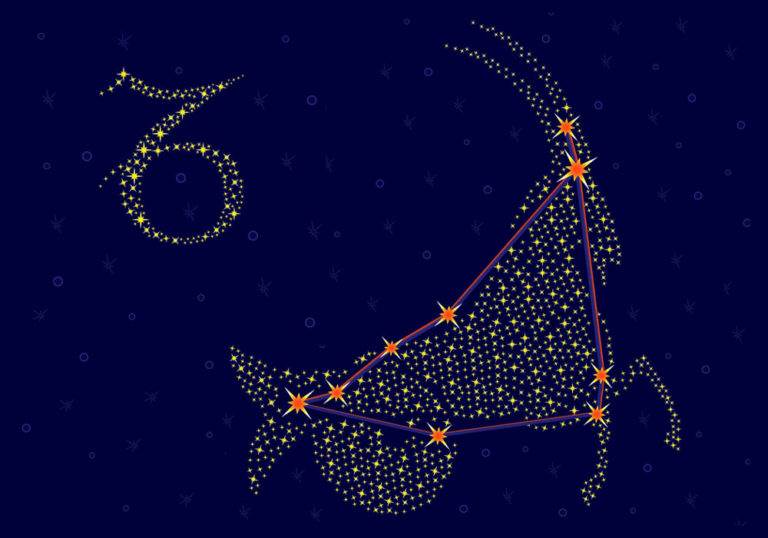
Andromeda Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Andromeda Constellation
Abbreviation: And
Symbolism: The Chained Woman
R.A. position: 23h 25m 48.6945s – 02h 39m 32.5149s
Dec. position: 53.1870041° – 21.6766376°
Distance from earth: The average distance is 213 light-years
Area: 722 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Alpheratz (α And)
Visible at: Latitudes between +90° and −40°
Best viewed: During the month of November at 9.00 pm
- Andromeda constellation
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Andromeda Constellation
The Andromeda constellation is the 19th largest in the sky. It is also known as the Chained Woman. It is an ancient constellation that dates back to Greek times and is associated with a beautiful princess who was sacrificed to the Sea Monster, Cetus, as a result of her mother’s vanity.
Andromeda can be found in the sky by locating the Great Square of Pegasus, or the constellation of Cassiopeia. Andromeda is an exciting constellation to explore, offering the spectacular Andromeda Galaxy, a favorite amongst stargazers,
Read on to learn more about the Andromeda constellations and interesting Andromeda facts.
Characteristics
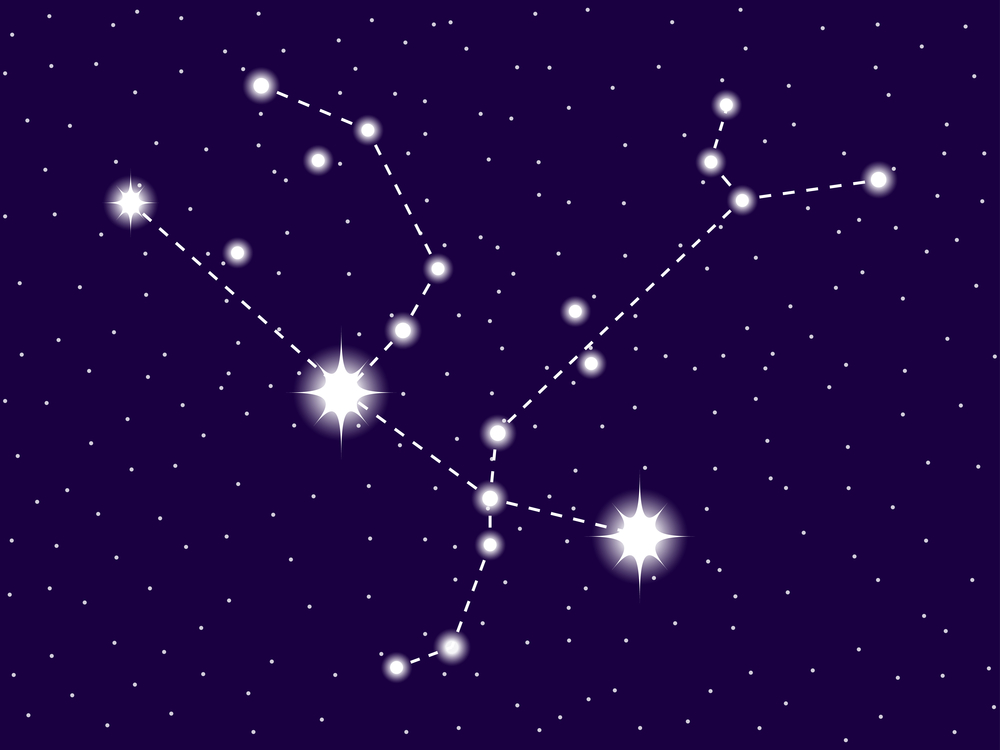
Andromeda constellation

The constellation Andromeda is a medium-sized constellation located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It has many bright stars with fascinating names like Alpheratz, Mirach, and Almach.
