightest star, the blue-white giant Spica.
It also offers the binary star Porrima (γ Virginis), named after two goddesses of prophecy, the Carmenae. Inside the constellation is the sensational Virgo Galaxy Cluster, a massive sky region containing hundreds of galaxies and deep-sky objects.
In the case of Virgo, both the constellations Virgo and the Zodiac sign have the same name. The age of Virgo greek mythology dates back over 3000 years (1).
What does Virgo constellation look like?
You may be asking – what does Virgo look like? With many bright stars at strategic points, the Virgin is a constellation that you can draw with your eye in the sky.
The constellation of Virgo looks like a beautiful Goddess standing in the sky. She has a full body, unlike some other constellations that are only partly formed. Her two arms are slightly outstretched.
In her left hand, she holds a long ear of corn, which reaches up almost to her head. She is the Goddess of Wheat and Agriculture and is closely connected to the Earth and things that grow. At her hands are two bright stars. Spica is at the left hand, and Vindemiatrix is at the right hand.
To complete the question – what does the Virgo constellation look like? – you need to see the Virgo the maiden dressed in long flowing robes with flat sandals on her feet.
Many people love to imagine beautiful angel wings on her shoulders, flowing outwards on either side. In the sky, the Virgin stands between Leo the Lion and Libra the Scales, but there is no mythological connection between them in the Virgo story.
How far is Virgo constellation from Earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it looks as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. This is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some may be as close as 60 light-years, and others as far as millions of light-years.
To give some idea, the brightest star in Virgo is Spica which is about 260 light-years away from Earth. Another important star is Porrima, which is close to Earth at only 38.1 light-years away (2) (3).

The beautiful Virgo Cluster in the NASA Virgo constellation lies about 65 million light-years away (4).
Messier 49, also known as NGC 4472 is the brightest galaxy in the Virgo Cluster and is about 55.9 million light-years distant (5).
Other famous Messier objects, like Messier 61, Messier 60, and Messier 59, lie about 50 million to 60 million light-years away.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Virgo constellation from Earth is 117 light-years. If you consider the Messier objects, the distance is around 60 million light-years!
Zodiac family
The Virgo symbol is the sixth sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between August 23 and September 22.
It is one of three Earth signs, the others being Taurus and Capricorn. Virgo is more connected to Earth than the other two Earth signs – in the Virgo myth, she is the Goddess of Agriculture.

The real Virgo star constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Leo the Lion is above her head. Libra the scales lie underneath her feet.
Like all the Zodiac constellations, Virgo the virgin constellation lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year. The Sun passes through Virgo each year from around mid-September to the end of October (6).
One of the most interesting Virgo fun facts is that she is the only female figure out of the 12 Zodiac signs (7).
Virgo does not connect in any direct way to any other Zodiac creature or symbol. She is, however, connected to the King of the Gods, Zeus. In Greek mythology, Zeus was responsible for placing many Zodiac figures into the night sky, including Virgo.
Features
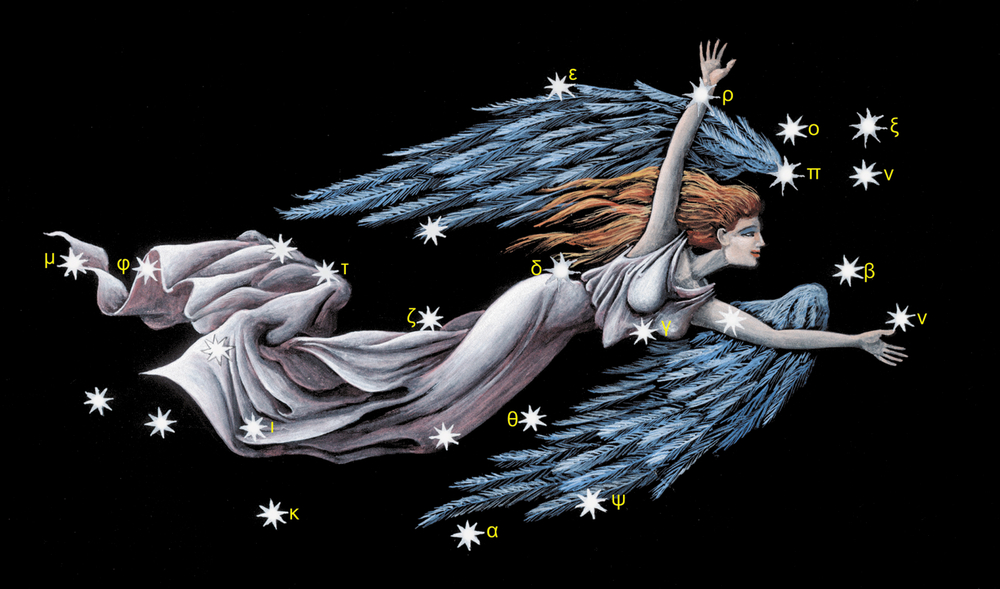
Major stars in Virgo
Here is a list of the major Virgo stars. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in the Virgo constellation? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most interesting stars to look for.
