Draco Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Draco Constellation
Abbreviation: Dra
Symbolism: The Dragon
R.A. position: 17h
Dec. position: +65°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 168 light-years
Area: 1083 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Eltanin (γ Dra)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −15°
Best viewed: During the month of July 9.00pm
The Draco constellation is the 8th largest in the sky. It is also known as the Dragon. It is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek times and is associated with a mythical dragon, Ladon, who guarded the Golden Apple Tree in the Garden of the Hesperides.
Draco can be found in the sky in a twisted shape between the two bears, Ursa Major and Ursa Minor. Draco is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the spectacular Tadpole Galaxy.
Read on to learn more about Draco the dragon story and the Draco constellation.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
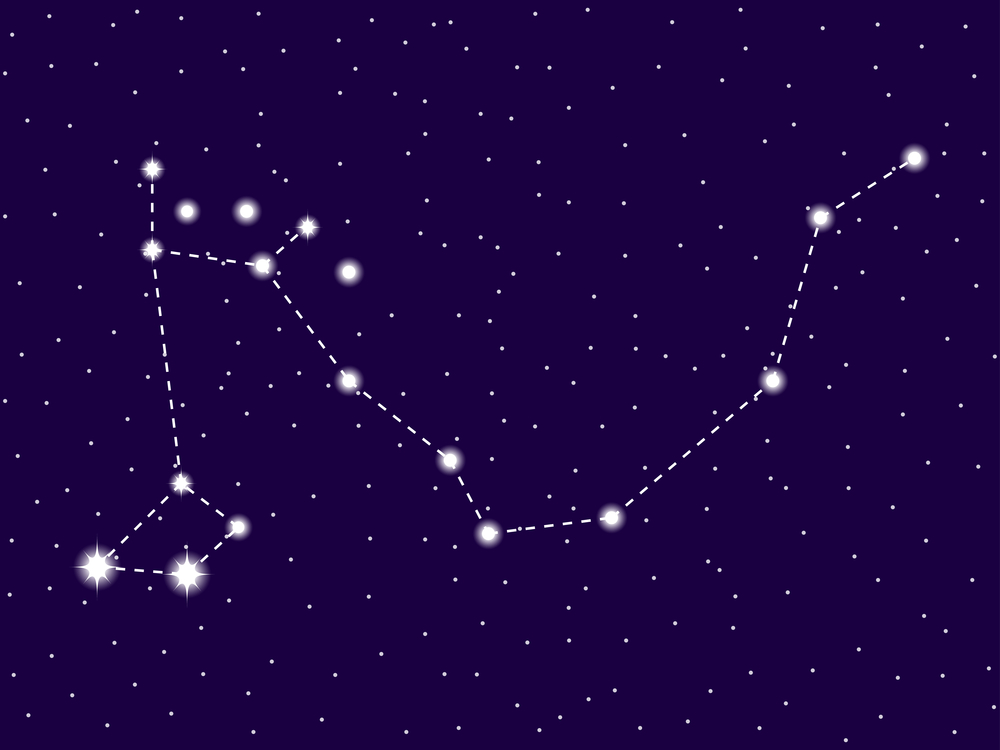
Draco constellation
Draco is a large constellation located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It has many bright stars with fascinating names like Thuban, Eltanin, and Aldibain.
The story of Draco comes from the Greek myth of a massive dragon who was tasked by Hera to guard her Golden Apple Tree in the Garden of Hesperides.

While he was guarding the Tree, the warrior Heracles killed him with a poisoned arrow and flung him into the sky, near to the Celestial north pole. Because he is so close to the pole, he can only be seen in the northern hemisphere.
The Draco (constellation) occupies an area of 1083 square degrees. Draco is an area of the sky that does not contain any of the Zodiac constellations. He lies near Boötes, Hercules, Lyra, Cygnus, Ursa Minor, and Ursa Major.
For home astronomers, the Draco system has many fascinating Draco constellation facts. It contains the amazing Spindle Galaxy and the beautiful Cat’s Eye Galaxy – a must-see for feline lovers.
There is no Draco zodiac sign, as Draco is not one of the 12 zodiac symbols. The Draco symbol is a huge, twisted dragon in the sky. The mythology of Draco dates back over 3000 years (1).
What does Draco constellation look like?