Andromeda comes from the Greek myth of a beautiful princess who was sacrificed to the Sea Monster, Cetus. This was due to her mother’s vanity, which angered the Sea Nymphs and caused her father’s kingdom to flood and be destroyed.
The princess constellation Perseus family of constellations. They are all connected to the Great Warrior and his adventures. These constellations include Cassiopeia, her Mother, Cetus the Sea Monster, Auriga, Cepheus, Lacerta, Pegasus the Winged Horse, Perseus, and Triangulum (1).
The Andromeda (constellation) occupies an area of 722 square degrees. The neighboring Zodiac constellations are Pisces the Fish. Neighboring constellations that are not part of the Zodiac constellations are Perseus, Cassiopeia, Lacerta, Pegasus, and Triangulum.
For home astronomers, Andromeda has many awesome Andromeda constellation facts. It contains the amazing Andromeda Galaxy, the most well-known in the Universe. It also offers the beautiful Messier 32 and Messier 110.
Andromeda is not a Zodiac sign, she is a beautiful princess from the Greek Myth. The Andromeda star system dates back over 3000 years (2).
What does Andromeda constellation look like?
You may be asking – what does Andromeda look like?
Andromeda is a beautiful young princess. She stands in the sky, with chains on her arms and feet, as she was when her father, King Cepheus of Ethiopia, sacrificed her to the dreaded Sea Monster, Cetus.
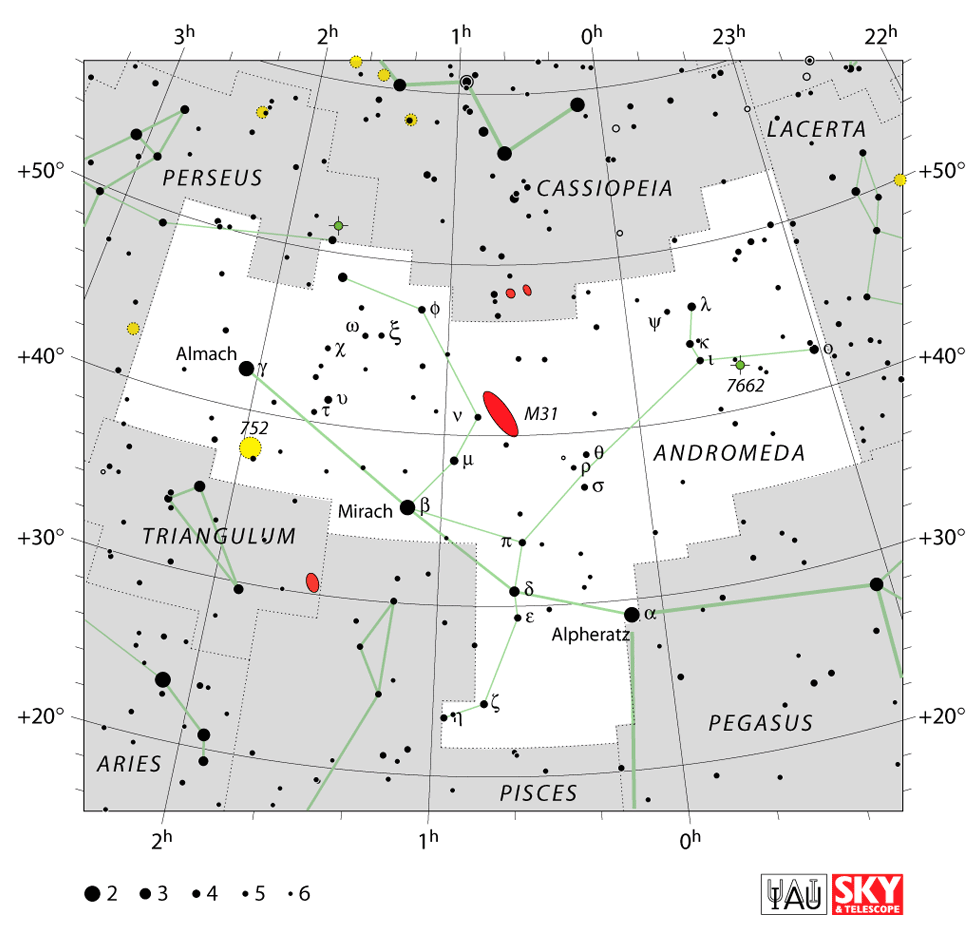
Image credit: IAU and Sky & Telescope magazine CC-BY-3.0.