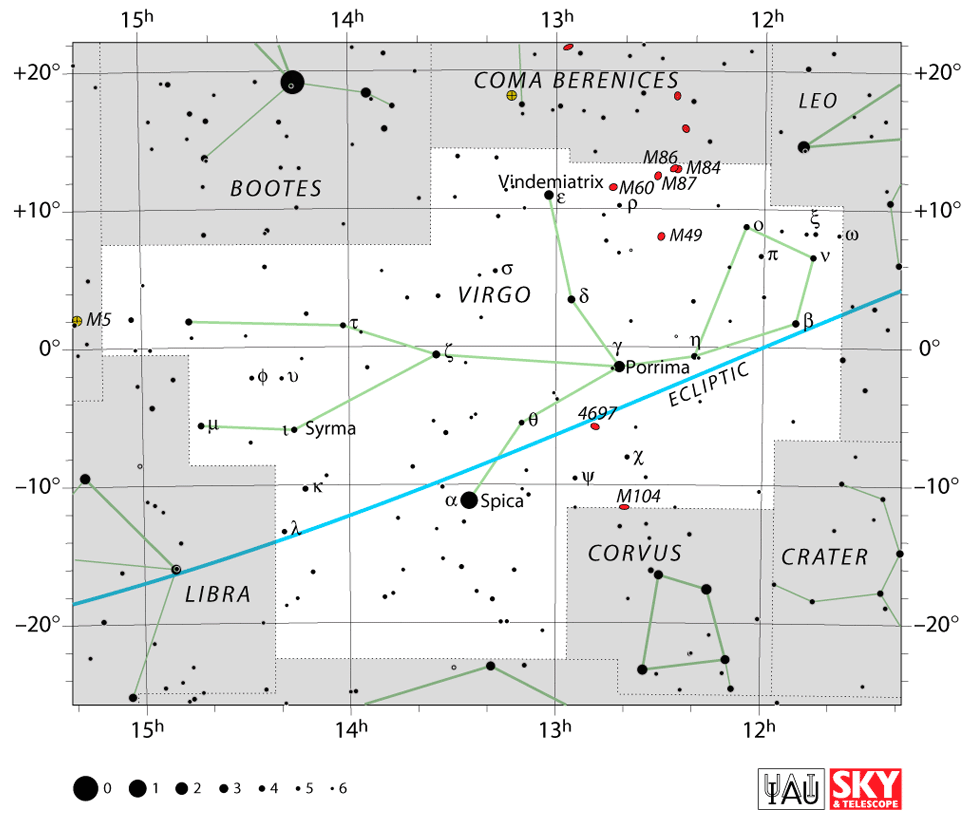
Spica – α Virginis (Alpha Virginis)
Spica is the brightest star in Virgo and the 15th brightest star in the sky. With an apparent magnitude of 1.04, you can see it without a telescope. The name Spica comes from the Latin word ‘spīca virginis’ which translates as “Virgo’s ear of grain.”
Spica is a binary star system, consisting of one very bright star and a dimmer partner. At about 260 light-years away, it is one of the closest large double star systems to our Earth (8).