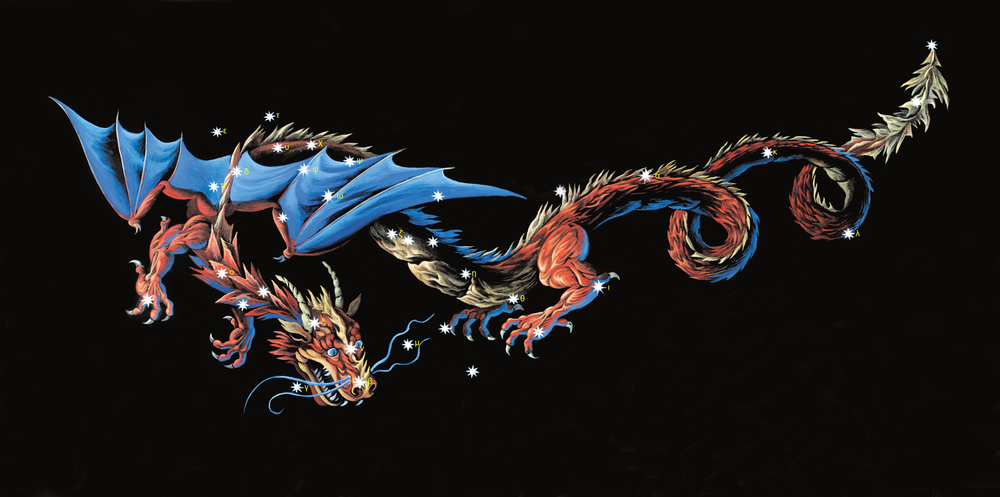
Draco is a huge dragon in the sky. He is frozen in time, lying near the icy north pole. He represents power and magic. He can be a friend or a foe.
In the sky, the constellation Draco is a huge snake-like dragon. He circles endlessly around the celestial north pole. A prominent pattern of stars, known as an asterism, defines the head of the dragon.
Two bright stars mark his eyes. A third star marks his fiery mouth from which the Draconids meteor shower throws out burning flames.
In the Draco constellation story, his head faces Heracles, the warrior who killed him. His body is a long, curved shape, forming a semi-circle, looping between and around the small and large bears.
Imagine an imposing creature, breathing out fire in anger and ready to destroy all around him! If you go even further, add wings and create a mystical creature that brings magic with him. To complete the Draco story, color his body in green and his forked tongue in a fiery red.
How far is Draco constellation from earth?
When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. In reality, this is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some stars may be as close as 40 light-years. Deep-sky objects may be as far as 80 million light-years away.
To give some idea – Thuban in the dragon constellation lies about 303 light-years away. Eltanin is 154 light-years distant. Aldibain lies about 92.1 light-years away. Altais, the yellow giant star is 97.4 light-years away from Earth.

Iota Draconis is about 101.2 light-years away. Aldhibah, also known as Zeta Draconis, lies 330 light-years away. Chi Draconis is a star system in the Draco galaxy that is relatively close to Earth at only 26.3 light-years.
Much further away is the spectacular Cat’s Eye Nebula, about 3300 light-years. The Spindle Galaxy lies 50 million light-years distant. Q1634+706 is roughly 12.9 billion light-years away from our Solar System.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the Draco constellation from Earth is about 168 light-years. If you consider the deep-sky galaxies, the distance is millions and billions of light-years!
Features
Major stars in Draco
Here is a list of the major stars in Draco. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in Draco? There are thousands! Read on to learn all about Draco stars.
The name Thuban comes from the Arabic word thuʿbān, meaning a large snake. The Draco star Thuban lies at the lower end of the twisted dragon’s body. Thuban is a white giant with an apparent magnitude of 3.64.
You can see it without using a telescope. It is about 303 light-years away from Earth and is 250 times more luminous than our Sun. Alpha Draconis is a double star, with a red dwarf companion.
The two-orbit one another every 51 days. Thuban is one of the stars that was a North Star during the Earth’s precession cycle. This occurred from 3942 BCE to 1793 BCE, when some of ancient Egypt’s pyramids were built (3).
Rastaban – β Draconis (Beta Draconis)
Rastaban, also known as Beta Draconis, the third brightest star in drago the dragon constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.79, which is bright and you can see it with the naked eye.
Rastaban marks the left eye of the Dragon. The star lies 380 light-years away. It has a radius 40 times that of the Sun and is 950 times more luminous.
The traditional name comes from the Arabic ra’s ath-thu’ban, meaning “the head of the serpent”. This star in Draco is about 67 million years old. Beta Draconis is a binary star with a dwarf star companion.