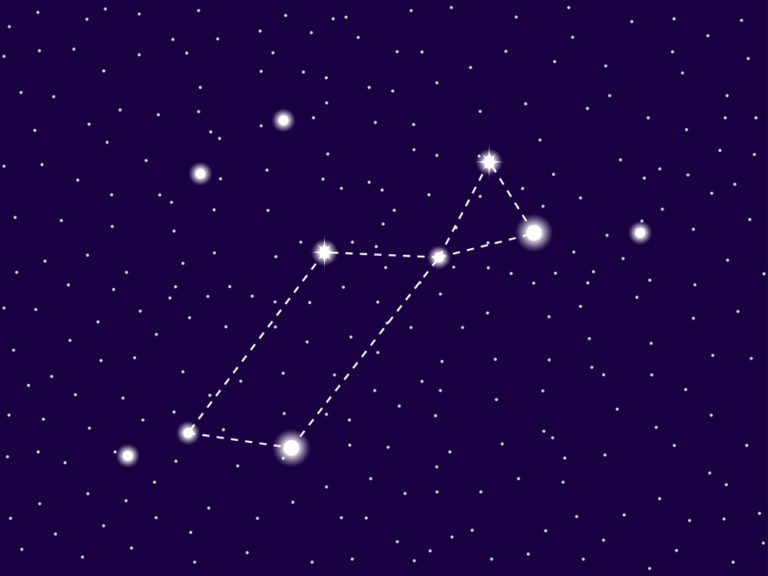
In the sky, the constellation Andromeda is depicted by a number of bright stars. It is up to you to imagine a young woman, lying in a rather sideways position with her arms outspread on either side of her body. In the northern sky, her feet point upwards. In the south, she appears more normal, with feet pointed downwards.
A prominent pattern of stars, known as an asterism, defines the main
Andromeda star at the top of her head. This star is Alpheratz, and also forms part of the Great Square of Pegasus.
Andromeda has long, flowing hair that falls around her shoulders. The stars Eta Andromedae and Sigma Andromedae pinpoint her arms. The bright star Mirach is known as the girdle. It lies in the center of her body, and you can imagine a long flowing red robe, secured at the waist by a rope tie.
To complete the image of Andromeda the princess constellation,
wrap chains around her wrists and ankles. The chains are free and loose and the great warrior Perseus is rescuing her from the monster. He is about to carry her off to become his wife and live happily ever after.
How far is Andromeda constellation from earth?
An important question for new stargazers is – how far is Andromeda from earth? When viewing a constellation from Earth, it appears as if all the stars and celestial bodies are on one flat plane. In reality, this is not correct! They all lie at different distances away, measured in light-years. Some stars may be as close as 40 light-years. Deep-sky objects may be as far as 60 million light-years away.
To give some idea, Alpheratz is 97 light-years away. The well-known star Mirach is about 200 light-years away. Almach is a bright star that is 350 light-years away. Delta Andromedae is a double star, 101 light-years away. Iota Andromedae is a blue-white star, 503 light-years away. Upsilon Andromedae is 44 light-years away from Earth. Adhil is a double star and lies about 196 light-years away.
The distance from milky way to Andromeda galaxy is a massive 2.5 million light-years. NGC 206 is about 400 light-years away.
Taking into account the brightest stars and their individual distances, the average distance to the Andromeda constellation from Earth is about 213 light-years. If you consider the deep sky galaxies, the distance is around millions of light-years.
Features
Major stars in Andromeda
Here is a list of major stars in the Andromeda galaxy. Home stargazers ask – how many stars are in the constellation Andromeda? There are thousands! Read on to learn about the most important stars in Andromeda.
Alpheratz – α Andromedae (Alpha Andromedae)
Alpheratz, also known as Alpha Andromedae, is one of the most prominent stars in Andromeda galaxy. It is a hot blue subgiant star with an apparent magnitude of 2.06 and lies about 97 light-years away from Earth. Alpheratz is a binary star system. The brighter of the two stars has an unusual chemical composition with extremely high levels of manganese, mercury, and other elements.
Alpheratz is 200 times more luminous than the Sun and has a surface temperature of around 13,800 K. in comparison, our Sun’s temperature is around 6000 K. The two binary stars in the system orbit each other every 96.7 days. The name comes from the Arabic surrat al-faras, meaning ‘navel of the horse’ as it defines the center of the body of Pegasus in Andromeda astronomy (3).
Mirach – β Andromedae (Beta Andromedae)
Beta Andromedae is also known as Mirach. The name comes from the partially-related Arabic word mizar meaning “girdle”. Mirach lies at Andromeda’s left hip, where her rope tie holds her robe closed. Mirach has an apparent magnitude of 2.01 and you can see this Andromeda naked eye star without a telescope.
Andromeda beta is a cool, bright red class M giant that lies about 200 light-years away from earth. It is 1,900 times more luminous than the Sun. Mirach is an exciting star in the woman constellation. It lies close to the galaxy NGC 404, with the nickname, the Ghost of Mirach (4).
Almach – γ Andromedae (Gamma Andromedae)
Almach, also known as Gamma Andromedae, is the third brightest star in the Andromeda constellation. It is a multiple-star system. The name comes from the Arabic al-‘anaq al-‘ard, meaning “the desert lynx”.
Almach lies about 350 light-years away from Earth. The brighter star in the system has an apparent magnitude of 2.26 and you can see it with the naked eye. The fainter companion is Gamma2 Andromedae. It is itself a binary star, comprising a fifth and sixth magnitude white dwarf stars. The star indicates the left foot of the princess (25).
δ Andromedae (Delta Andromedae)
Delta Andromedae is a yellow-white double star with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.27. It lies about 101 light-years distant from the Sun. The brighter component is a K-type giant, and the dimmer companion is either a G-type main-sequence star or a white dwarf. The star is not named and lies at the neck of the princess.
ι Andromedae (Iota Andromedae)
Iota Andromedae is not a named star. It lies near to the right hand of Andromeda. It is a B-type main sequence dwarf with a blue-white color. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.29 and is 503 light-years away from our Solar System.