Zavijava – β Virginis (Beta Virginis)
Beta Virginis, another star of Virgo, is also known as Zavijava. The name comes from the Arabic zāwiyat al-cawwa’, which means “the corner of the barking dog” (9).
It is a pale yellow star at the left-wing of the Virgin. Beta Virginis is the 5th brightest stars in Virgo constellation and lies about 35.65 light-years away from Earth (10).
Porrima – γ Virginis (Gamma Virginis)
On the Virgo star map, Porrima, also known as Gamma Virginis, is a binary star. The two stars orbit one another every 169 years. Both stars are of the spectral type F0V and have similar visual magnitudes of 3.65 and 3.56.
Each star is about twice as big as the sun and lies about 38 light-years away. To the ancient Romans, Porrima was a Virgo goddess of the future and prophecy. Combined with Beta, Eta, Delta, and Epsilon Virginis, the stars form an asterism known as Barker, or Al ʽAwwāʼ (11) (12).
Auva – δ Virginis (Delta Virginis)
Delta Virginis is another interesting star in Virgo. It is an orange-red giant that lies about 198 light-years away. This bright star has an apparent magnitude of 3.4 and you can see it with the naked eye.
It has a radius of 48 times that of our Sun and is about 468 times more luminous. The traditional name of this Virgo star is Auva or Minelauva. It comes from the Arabic ‘cawwa’, which means “barking (dog)” (13).
Vindemiatrix – ε Virginis (Epsilon Virginis)
Vindemiatrix is the 3rd brightest star in the constellation Virgo. It is a yellow giant and lies about 102 light-years away. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.8. Epsilon Virginis is about 11 times bigger than the Sun and 77 times brighter.
The name Vindemiatrix comes from the Latin phrase meaning “the grape harvester” or“the grape gatherer” (14) (15).
Heze – ζ Virginis (Zeta Virginis)
Heze is a blue-white sub-giant Virgo constellation star about 74.08 light-years away. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.376 and you can see it without a telescope. Heze lies in the middle of the Virgin’s body (16) (17).
Zaniah – η Virginis (Eta Virginis)
Eta Virginis is a triple star system in the Virgo star constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 3.890 and you can see it with the naked eye. The system lies about 265 light-years away.
The three stars are so close to one another, that even with a powerful telescope, they appear as one bright star. The 2 inner stars orbit one another every 72 days. The 3rd outer star orbits every 13.1 years. Eta Virginis lies at the neck of the Goddess. The name Zaniah, comes from the Arabic zāwiyah, which means “the corner” (18) (19).
Syrma – ι Virginis (Iota Virginis)
Iota Virginis is about 69.8 light-years away. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.44. The star’s traditional name, Syrma, comes from the Arabic word sirmā, which means “train (of a garment)”. This is one of the Virgo constellation stars that lie at the foot of the robe of the Virgo goddess (20) (21).
Deep-sky objects in Virgo
Virgo Cluster
The amazing Virgo Cluster lies partially in the star constellation Virgo and partially in the Coma Berenices constellation. It is about 53.8 million light-years away. This massive cluster contains around 2,000 galaxies. It also has three clearly identifiable sub-clusters.
The Virgo Cluster has a property called the Virgo-centric flow. Due to its size, it attracts other galaxies in the neighborhood, drawing them into its space. The Virgo Cluster is part of a larger cluster of galaxies that include Local Group, which in turn includes the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way (22).
Messier 49 (M49, NGC 4472)
Messier 49 was the first galaxy discovered in the Virgo Cluster. It is the brightest with a magnitude of 9.4 and lies about 55.9 million light-years away. Charles Messier documented it in February 1771.
M49 contains about 5900 globular clusters which are on average 10 billion years old. M49 is an elliptical galaxy that has little structure, unlike spiral galaxies that have well-defined structures and spiral arms (23).
Messier 58 (M58, NGC 4579)
Messier 58 is a barred spiral galaxy in Virgo. A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. M58 is one of the brightest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster with an apparent magnitude of 10.5. It lies about 62 million light-years away. Charles Messier discovered it in April 1779 (24).