Aldibain – η Draconis (Eta Draconis)
Eta Draconis is the second brightest star in Draco. It is a yellow giant and has a companion main-sequence star. The two-orbit one another in a time period of at least a millennium.
Aldibain has an apparent magnitude of 2.73 and lies about 92.1 light-years away from the Solar System.
Its estimated age is about 550 million years and it is 60 times more luminous than the Sun. Eta Draconis, together with Zeta Draconis, is a Draconian star system that gets their names from the Arabic name al-dhiʼbayn, meaning the (two) wolves.
Eltanin – γ Draconis (Gamma Draconis)
Eltanin, also known as Gamma Draconis, is the brightest star in Draco. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.36 and lies 154 light-years away from the Solar System. The name comes from the Arabic At-Tinnin, which means “the great serpent”.
The star marks the right eye of the Dragon. Eltanin has a surface temperature of about half of our Sun’s at 3930 K. In the British Isles, Eltanin is the zenith star, as it lies almost exactly in the zenith when observed from Greenwich.
Gamma Draconis in the red dragon constellation has a companion star with a faint magnitude of 13.4 and is thought to be a red dwarf (2).
Altais – δ Draconis (Delta Draconis)
Altais, also known as Delta Draconis is a yellow giant star with an apparent magnitude of 3.07. You can see it without using a telescope. It lies about 97.4 light-years away from Earth.
The star is 59 times more luminous than the Sun and is thought to be about 800 million years old. The name comes from the Arabic Al Tāis, which means “the goat”. Altais lies on the body of Draco the dragon, just before the major loop that turns back on itself (4).
Aldhibah – ζ Draconis (Zeta Draconis)
Zeta Draconis is the fifth brightest Draconis star. It is a blue giant star with an apparent magnitude of 3.17. The star lies 330 light-years away from the Solar System. The name, Aldhibah, comes from the Arabic word which means “the hyenas”.
It is also sometimes known as Nodus, the 3rd Knot, referring to a loop in the Dragon’s tail. Zeta Draconis is 2.5 times larger than our Sun and 148 times more luminous (5).
Edasich – ι Draconis (Iota Draconis)
Iota Draconis is an important yellow-white double stars in Draco constellation. It lies about 101.2 light-years away from Earth. It has a visual magnitude of 3.29 and you can see it with the naked eye.
Edasich is famous! It was the first giant star discovered to have a planet that orbits it. The planet discovery was in 2002. Edasich has a radius 12 times that of our Sun and is 55 times more luminous. It lies on the body of the dragon, between the Draco star names Thuban and Aldhibain.
Batentaban Borealis – χ Draconis (Chi Draconis)
Chi Draconi is a star system that lies relatively close to Earth at only 26.3 light-years. It is a double star system comprising a yellow-white giant and an orange star. The combined magnitude of the system is 3.57.
The stars orbit one another with a period of 280.55 days. Chi Draconis lies in the middle of the dragon’s body.
The name Batentaban comes from Arabic for ‘belly of the serpent’, This star is one of two dragon stars that represent the belly. The other, called Batentaban Australis, lies close to the south of Batentaban Borealis (6).
Batentaban Australis – φ Draconis (Phi Draconis)
Batentaban Australis and Batentaban Borealis lie at the belly of the Dragon. Also known as Phi Draconis, this Draco star lies about 300 light-years distant. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.20.
Like many of the stars in Draco, you cannot see it in the southern latitudes. Phi Draconis is a multiple star composed of hydrogen fusing dwarfs. They orbit one another for a period of 307.8 years (7).
Deep-sky objects in Draco
Cat’s Eye Nebula – NGC 6543 (Caldwell 6)
The spectacular Cat’s Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula that lies about 3300 light-years away from Earth. It has a visual magnitude of 9.8 and you can see it using a telescope. A planetary nebula forms when Sun-like stars eject their outer layers of gas. This forms a bright nebula with amazing twisting shapes.
Observations suggest the dragon star that created the Cat’s Eye Nebula ejected its mass in pulses, 1500 years apart. The central star of the Cat’s Eye Nebula is about 10,000 times more luminous than our Sun. William Herschel discovered the nebula in 1786 (8).
Spindle Galaxy – Messier 102 – NGC 5866
The amazing Spindle Galaxy in Draco the constellation is a spiral or lenticular galaxy. Either Pierre Méchain, a colleague of Charles Messier discovered it in 1781. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.7 and is about 50 million light-years distant.