υ Andromedae (Upsilon Andromedae)
Upsilon Andromedae is 44 light-years away from earth. It lies on the lef5t calf of the princess. This star is an exciting celestial object, ranked 21st on the list of the top 100 target stars for the NASA Terrestrial Planet Finder mission. It has 4 exoplanets orbiting around it. Scientists looking for more planets in Andromeda, will continue to study this star.
Upsilon Andromedae is a binary star system, composed of a yellow-white dwarf and a faint red dwarf. The age of the star is around 3.1 billion years. (5).
Adhil – ξ Andromedae (Xi Andromedae)
Adhil, also known as Xi Andromedae, gets its name from the Arabic word al-dhayl, meaning “train” or “tail”. The star is one of a number of stars in Andromeda galaxy that lie on the right lower leg of the princess. Adhil is a double star with an orange-red color and lies about 196 light-years away from our Solar System. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.87. Adhil is not as hot as our Sun, with a surface temperature of around 4,656 K (6).
μ Andromedae (Mu Andromedae)
Mu Andromedae is a white A-type dwarf located approximately 136 light-years from Earth. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.86. The star lies in the Andromeda solar system on the right thigh of the princess.
Deep-sky objects in Andromeda
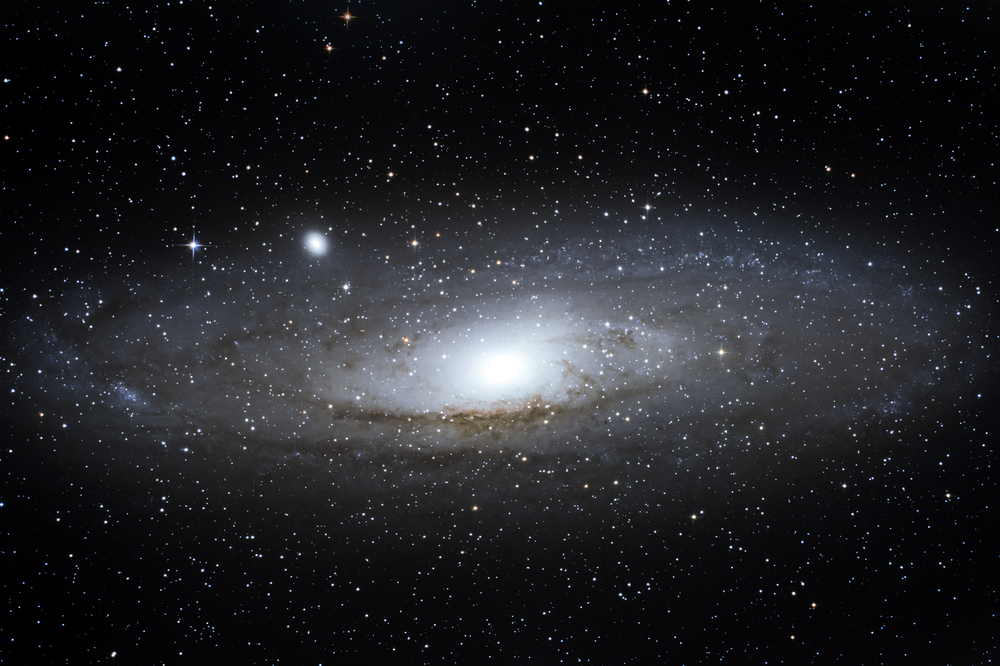
Andromeda Galaxy (Messier 31, M31, NGC 224)
The Andromeda galaxy, also known as Messier 31, is a very beautiful deep sky object. The Andromeda galaxy distance to earth is around 2.5 million light-years. In the past, astronomers called it the Great Andromeda Nebula.
The Andromeda Galaxy is the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way. It is also the farthest object in the night sky visible that you can see without a telescope. It is one of the brighter Messier objects, with an apparent visual Andromeda magnitude of 3.4.
New stargazers ask – what type of galaxy is Andromeda and how many stars are in the Andromeda galaxy? It is a classic spiral galaxy containing around a trillion stars. In comparison, our Milky way has about 200-400 billion stars. This is a massive galaxy with an Andromeda size diameter of about 200,000 light-years (7).
Andromeda satellites
Andromeda has about 14 dwarf galaxies orbiting around it, known as satellite galaxies. These include Messier 32, Messier 110, NGC 147, NGC 185, and the Cassiopeia Dwarf as well as many others. The amazing Triangulum Galaxy in the constellation Triangulum is also a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy (8).
NGC 206
If you are looking for a great nebula in Andromeda, NGC 206 is a massive star cloud in the Andromeda galaxy. This bright star cloud is also known as M31 and is one of the largest star-forming regions in the Local Group of galaxies. Astronomers detect star-forming regions by the telltale reddish emission from clouds of ionized hydrogen gas. The distance to the Andromeda galaxy is about 2.5 million light-years! The cloud contains a number of very bright stars and lies in one of Andromeda’s spiral arms. The diameter of the NGC 206 Andromeda galaxy size is about 4000 light-years (9).
