Scorpio Constellation: Stars, Myth, and Location (2024)
Object name: Scorpio Constellation
Abbreviation: Sco
Symbolism: The Scorpion
R.A. position: 16.8875h
Dec. position: −30.7367°
Distance from Earth: The average distance is 950 light-years.
Area: 497 sq. deg.
Brightest star: Antares (α Sco)
Visible at: Latitudes between +40° and −90°
Best viewed: During the month of July at 9.00 pm
The Scorpio Constellation is one of the twelve constellations of the Zodiac. It is also known as the Scorpion and has its roots in Greek mythology, where it appears in the fascinating story of Orion.
Scorpio is easy to find as it lies near the center of the Milky Way. You can observe it best in the southern hemisphere, with limited views in the northern hemisphere. It contains a number of interesting bright Scorpio stars, including Antares, the most luminous Scorpion star in the constellation. The name means ‘Rival Of Mars’ because they both have a red hue.
Read on to find out all about Scorpius and Scorpio constellation facts.
- Characteristics
- Features
- Location and visibility
- History of observation
- Mythology and meaning
- Future
Characteristics
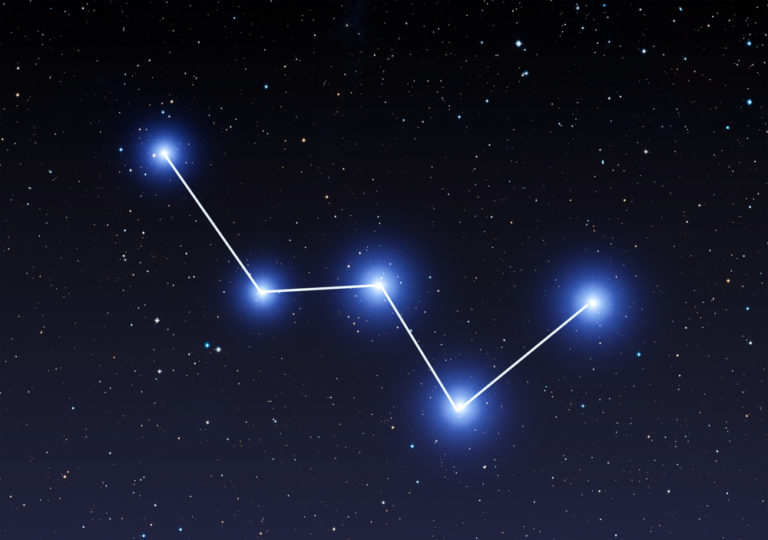
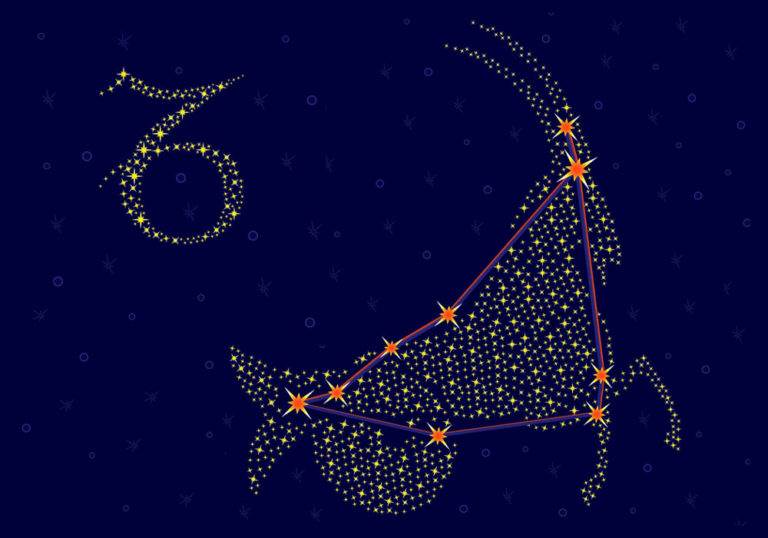
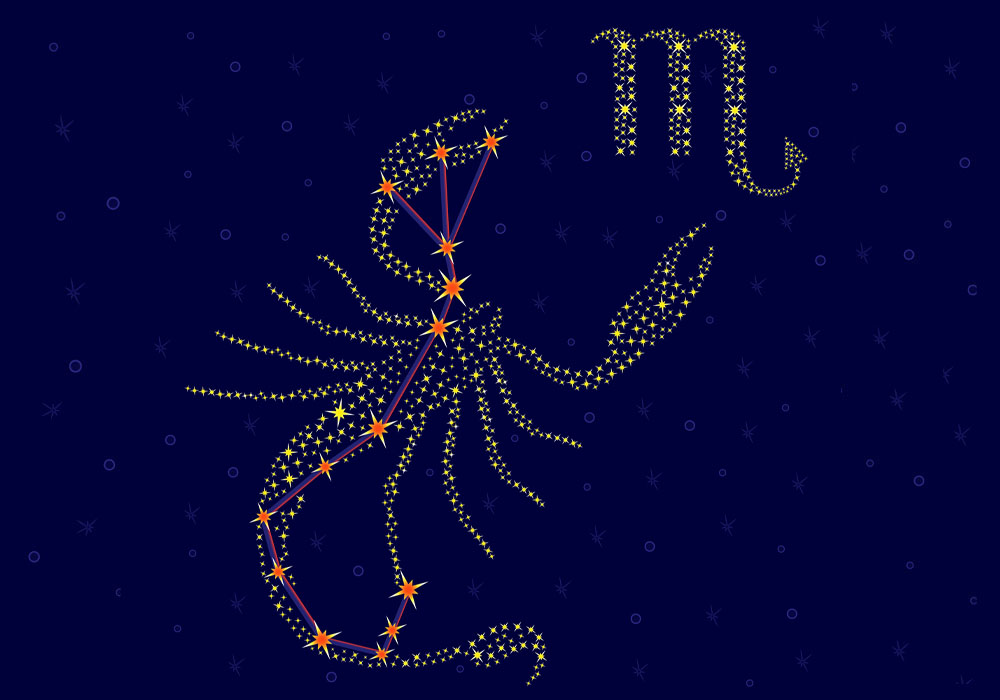
Scorpio constellation
Scorpio is one of the most distinctive constellations to spot in the sky, complete with stinging tail and pincers. The name comes from the Latin word for Scorpion, which translated means “creature with the burning sting” (2).
The Scorpius constellation is the 33rd biggest constellation. It occupies an area of 497 square degrees. It was officially listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Claudius Ptolemy.