Messier 59 (M59, NGC 4621)
Messier 59 (M59) is an elliptical galaxy with an apparent magnitude of 10.6. It lies about 60 million light-years from Earth. Using a telescope, you can see it between the bright stars Vindemiatrix in Virgo and Denebola in Leo. With a strong scope, you will see that one side of the galaxy is longer than the other. The name for this is an ellipsoidal shape (25).
Messier 60 (M60, NGC 4649)
Messier 60 is another elliptical galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.8 and is about 55 million light-years away. It is the 3rd brightest giant elliptical galaxy in the cluster. Johann Gottfried Koehler discovered it in April 1779. When looking at M60 through a telescope, you will usually see it together with its dimmer neighbor, NGC 4647 (26) (27).
Messier 61 (M61, NGC 4303)
Messier 61 (M61) is another barred spiral galaxy located in Virgo. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.18 and lies at a distance of about 52.5 million light-years from Earth.
Messier 84 (M84, NGC 4374)
Messier 84 is a lenticular galaxy, discovered by Charles Messier in March 1781. M84 has a visual magnitude of 10.1 and is approximately 60 million light-years away.
Messier galaxies M84 and M86 are part of Markarian’s Chain, an amazing stretch of galaxies that lie along a curved line near the heart of the Virgo Cluster. M84 has a disk of fast rotating gas and stars, which may indicate that it has a supermassive black hole at its center (28).
Exoplanets in Virgo
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars, other than our star, the sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to our solar system, with the possibility of life.
Draugr (PSR B1257+12 b)
Draugr is an exoplanet that revolves around its star, PSR B1257+12. The main star is a pulsar located 2,300 light-years from the Sun. Two other exoplanets revolve around this star, Poltergeist (PSR B1257+12 c), and Phobetor (PSR B1257+12 d). Draugar is the lowest-mass planet yet discovered, with a mass less than twice the mass of our moon (29).
61 Vir b
61 Vir b is an exoplanet that revolves around its main star 61 Vir. There are 2 other planets in the system. The main star has a mass of around 98% that of our Sun. 61 Vir B was discovered in 2009 (30) (31).
Gliese 504 b
Gliese 504 b is a purple-brown dwarf orbiting a G-type star known as Gliese 504. Scientists believe the planet is about 4 times Jupiter’s mass. Other properties of the star show that its age is probably several billion years. It was discovered using the s8.2-meter Subaru Telescope of Mauna Kea Observatory, Hawaii. (32) (33).
NY Virginis b
NY Virginis b is an exoplanet revolving around the star NY Virginis. Scientists claim that this body is a giant circumbinary planet orbiting its mother star at a distance of 3.3 astronomical units.
There is also another planet in this system called Y Virginis c, with an even longer orbital period of more than 15 years (34).
Meteor showers in Virgo
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up.
This creates a spectacular show, often known as Falling Stars. The Virgo constellation offers fabulous meteor showers that will delight home stargazers.
The Virginids
The Virginids are a group of meteor showers that originate in the constellation of Virgo. The showers start around 13 February and continue until early May. The showers are named Alpha Virginids, Eta Virginids, Mu Virginids, Pi Virginids, and Theta Virginids.
Their names indicate the nearest star from which they originate and they travel through the sky in different directions. The speed of the meteors is around 19km/s. Expect to see a fabulous show of around 10 or more meteors per hour. The Virginids are best viewed in April (35) (36).
The Mu Virginids
This is a minor stream which is part of the larger Virginids Shower. It originates from the star Rijl al Awwa. The shower peaks on April 24 and April 25. Expect to see about 7 to 10 meteors per hour at speeds of 19km/s (37) (38).