Andromeda’s Cluster – Mayall II
Also in orbit around the gigantic Andromeda galaxy is Andromeda’s Cluster, known as Mayall II. The cluster lies about 130,000 light-years from M31’s core. It is the brightest globular cluster in the Local Group of galaxies. Mayall II has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.7m which is faint and you can only see it with a powerful telescope. The largest globular cluster in our milky way is Omega Centauri.
The size of Andromeda galaxy Mayall II is double that of Omega Centauri. Astronomers think that it contains a black hole in its center. Nicholas Mayall discovered the cluster in 1953 and gave it its name (26).
Messier 32 (Le Gentil, NGC 221)
Messier 32 is a dwarf elliptical galaxy that lies about 2.65 million light-years away from our Solar System. The French astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil found it in 1749, and it sometimes takes its name from him, as Le Gentil. Messier 32 was the first elliptical galaxy ever discovered and is also one of the satellites galaxies of Andromeda. M32 is fairly bright, and you can see it using a home telescope. M32 contains predominantly old stars, with no active star formation. It has a supermassive black hole in its center.
Messier 110 (NGC 205)
M110 is about 2.9 million light-years away from Earth. It is an elliptical dwarf galaxy with 8 globular clusters in a halo that surrounds it. Messier 110 was observed and described by Charles Messier in 1773. It was also found by Caroline Herschel a decade later. Her discovery was documented by her brother William Herschel in 1785. Messier 110 may contain a supermassive black hole at its center.
NGC 752
NGC 752, also known as Caldwell 28, is an open cluster. It lies about 1,300 light-years away and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.7. NGC 752 is bright and you can see it with binoculars or a telescope for even better views. It is a large, sprawling cluster. You may ask – how many stars are in Andromeda NGC 752 Cluster? There are at least 70 (10).
NGC 891
NGC 891 is an edge-on spiral galaxy that lies about 27.3 million light-years away. It is close to the star Almach, Gamma Andromedae, on the east side. You can see NGC 891 using a home telescope and it is an amazing sight. The galaxy has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.8. NGC 891 discovery was in 1784 by William Herschel.
Blue Snowball Nebula – NGC 7662
The Blue Snowball Nebula is a sight not to miss, but unfortunately, you can only see it with a very powerful telescope! It is a planetary nebula with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.6 and lies to the west of Kappa Andromedae. The blue light comes from the central star, which is a bluish dwarf star with a very hot temperature of around 75,000 K. Astronomers believe the Andromeda galaxy distance of Snowball Nebula is around 2,000 to 6,000 light-years (11).
Arp 65 – NGC 90 and NGC 93
NGC 90 and NGC 93 are a pair of interacting spiral galaxies in the Andromeda constellation. NGC 90 lies about 333.8 million light-years away and NGC 93 is 259.7 million light-years away. GC 90 has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.7. It has a significant shape of two distorted, elongated spiral arms. NGC 93 has a visual magnitude of 14.34. The shapes are most likely caused by the interaction of gravitational forces between the two galaxies. The galaxy’s discovery was in 1854, by R.J. Mitchell (12).
Exoplanets in Andromeda
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around stars, other than our star, the Sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to those in our Solar System, with the possibility of life. There are many planets in the Andromeda galaxy. Read on for more facts!
Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae is also known as Titawin. It is 44 light-years away from earth. This star is an interesting celestial object, ranked 21st on the list of the top 100 target stars for the NASA Terrestrial Planet Finder mission. It has 4 Andromeda galaxy planets orbiting around it. One of them is Upsilon Andromedae d, a gas giant exoplanet with a mass of 4.132 Jupiters. It takes 3.5 years to complete one orbit of its star (13).
HD 16175
HD 16175 is also known as Buna. It is a yellow star about 188 light-years away. Orbiting the star is an exoplanet called Abol, or HD 16175 b. Many exoplanets get their name from members of the public who participate in the NameExoWorlds campaign by Ethiopia, established during the 100th anniversary of the IAU. Abol is the first of three rounds of coffee in the Ethiopian traditional coffee ceremony. HD 16175 b is a gas giant with a mass of 5.1 Jupiters. It takes 2.7 years to complete one orbit of its star.
Kappa Andromedae
Kappa Andromedae has one exoplanet known as kappa And b. It has an orbital period of about 600 years. Kappa Andromedae is a blue subgiant star that lies about 168 light-years away from earth. The star indicates the right hand of the Andromeda (constellation).
HAT-P-32
HAT-P-32 is a yellow-white star that lies about 1043 light tears away. It has one exoplanet known as HAT-P-32 b. HAT-P-32 b is a gas giant with a mass of 0.68 Jupiters. It flies around its star, with an orbit of only 2.2 days. Its discovery was in 2011.
Meteor showers in Andromeda
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Dust and debris from the remnants of the comet enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. This creates a spectacular show, often known as shooting stars.
The Andromedids
The Andromedids is not a spectacular shower in recent times. The origin comet is the famous Comet Biela, first seen by Frenchman Jacques Lebaix Montaigne, in 1772. It was seen again in 1805 and 1826. In 1826, a German skywatcher, Wilhelm von Biela, tracked it and discovered that it orbits the sun every 6.5 years. This is a significant observation as very few comets have had their orbits successfully calculated.