You can see this amazing big Draco sight with a home telescope and is best observed in July. The Spindle Galaxy is part of the NGC 5866 group. As the image shows, the galaxy has a massive disk of dust, seen here edge-on (9).
Draco Dwarf Galaxy
The Draco Dwarf Galaxy is a spheroidal galaxy. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.9 and you can see it with a home telescope. It lies about 260,000 light-years away from earth.
Draco Dwarf Galaxy is part of the Local Group and is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. American astronomer Albert George Wilson discovered it in 1954.
It has a mass of about a hundredth that of the Milky Way, which makes it a fairly large dwarf galaxy. Scientists believe that the galaxy contains large amounts of dark matter (10).
Abell 2218
Abell 2218 is a galaxy cluster that lies about 2.345 million light-years away. It contains thousands of galaxies. In the photo, scientists isolate stars of different ages, distances, and temperatures.
Blue indicates hot young stars. The yellow-white color represents the combined light of many stars. Red identifies cool stars and old stars, and the glow of stars in distant galaxies.
The cluster is so large that its gravitational field deflects light rays that pass through it. This simulates an optical lens, bending light to form an image. This phenomenon is gravitational lensing.
In effect, the entire galaxy is a huge “zoom lens” that scientists can use to view distant galaxies. These distant galaxies can not currently be viewed, even with the largest telescopes (11).
Tadpole Galaxy – Arp 188
The Tadpole Galaxy gets its name from the distinctive shape that looks like a swimming tadpole. It is a disrupted or collided barred spiral galaxy. With a faint visual magnitude of 14.4, you need a telescope to view it.
The Tadpole Galaxy lies about 400 million light-years away. It contains a large number of massive, bright blue stars and is known for its enormous trail of stars, which is about 280 thousand light-years long (12).
Q1634+706
Q1634+706 is a quasar in the Draco constellation. A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus. It has a supermassive black hole with a mass a billion times that of the Sun. The black hole is surrounded by a gaseous disk. Q1634+706 has an apparent magnitude of 14.4 and is about 12.9 billion light-years away.
NGC 5879
NGC 5879 is a spiral galaxy, part of the NGC 5866 Group. The NGC 5866 group is thought to have been first seen by Pierre Méchain in March 1781, or by Charles Messier shortly after that time.
The discovery of NGC 5879 was in 1788 by William Herschel. With an apparent magnitude of 12.4, you will need a telescope to view this amazing sight. NGC 5879 lies just below the loop in the tail of the dragon (13).
NGC 4319 and Markarian 205
NGC 4319 is a barred spiral galaxy with a visual magnitude of 12.8. It lies about 92 million light-years away from our Solar System. Markarian 205 is a quasar that is believed to lie in the vicinity of the galaxy.
Markarian 205 is about 1.2 billion light-years from Earth. In 1971, a luminous bridge was discovered between the two objects. But, NASA disputed the existence of the bridge in 2002. This bridge is a source of debate between astronomers. Using the redshift theory, if a bridge does exist, then the distance between the two objects would be much closer (14).
Exoplanets in Draco
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life. The Draco dragon constellation has a large number of exoplanets – 97 in total so far! (15).
HIP 75458 – Iota Draconis
Iota Draconis is a yellow-white double that lies about 101.2 light-years away from Earth. It has one planet in its orbit, known as HIP 75458 b. this planet is notable in that it is the first planet discovered that orbits a giant star. This discovery was in 2002. the planet orbits its mother star every 510 days (16).
HD 113337
HD 113337 is a yellow-white main-sequence star. It has 2 exoplanets orbiting around it. HD 113337 b has an orbital period of 324 days. Its mass is 2.83 Jupiters. Its discovery was in 2013. the second exoplanet has an orbital period of about 9 years (17).
Kepler-230
Kepler-230 is a G-type star with a radius of 0.82 times that of the Sun. it has 2 exoplanets revolving around it. Kepler-230 b is a Neptune-like exoplanet, with a mass of 16.8 Earths. It takes 32.6 days to complete one orbit of its star. Kepler-230 b is a Neptune-like exoplanet that orbits its mother star every 32.6 days. It has a mass of is 16.8 Earths (18).
Kepler-920
Kepler-920 is a G-type star, 3020 light-years away from earth. It has 2 exoplanets orbiting it. The first is Kepler-920, a Neptune-like exoplanet with a mass of 6.44 Earths.