Location and visibility
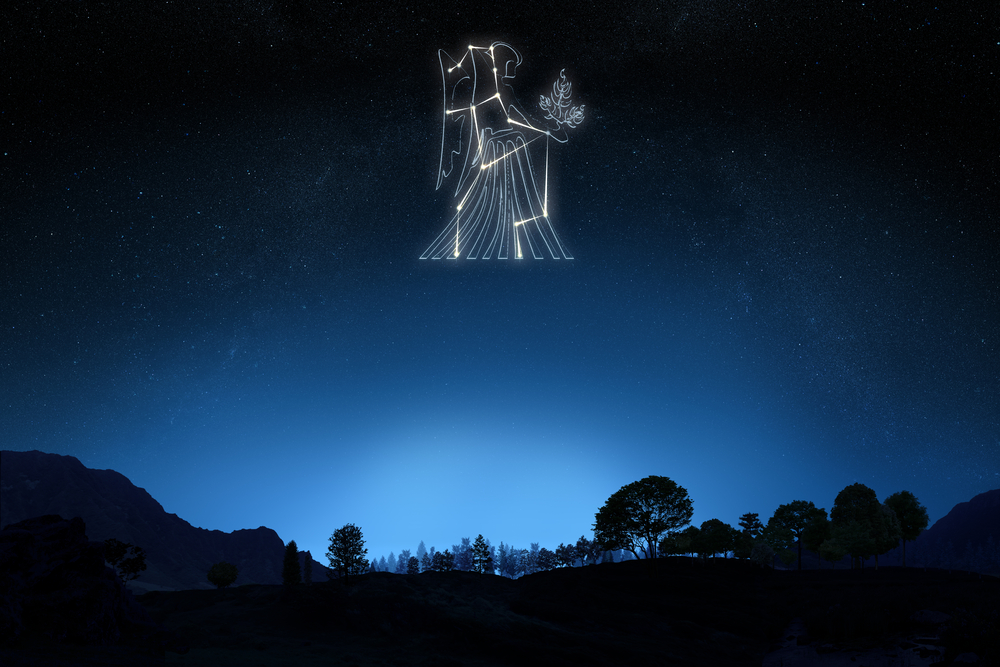
Where is Virgo constellation located?
Virgo is easy to find once you know what to look for. The bright stars can be seen without the need for a telescope and then you can imagine the beautiful Goddess in the sky.
The September constellation is the largest of the zodiac constellations occupying an area of 1294 square degrees.

The Virgo constellation location is in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere, SQ3. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the
Virgo constellation location at latitudes +80° and −80°.
To find Virgo you can locate the two zodiac constellations of Libra the Scales and Leo the Lion. Leo the Lion stands above her head. Libra the Scales lies underneath her feet.
If you are in the Northern Hemisphere and are familiar with the Big Dipper, you can follow a curved line downwards to Arcturus and then to
Spica, the blue-white bright star that indicates the left hand of the Goddess. Use this rhyme to remember – arc to Arcturus and spike Spica! (39).
When is Virgo constellation visible?
Virgo the constellation is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres.

Northern Hemisphere
In the northern hemisphere, in March and April, Virgo appears low on the eastern horizon from about 9.00pm. She slowly moves south towards 1.00am. In May, June and July look towards the southern to western sky at around 10.00pm.
Southern Hemisphere
In the southern hemisphere, in March, Virgo appears at around midnight low on the eastern horizon. The constellation moves north until about 4.00am.
In April the constellation will appear low on the eastern horizon at around 9pm. In May to August look out a bit earlier at 8.00pm and watch her disappear at about midnight. This early time is great to take the kids for some stargazing!
Remember that in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so the Virgo constellation will be standing on her head! (40).
How to find Virgo constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here are 5 steps on how to find Virgo constellation.
- To locate Virgo, it is easiest to first find the Big Dipper in the northern sky
- Using the curve of the handle, imagine a curved line, downwards to the left from the end of the dipper to the bright star Arcturus
- Extend that line to Spica, indicating the left hand
- Straight up above Spica is Vindemiatrix at the right hand
- Now imagine her head above these stars and her flowing robe falling downwards
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down.
- To locate Virgo, it is easiest to first find the Big Dipper in the northern sky
- Using the curve of the handle, imagine a curved line, upwards to the right from the end of the dipper to the bright star Arcturus
- Extend that line to Spica, one of the stars in Virgo, indicating the left hand
- Straight down from Spica is Vindemiatrix, at the right hand
- Now imagine her head below these stars and her flowing robe falling upwards!
How to view Virgo Constellation?
Getting away from city lights and pollution is the best way to see any sky objects. You can see the main stars of the virgin with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make the experience so much more exciting! For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Virgo in the sky.
Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
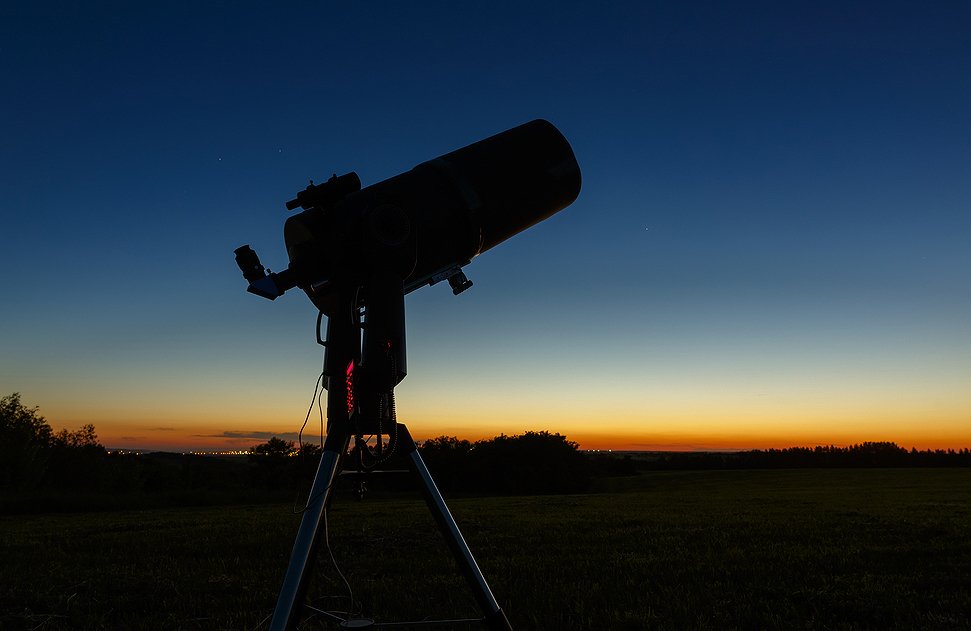

The Orion SkyQuest XT8 Classic Dobsonian Telescope is ideal for beginners who want to grow into experienced stargazers. At around $400 it offers a large 8” aperture for viewing deep space objects. It comes with a sturdy hand-guided Dobsonian base mount that moves horizontally and vertically.
The mount ensures that the telescope is perfectly balanced for easy point-and-view use. Included in the set is a 2″ Crayford focuser that accepts 1.25″ and 2″ telescope eyepieces. Also included is an EZ Finder II reflex sight, a 25mm Sirius Plossl eyepiece, and Starry Night software that you can download.
History of observation
Who discovered Virgo constellation?
The origin of Virgo was documented by many ancient cultures in stories, folklore, and myths over thousands of years.
Greek mythology of Virgo dates back to 3000BC. It tells the story of Persephone who was abducted by the God of the Underworld. The Babylonian astronomers around 2300BC knew the constellation as “The Furrow”, representing the Goddess Shala’s ear of grain.

The Romans at the height of the Roman Empire, 27 BC to 476 AD, knew Virgo as their Goddess Ceres. In this Virgo constellation myth, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, and fertility.
During the Middle Ages, around the 5th to the 14th century, the church associated the meaning of Virgo with the Virgin Mary.
In ancient Chinese Astronomy, we also find Virgo constellation history.
Virgo falls into the Second Enclosure, known as the Supreme Palace Enclosure. Also in this enclosure are the constellations of Leo, and sections of Ursa Major and Coma Berenices.
In recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Virgo constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD (41) (42) (43).
How old is Virgo constellation?
Virgo is an ancient constellation that dates back to the age of Greek Mythology around 3000BC. The Virgo constellation myths tell of Persephone, who was abducted by the Virgo greek god of the Underworld.
Ancient Babylonian astronomers also knew of the virgin constellation. The Virgo origin dates back to around 2300BC and she is known as the Goddess Shala.

Virgo history was also documented by the Romans at the height of the Roman Empire, 27 BC to 476 AD. She was known as the Goddess Ceres, who ruled over agriculture, grain, crops, and fertility.