The shower occurs from the end September to early December. The peak is in mid-November, around the 19th. You probably won’t see any comets with the naked eye. The rate is around 3 per hour, traveling at speeds of 19km/s (14).
For those wanting to see a meteor shower near to Andromeda constellation, the amazing Perseids radiate outwards from Perseus, Andromeda’s husband in the Andromeda myth. The Perseids is one of the more spectacular showers, occurring between 17 July to 24 August, with the peak on 13 August. Expect to see over 50 per hour, traveling at speeds of up to 60km/s.
Location and visibility
Where is Andromeda constellation located?
Andromeda is a large constellation with many bright stars and you can easily spot it once you know what to look for. In dark skies, you can see the main stars without a telescope. Then, you can imagine the beautiful princess chained to a rock in the sea, at the mercy of the Sea Monster.
Where is Andromeda in the sky?

Andromeda is a northern constellation and is the 19th largest constellation of the 88 named constellations. It occupies an area of 722 square degrees. Andromeda lies in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, NQ1. A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes between +90° and −40°.
To find the Andromeda constellation location, you can find the four bright stars that make up the Great Square of Pegasus. Andromeda shares one of the stars with the mythical horse. Andromeda and pegasus connect in the myth, as Perseus rode Pegasus when he came to rescue her. In fact, Andromeda’s head is almost on top of the horse. You can also locate Pisces the Fish. Andromeda lies just above the top-most fish, with her feet pointing towards Perseus, her savior.
Andromeda belongs to the Perseus family of constellations. They are all connected to the Great Warrior and his adventures. These constellations include Cassiopeia, her Mother, Cetus the Sea Monster, Auriga, Cepheus, Lacerta, Pegasus the Winged Horse, Perseus, and Triangulum (15).
When is Andromeda constellation visible?
When is Andromeda visible? Andromeda is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres. In the northern hemisphere, you can see Andromeda August to February. In the southern hemisphere, you can view the Andromeda galaxy location in sky from October to December.
If you are in the northern hemisphere – From August to September, Andromeda galaxy constellation appears low on the north-eastern horizon around 10pm and climbs slowly overhead. From October to November the constellation is visible in the eastern sky around 8pm. In December and January it will appear overhead at around 6pm in the Andromeda night sky, gradually moving towards the north-west horizon.

This is a great time to take the kids to view the galaxy Andromeda. In February, the Andromeda star system is visible in the western sky from around 7pm, moving westwards and sinking below the horizon by midnight.
In the southern hemisphere – In October and November Andromeda visible at around 10pm low on the north-eastern horizon. It slowly moves north-west but never rises high in the sky. In December the Andromeda galaxy constellation appears low on the northern horizon at around 10pm before disappearing below the north-western horizon after midnight.
Remember – in the southern hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down. In this case, Andromeda in the night sky is more “right-side up” than she is in the North! (16).
How to find Andromeda constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Read on to learn how to find Andromeda in the night sky.
- To find the Andromeda location, it is easiest to first locate the Giant Square of Pegasus
- First, find the Big Dipper in Ursa Major, then star-hop downwards to Polaris, the bright North Star
- Draw an imaginary line from any Big Dipper handle star through Polaris, double the distance and you will land on the W-shaped constellation Cassiopeia
- Continue your line to the bright star, Alpheratz at the top corner of the Great Square of Pegasus
- Andromeda’s head lies at the star Alpheratz.
- She lies sideways in the sky with her feet pointing towards Perseus
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, Andromeda appears more right-side-up than she does in the north. So, where is the Andromeda galaxy location?
- To find the Andromeda location, it is easiest to first locate the Giant Square of Pegasus
- First, find the Big Dipper in Ursa Major, then star-hop upwards to Polaris, the bright North Star
- Draw an imaginary line from any Big Dipper handle star through Polaris, double the distance and you will land on the M-shaped constellation Cassiopeia
- Continue your line to the bright star, Alpheratz at the lower corner of the Great Square of Pegasus
- Constellation Andromeda head lies at the star Alpheratz
- She lies sideways in the sky with her feet pointing towards Perseus
How to view Andromeda Constellation?
Andromeda is the 19th largest constellation in the sky. It shares a star with the well-defined star pattern or asterism, known as the Great Square of Pegasus. By locating these stars, you can imagine the beautiful chained Princess abandoned in the ocean, at the mercy of the Sea Monster.
Like all stargazing experiences, getting away from city lights is the best way to see constellations and deep-sky objects. You can see the princess Andromeda with the naked eye, but using a telescope will make it so much more exciting. For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous images of Andromeda.

Depending on your budget, plan to spend from $250 to $900 on a telescope that will give a lifetime of viewing.
The Orion StarBlast 6 Astro Reflector Telescope has a large 150mm (6 inch) light-gathering lens and a focal length of 750mm. At under $400, it offers exceptional value for money. The scope features a smooth Altazimuth mount. This mount allows you to move the telescope both up and down, and sideways with ease to track any object you desire. It also has a compact table-top design, offering exceptional ease of use. The scope comes pre-assembled – a bonus for people who are not great at DIY. Although the lens is large, the scope weighs only 23.5lbs, making it easy to take along on a family stargazing outing.