It takes 6.5 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was in 2016. Kepler-920 c is a Neptune-like exoplanet with a mass of 13.8 Earths. It takes 100.8 days to complete one orbit of its star. Its discovery was in 2016 (19).
Meteor showers in Draco
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars.
The Draconids
The meteor shower occurs between 6 October and 10 October with a peak on 8 October. This is a spectacular shower to observe in the northern hemisphere – a huge dragon spitting out fireballs!
In the southern hemisphere, Draco the constellation is difficult to see, as it barely rises above the horizon, so your chance of spotting shooting stars is very low. In the northern regions, expect to see about 5 meteors per hour in the early evening, traveling at speeds of 21km/s.
The comet linked to the Draconids is the Giacobini-Zinner comet. In years where the Earth passes closest to the debris of the comet, thousands of meteors can be seen. The Draconid meteor shower produced amazing displays in 1933 and 1946, and observers saw over 600 meteors per hour in 2011 (20).
The radiant of the shower is the point from where it originates. The Draconids appear to radiate outwards from the fiery mouth of the Dragon. The two brightest stars in Draco, Eltanin, and Rastaban are the eyes of the dragon and are close to the radiant point of the Draconids.
The February eta Draconids
This is a minor shower that occurs between 3 February and 5 February, with the peak on 4 February. Expect to see 2 meteors per hour traveling at speeds of 35km/s (21).
Location and visibility
Where is Draco constellation located?
The Draconis constellation is a large constellation with many bright stars, and you can easily spot it without a telescope. Then, you can imagine the mythical dragon, with a twisted snake-like shape, winding his way across the heavens.
Where is Draco in the sky? Draco is a northern constellation and is the 8th largest constellation in the 88 named constellations. It occupies an area of 1083 square degrees.

Draco lies in the third quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ3. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes between +90° and −15°.
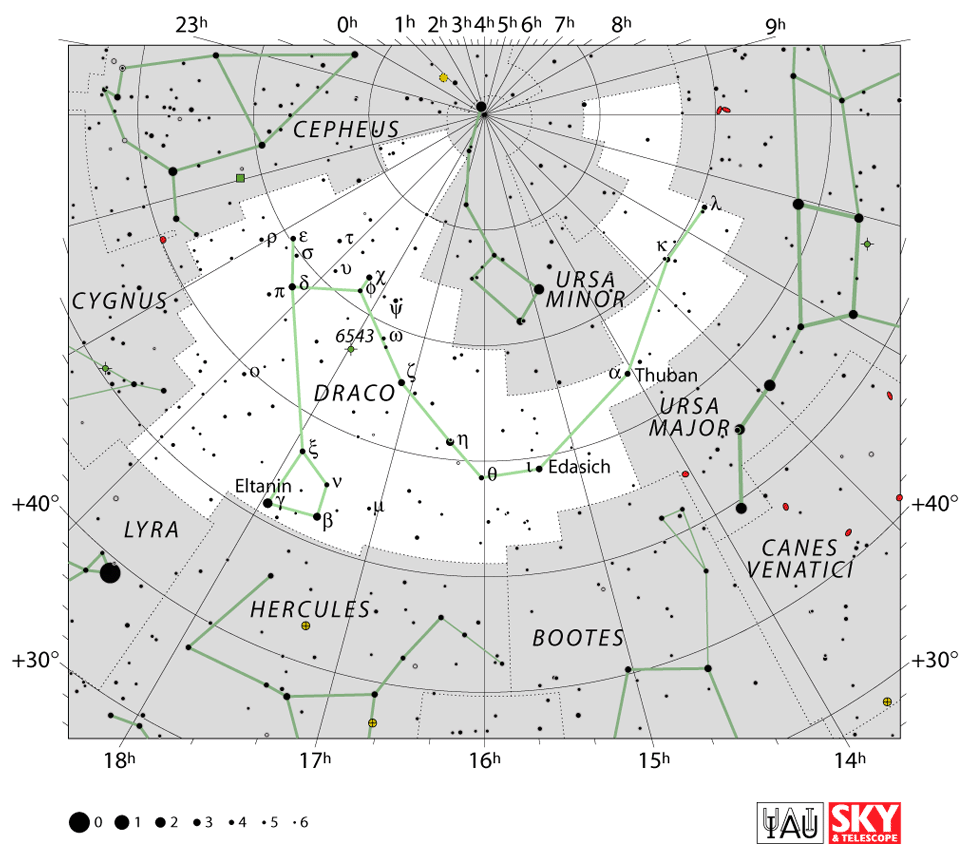
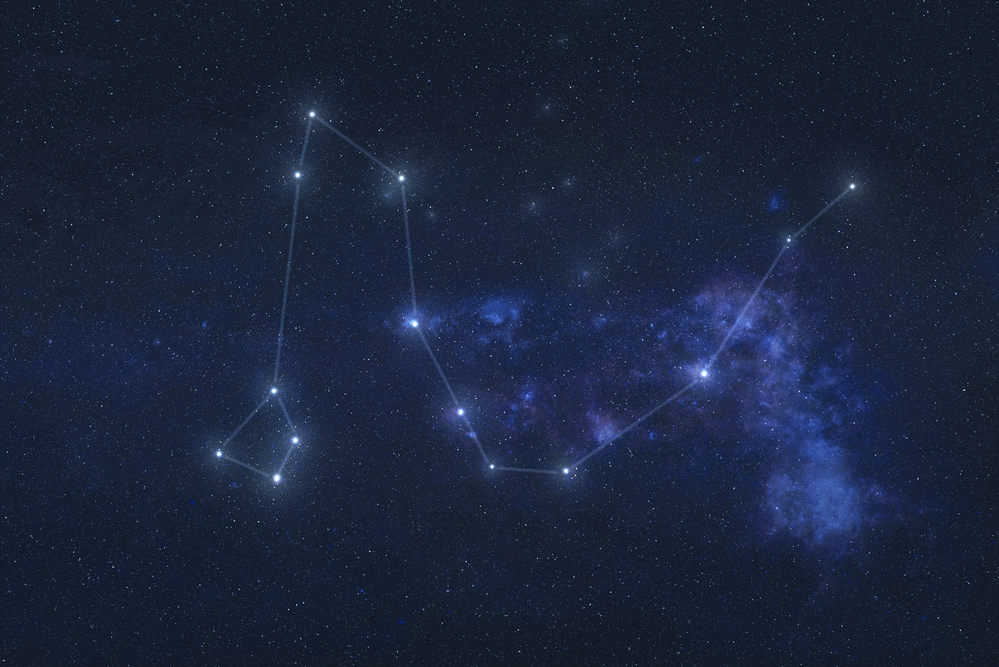
To find the Draco (constellation) location, you can locate the two Dipper star patterns, or asterisms, known as the Big Dipper and the Small Dipper. They lie in the constellations of Ursa Major and Ursa Minor. The twisted body of Draco, winds its way between these two constellations.