In Chinese astronomy, during the Ming Dynasty, between 70 BC and 50 BCE, the celestial globe was defined and included the Enclosures. The Second Enclosure includes Virgo. Most ancient cultures saw the Virgo legend as a symbol of harvest and agriculture (44) (45) (46) (47).
How did the Virgo constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore or mythology. So, what does Virgo mean? Most ancient cultures see Virgo as a Goddess linked to the Earth. She represents harvests, fertility, grain, and crops.
She stands in the sky, with an ear of corn in her hand. In the myth, Persephone has to live underground for half the year, and she is only seen at the end of summer and into fall. The word Virgo in virgin etymology comes from Latin and the Virgo meaning is ‘Virgin’.

Some cultures preferred the word ‘Maiden; to describe the female Goddess. In Greek, the word Virgo is Παρθένος, read as Parthénos.
Kleins Comprehensive Etymological Dictionary of the English Language explains the Virgo etymology. The word Virgo is probably related to virga, ‘a young shoot, or twig. It also relates to virgate, meaning ‘shaped like a wand or rod’.
The word virgate from Latin Virgo was an old English land measure, “used also in the sense of measuring rod, a measure of length” (48) (49).
Mythology and meaning
Virgo myth
Like many of the constellations, there are different Virgo mythology stories. The most well-known is the story of Persephone, daughter of Demeter, the harvest goddess.
In this Virgo constellation story, the world had eternal spring. One fateful day, Hades God of the Underworld, abducted Persephone and carried her away into the dark underground. Demeter was so overwhelmed with grief that she gave up her role as the goddess of fruitfulness and fertility and winter was the only season.

Zeus, King of the Gods, intervened. He insisted that Hades send Persephone home. There was a condition – Persephone could not eat until her return. Hades gave Persephone a pomegranate, hoping he could tempt her to eat it, which she did.
Zeus then decided that Persephone would have to return to the underworld for part of the year. Virgo symbolism shows that during those months, it is winter. When she returns to Earth, spring arrives, and crops flourish.
In another myth of Virgo, she is Erigone, the daughter of Icarius, who hanged herself after her father’s death and was placed in the sky (50).
What does Virgo symbolize?
What does Virgo represent? Virgo symbolizes life, crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She brings life to the planet and allows crops to grow. When she is away, winter comes and life dies.
The Virgo modality is mutable. This Virgo symbol meaning indicates that people born under this sign tend to be cheerful, loyal, and passionate. They bring life into a room and uplift the mood.

Virgos are known for their intellectual abilities, their practicality, and smart analytical abilities. Born under the Virgo symbol, they are great healers, wanting to repair and fix everything from inanimate objects to people.
They are usually gentle people. Their biggest weakness is their disconnect with the emotional side of life and a tendency to underestimate their self-worth.
Many people ask – what planet is Virgo? Mercury is the Virgo planet and rules this sign.
Here are some famous Virgo personalities – Queen Elizabeth I, Sophia Loren, Michael Jackson, Mother Teresa, and Cameron Diaz (51).
Future of Virgo constellation
Over millions of years, stars and deep-sky objects change the form, move or even explode. Here are some interesting Virgo facts.
The Virgo Cluster thrills astronomers because it is still forming. It has a mass of approximately 100,000 billion that of our sun.
The cluster contains around 2,000 galaxies. The irregular distribution of the X-ray halo of the cluster indicates that sub-clusters are still in the process of creation.

Scientists studying Virgo astronomy, tell us that because the Virgo Cluster is so big, its energy draws nearby objects towards it. This is known as the Virgo-centric flow. The Local Group, a nearby cluster is currently moving away from the Virgo Cluster. But, because of this immense pull, it will eventually slow down, change direction and merge into the Virgo Cluster (52).
Another fascinating object to watch in the Virgo galaxy is Messier 90, known as M90. In the universe, most galaxies move away from us. But, observations have shown that M90 is in fact getting closer.
This phenomenon is known as ‘blueshift’. By measuring light frequencies, scientists determine that galaxies that are receding show a ‘redshift’. In the future of Virgo, M90 will move closer to Earth for more amazing observation (53).