The Orion StarBlast 6 Astro comes with two eyepieces – a 25mm and a 10mm Sirius Plossl 1.25″. It also includes an EZ Finder II aiming device and an eyepiece rack for easy accessibility to your eyepieces when viewing. The Starry Night Software is full of interesting celestial objects to view, including the Andromeda galaxy stars.
History of observation
Who discovered Andromeda constellation?
Andromeda constellation history dates back to ancient civilizations of the Greeks, Chinese and Hindus, and was documented in stories, folklore, and myths.
The Andromeda story dates as far back as 3000BC. It associates with a beautiful princess, daughter of King Cepheus of Ethiopia and his Queen, Cassiopeia. Due to Cassiopeia’s vanity, the King had to sacrifice Andromeda to the Sea Monster, to save his lands. Perseus, the great warrior, rescued her and swept her away to safety. They later married and she bore him 7 sons and 2 daughters (17).

Hindu astronomy around the 5th and 6th century also documents Andromeda mythology facts. Andromeda is the Devyani Constellation. Her mother, Cassiopeia is the Sharmishta Constellation. Devyani and Sharmishta are wives of King Yayati, indicated by the Perseus Constellation.
Andromeda is also an old Chinese constellation known as far back as 750BC. The modern constellation Andromeda lies across two of the quadrants, symbolized by the Black Tortoise of the North, and the White Tiger of the West. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is xiān nǚ zuò, meaning “the immortal woman” or the “fairy constellation”. Nine stars from Andromeda and seven stars from Pisces form an elliptical constellation called “Legs”. This constellation is thought to represent the foot of a walking person or a wild boar.
Around the 7th and 8th centuries, Babylonian astronomers wrote about the story of Andromeda. In this version, she is the Goddess of Primevil Chaos, Tiamat. She bore many dragon demons for her husband, Apsu, The God of Freshwater. Marduk, a younger-generation god, killed her in a great war (18).
During the 9th to 13th centuries, an Arab constellation called “al-Hut” (the fish) was made up of a number of stars in Andromeda, the M31 galaxy, and several stars in Pisces.
In more recent times, Andromeda was one of the original 48 constellations formulated by Ptolemy in his 2nd-century work, the Almagest. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Andromeda constellation?
You may be asking how old is the Andromeda galaxy and when was Andromeda discovered?
Andromeda is an ancient constellation, and Andromeda history dates back to the era of Greek mythology around 3000BC. The constellation depicts the myth of the beautiful princess, daughter of King Cepheus of Ethiopia and his Queen, Cassiopeia. Due to Cassiopeia’s vanity, the King had to sacrifice Andromeda to the Sea Monster. Perseus rescued her and swept her away to safety (19).

Andromeda is also an old Chinese constellation known as far back as 750BC. The modern constellation Andromeda lies across two of the quadrants, symbolized by the Black Tortoise of the North, and the White Tiger of the West.
Around the 7th and 8th centuries, Babylonian astronomers wrote about the story of Andromeda. In this version, she is the Goddess of Primevil Chaos, Tiamat. She bore many dragon demons for her husband, Apsu (20).
How old is Andromeda galaxy in Arabian astronomy? The Arabian astronomers in the 9th to 13th centuries knew of Andromeda stars. The constellation is the “al-Hut” (the fish) and is composed of several stars in Andromeda, M31, and several stars in Pisces.
How did the Andromeda constellation get its name?
Most constellations get their names from ancient cultures, folklore, or mythology. So, what does the name Andromeda mean?
The Andromeda name means “to be mindful of a man”. It comes from the Greek ἀνήρ (aner) meaning “man”, combined with μέδομαι (medomai) meaning “to be mindful of”. In Greek mythology Andromeda is an Ethiopian princess rescued from sacrifice by the hero Perseus. He managed to kill the Sea Monster, Cetus, who was about to kill the princess. He then took Andromeda to safety and married her.
The prefix andro- in Andromeda’s name means ‘man’ in Greek. The Greeks used the word andreia, for courage, in the context of manly courage. The Greek name -andros has the female counterparts in names such as -aneira, Leandros/Leaneira, and Deiandros/Deianeira.
So what does Andromeda mean? In Andromeda etymology, she is the chained woman and the Romans used the term catena from which the English word chain is ultimately derived. The Andromeda nickname or abbreviation is And (21).
Mythology and meaning
Andromeda myth
The Andromeda constellation myth comes from the Greek mythology story that starts with King Cepheus of Ethiopia and his Queen, Cassiopeia. They had a beautiful daughter, Andromeda. Queen Cassiopeia offended the sea nymphs, the Nereids, by claiming she was more beautiful than they were.

The nymphs complained to Poseidon, God of the Sea. He sent a sea monster, Cetus, to take revenge by flooding and destroying Cepheus’ lands. In desperation, King Cepheus approached the Oracle of Ammon for advice on how to save his lands. The solution was a terrible choice! He was to sacrifice his daughter to Cetus.