Another tip to find the head of the red dragon constellation is to locate Hercules the Kneeling Giant Warrior. The two bright stars, Rastaban and Elatin, are the eyes of the Dragon, glaring directly at the warrior (22).
When is Draco constellation visible?
As a home stargazer, you may ask – when is Draco visible? Here is one of the fascinating Draco constellation facts – the Dragon is only fully visible in the northern hemisphere!
In the southern hemisphere, you will only see a small part of the dragon, very low on the horizon. In the northern regions the constellation Draco never sets below the horizon, so you can see it all year round.

From January to March the dragon first appears low on the horizon in a northerly direction at about 6pm. This is a great time to take the kids out for some amazing stargazing. In April, May, and June, Draco appears in a more north-easterly position at about 9pm. At 2am, he is directly overhead and then sinks down towards the northwest horizon.
In July, August, and September, the constellation is visible directly overhead at about 10pm. From October to December, drako the dragon appears high in the sky in the northwest at about 6pm and moves overhead at about midnight. A great time to plan a romantic midnight feast and experience some dragon magic.
In the southern hemisphere, the dragon constellations are only partly visible in the months of July, August, and September. Look very low on the northern horizon at around 7pm. You may spot a part of the twisted body before he vanishes at midnight.
How to find Draco constellation?
Draco constellation with his head facing Heracles and his body winding between Ursa Minor and Ursa Major
Northern Hemisphere
Here are 11 steps to find the Draco constellation location.
- To find the Draco location, it is easiest to first find the Little Dipper
- The Little dipper resembles a ladle with the bright star Polaris at the tip of the handle
- Now locate a similar shape to the north, which is the Big Dipper
- The tail of Draco winds between the two Dippers, arching over the Little Dipper is a semi-circle
- Imagine the tail turning upwards at a point to the right, in line with the star Polaris
- Now look upwards and find three bright stars forming a small triangle
- This is the head of the dragon!
- You can also find Hercules, also known as Heracles, the Kneeling Giant Warrior
- Locate Hercules by finding the stars Arcturus in the constellation Boötis, and Vega in the constellation Lyra
- Hercules stands between these two constellations, directly in front of the Dragon’s head
- Imagine him ready to slay Draco with a poisoned bow and arrow
Southern Hemisphere
If you live in the Southern Hemisphere, you may ask – how to find the Draco constellation? You will find it difficult to spot the star dragon!
That is because he lies close to the Celestial North Pole and circles endlessly around it.
He only dips very slightly onto your horizon, and only a small part of his twisted body may show. You will have to plan a stargazing vacation with the family to see the Draco star system.
How to view Draco Constellation?
Draco is the 8th largest constellation in the sky. It has bright stars that are easy to spot in dark skies. By locating these stars, you can imagine the twisted dragon Draco circling in the skies.
Like all stargazing experiences, getting away from city lights is the best way to see constellations and deep-sky objects. You can see the Drago constellation with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make it so much more exciting. For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Draco in the sky.

Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Celestron NexStar 130SLT Computerized Telescope offers an affordable, small but powerful option for intermediate stargazers. It has a computerized mount that automatically tracks your celestial object as it moves across the sky.
The scope comes with 2 eyepieces, a 25mm, and a 9mm. You can advance the mount with 9 slew speeds, SkyAlign, Auto 2-Star Align, 1-Star Align, 2-Star Align, and Solar System Align. Just pick an object and it aligns for you. It features a 3.54” aperture that gives amazing views of the dragon in the sky.
The scope weighs only 12 lbs and is great to take along on a family outing for stargazing. The design is very impressive – it totally eliminates cord-wrap issues. The ergonomic hand control allows you to remove it from the holder for remote use or leave it cradled for hands-free operation.
History of observation
Who discovered Draco constellation?
Draco constellation history dates back to ancient civilizations of the Greeks, Romans, Egyptians, and Arabians, and was documented in stories, folklore, and myths.
The greek Draco dates as far back as 3000BC. It associates with the Dragon Ladon, who was tasked with guarding the Golden Apple Tree in the Garden of the Hesperides.

The tree was placed into the Garden by Hera, who received it as a gift from Gaia. The warrior Heracles killed the dragon with a poisoned arrow.
In Islamic astronomy, in the story of Draco constellation, the dragon appears in the Book on the Constellations of the Fixed Stars. It was written by Al Sufi a Persian astronomer during the 10th century (23).
The Draco stars also feature in Chinese astronomy dating back to 750BC. The constellation Draco lies in the area of the sky known as the Black Tortoise of the North. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is tiān lóng zuò, which means “the heaven dragon constellation”.
In more recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy officially named the Draco constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Draco constellation?
Draco is an ancient constellation The myth of Draco dates back to the era of Greek mythology around 3000BC. The constellation depicts a mighty dragon, twisted across the skies.
He is Ladon, the Dragon who guarded the Golden Apple Tree in the Garden of the Hesperides. Heracles, a Greek warrior hero, killed the dragon with a poisoned bow and arrow, allowing the Hesperides to eat the apples.

In Islamic astronomy, the famous Persian Astronomer, Al Sufi, wrote about the dragon constellation in his Book on the Constellations of the Fixed Stars. He lived during the 10th century (24).
Chinese astronomers around 750BC also identified the constellation Draco. He lies in the area of the sky known as the Black Tortoise of the North.
Ancient findings in the tombs of Xiongnu aristocrats in north-central Mongolia, revealed beautiful golden dragons from Draco the dragon myth, dating back to Western Han Dynasty, 206BC to 25AD (25).
How did the Draco constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, what is the dragon name meaning? It is a simple translation, the word Draco comes from the Latin word which means ‘Dragon’.
The Draco meaning is a powerful and imposing creature that strikes fear into all who see him. In the dragon story, Ladon belonged to Hera, who put him into her Garden to guard her Golden Apple Tree. Unfortunately, the dragon was easily slain by Heracles, using a poisoned arrow.

Draco also stems from the Greek word ‘drakon’, from drak, meaning ‘monster with the evil eye’. The word Draconian stems from Draco, meaning harsh, strict, or drastic. The dragon is a mythical creature, but he relates to the real snake family, being the largest of this family. In the sky in the Draco myth, he appears as a massive twisted snake.