Andromeda was chained to a large rock in the ocean and left to the mercy of the monster, Cetus. Perseus, a demi-god, the son of Zeus and a mortal named Danae came along, slew the sea monster and rescued Andromeda. The two married and had 7 sons and 2 daughters, each with a fascinating story of their own. The Goddess Athena placed Andromeda among the stars. Near to her in the sky, is Perseus her savior and husband, and Cassiopeia her mother. Also in the sky is Cetus, the sea monster.
In ancient Mesopotamia, Andromeda associates with the story of Tiamat, the goddess of Primeval Chaos. She bore many evil dragons for her husband, Apsu. She decided to destroy them in a war but was killed by her long-time foe, Marduk. He put her body into the sky (22).
What does Andromeda symbolize?
In Andromeda (mythology), Andromeda is a beautiful princess, daughter of King Cepheus of Ethiopia and his Queen, Cassiopeia. Cassiopeia was vain and boasted that Andromeda was more beautiful than the Sea Nymphs. Although Andromeda had done nothing wrong, she had to be sacrificed for her beauty.

The Andromeda symbol represents beauty and faith. She was chained to a large rock in the sea and left alone for the Sea Monster, Cetus, to devour her. She did not lose hope and the story ends well when Perseus rescues her and makes her his wife. You can see Andromeda as a symbol of hope, resolve and positiveness. She became a strong and powerful woman, bearing many children in her life.
She symbolizes the Andromedan characteristics of the ability to escape one’s chains, be they emotional or physical. Andromeda shows that there is always hope, no matter how bad the situation seems to be. Andromeda brings love and family values. She aspires to love her husband and create a happy and secure home for her children. The Andromeda story shows that she is steady and unshaken despite her terrible ordeal.
In modern times, the Andromeda constellation story resonates with many young girls who have troublesome relations with their Mothers. In the Andromeda symbols, the mother is the dominant figure and the daughter is at her mercy. But, there is salvation for the young woman. She will escape the bonds of her mother and find happiness in her own way. She will show Andromeda characteristics, and like the Princess, she will rise and become a force that can equal, for example, her powerful husband, Perseus, the Hero Warrior (23).
Future of Andromeda constellation
Andromeda is a constellation that is fascinating for astronomers to study.
The Andromeda Galaxy is the closest galaxy to our Milky Way. What you may not know, us that the two galaxies are on a course to collide and merge into one. This is going to take place in the future – in around 5 billion years from now. However, astronomers believe that the merge is already underway.
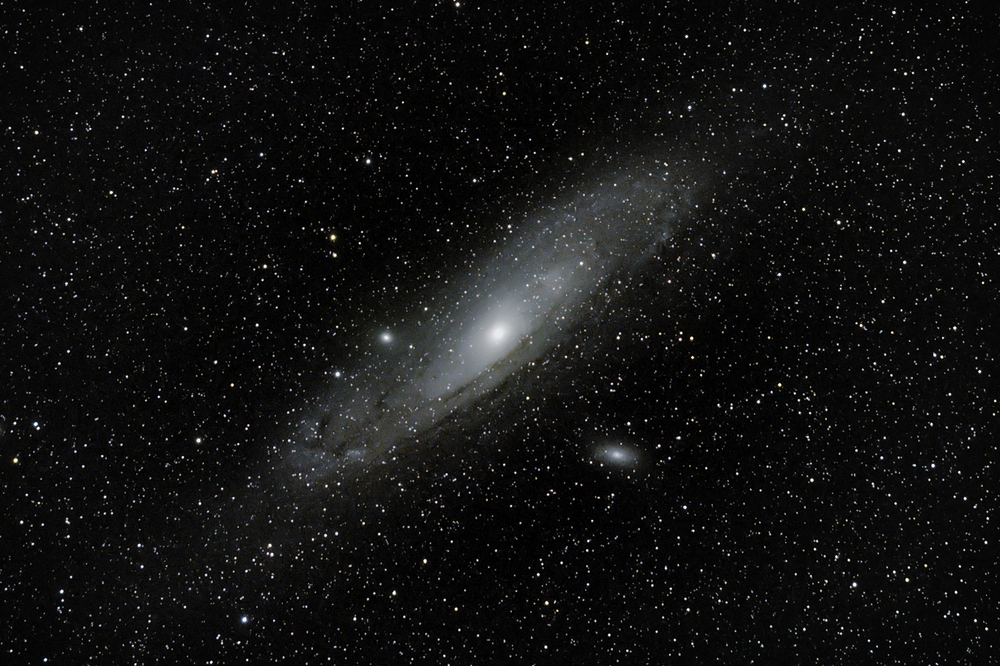

The Project AMIGA, which uses the Hubble Space Telescope to look at the deep-space, reported on this study earlier this year, calling it “the most comprehensive study of a halo surrounding a galaxy”. By measuring the size of the gas halo around the galaxies, they appear to be much closer than originally thought. It actually extends as far as half the distance to our Milky Way.
Also of interest to scientists are clusters that are active star-forming regions. Andromeda has many, and new stars are forming that they can observe. M31 is one of the largest star-forming regions in the Local Group of galaxies. Astronomers detect star-forming regions by the reddish emission from clouds of ionized hydrogen gas. In the photo, you can see astronomers tracking the Cepheid variable star which lies in M31 (24).