In Albania, the Devil is ‘Dreqi’ from the Latin Draco. ”Dracula’ in the Wallachian language means ‘devil’.
The Dragon Devil also features in the Bible – Revelation 12:7-9: “And the great dragon was cast out, That Old Serpent, called The Devil, and Satan, which deceiveth the whole world: he was cast out into the earth …” (26).
Here are some more Draco facts! The Draco constellation nickname is ‘Dra’. The famous Draco alien character, Draco Malfoy, in the Harry Potter series, takes his name from the constellation.
Mythology and meaning
Draco myth
Like many of the constellations, there are different Draco mythology stories. Draco features in Greek, Roman, and Arabic dragon mythology.
The most well-known story comes from Draco greek mythology. In this tale, Draco features in the 12 labors of Heracles. Draco represents Ladon, the dragon that guarded the Golden Apple Tree, Hera, wife of Zeus, was given the tree as a gift on her wedding day.
She planted it in her garden on Mount Atlas and asked Atlas’ daughters, the Hesperides, to guard it. She also placed Ladon in the garden, preventing the nymphs from picking the apples.

They called Heracles to help them. He secretly entered the Garden of the Hesperides. As a great warrior, who had won many battles, Ladon was an easy opponent. Heracles took up his bow and arrow and killed the dragon with a poisoned arrow (27).
In Roman legend, Draco was one of the Gigantes, a race of great strength who battled the Gods of Olympus for ten years. The Goddess Minerva killed the dragon and tossed him into the sky. As she threw the dragon, he became twisted and froze at the cold North Celestial Pole forever remaining in that shape.
In Arabic tales of the Draco constellation myth, the stars Eta Draconis and Zeta Draconis represent two hyenas who are attacking a baby camel, protected by four female camels.
In Draco constellation Egyptian mythology, it was prophesied that one of the sons of the Titan Cronus would dethrone him. Each time his wife Rhea bore a child, Cronus swallowed it.
When Rhea gave birth to Zeus, she tricked Cronus into swallowing a stone. He discovered the trick and went after Zeus who escaped by turning himself into a serpent. The constellation dragon commemorates his escape (28).
What does Draco symbolize?
Draco is a powerful and imposing creature of great strength and immense magical powers. He circles in the northern skies and is seen as a symbol of protection or a symbol to be feared. Will he be your foe or your friend?
In Draco astrology, you can beckon the Dragon when you need protection. He will stand by and protect you. He poses a great danger to those who seek to harm or hurt the innocent. With the Dragon at your side, you will gain confidence and power.
You will be invincible and able to conquer any challenges. You will have protection from outside evil forces from all directions. As a spiritual symbol, the Draconis meaning has hidden magic and comes in four forms.
The Fire Dragon represents energy and mastery. He helps you to overcome obstacles.
The Air dragon drako represents insight, vitality, and inspiration. He guides and helps you to solve problems.
The Earth Dragon represents power, potential, and riches. He helps you discover your hidden strengths. He will gather your scattered energy and turn it to good use.
The Water Draco constellation meaning represents depth and passion. He helps with emotional healing and offers compassion. He brings peace and allows you to face past experiences with renewed energy (29).
Draco is not a zodiac sign and has no related Draco planet.
Future of Draco constellation
Draco is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study.
Astronomers using data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) have noticed an interesting phenomenon. They see that the star Alpha Draconis, known as Thuban, has a companion and appears to eclipse one another. The eclipses are brief and only last about 6 hours. This is an exciting discovery and could lead to more findings like this in the universe. (30).

Thuban was the northern pole star from 3942 to 1793 BCE. Due to the effects of precession, it will once again be the pole star in the future. This will happen around 21,000 CE, so wait for it! (31).
The future of constellations is unfortunately measured in very long time periods. In about 1.5 million years, the star, Eltanin, which marks the right eye of the dragon, will pass very close to the Earth. The distance will be within 28 light-years and it will then be the brightest star in the sky (32).
Astronomers are always searching for exoplanets, but finding one orbiting a Giant dead star is a mystery. The star is in the Draco constellation, about 80 light-years from Earth. The exoplanet is WD 1586 b, and is the first recorded instance of this phenomenon. It has an orbital period of 34 hours. In millions of years, our Sun may also become a dead white dwarf and who knows if the Earth will continue to orbit it? (33).