For home astronomers, the constellation Scorpio offers some interesting objects. It contains bright stars Antares and Shaula and the lovely Butterfly Cluster (Messier 6). Also of interest to home astronomers is the Ptolemy Cluster (Messier 7), the Cat’s Paw Nebula, and the Butterfly Nebula.
Scorpio is one of the smaller of the Zodiac constellations, together with Gemini and Cancer. While the Zodiac sign is called Scorpio, the constellation is known as Scorpius.
The ancient Greeks considered the Libra constellation to be the claws of the Scorpion, making it a larger constellation. The age of Scorpio dates back to the times of Greek Mythology, over 3000 years ago (1).
Because this constellation is easy to spot, it is one of the favorites of home stargazers, especially those in the southern hemisphere.
What does Scorpio constellation look like?
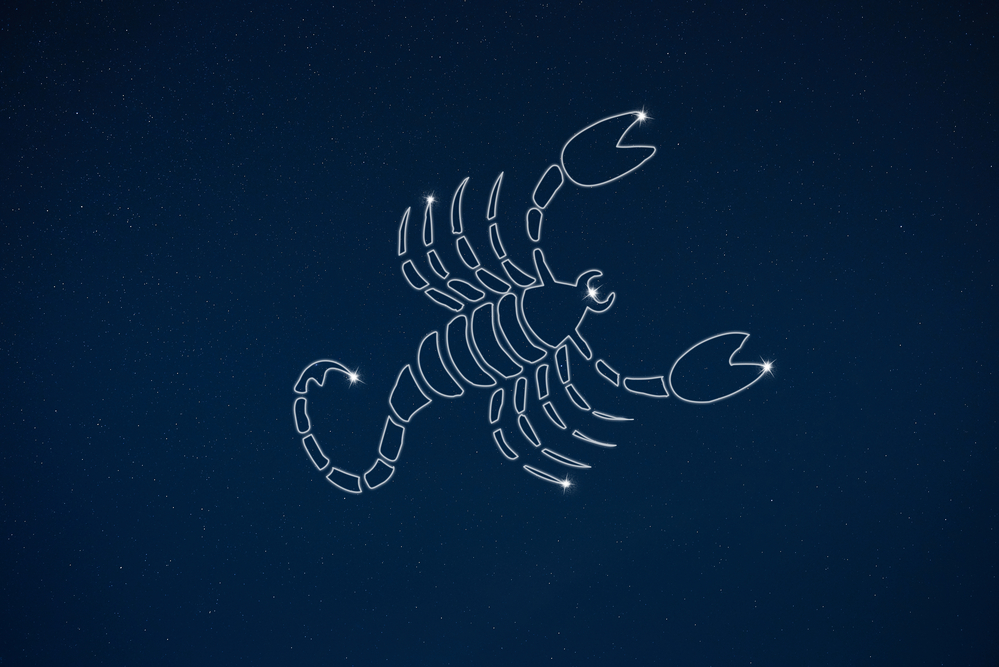
The Scorpio Constellation, known as the Scorpion, is a constellation that is easy to spot, even with the naked eye. So, what does Scorpio look like? The Scorpion stands in the sky with his long tail curled up behind him, ready to sting anyone who comes close.
Extending from the front of his head are two pincers curving around into a semi-circle. The body joins the tail and head and with some imagination, you can see the four legs extending downwards for walking.
You can best see the constellation Scorpius in the southern hemisphere. To imagine the Scorpion, there are some bright stars in Scorpio that identify the tail, head, and pincers. The bright star Shaula is at the tip of the tail. Forming the curve of the tail is Sargas. Antares is at the heart of the Scorpion and the pincers are identified by Jabbah, Graffias, and Dschubba (3).
How far is Scorpio constellation from Earth?
Like most constellations, the Scorpio star constellation is made up of numerous stars, exoplanets, and deep-sky objects.
When observed from planet Earth, the constellation looks as if all the objects lie on the same plane. In fact, each object is at a different distance from the Earth.

To give some idea, Scorpio’s brightest star is Antares, approximately 550 light-years away. Shaula is the second brightest star in the Scorpius constellation and is about 700 light-years from the solar system. The interesting Messier 6, known as the Butterfly Cluster, lies about 1600 light-years from Earth (4).
Messier 80 lies about 32 620 light-years away. Gliese 667Cc is a “super-Earth” that is roughly four times as massive as Earth. It lies at a close distance of only 22 light-years away.
Taking into account the objects and their individual distances, the average distance to the main stars of the Scorpion constellation from Earth is 950 light-years.
Zodiac family
Scorpio is the eighth sign of twelve in the Zodiac family and represents people born between October 23 and November 21. It is one of the three water signs, the others being Cancer and Pisces.
The Scorpio star constellation has two other zodiac constellations as neighbors in the night sky. Libra, the Scales, is a constellation next to Scorpius and lies to its right. Sagittarius, the Archer, is above and to its left.

Like all the Zodiac constellations, the constellation of Scorpius the Scorpion lies on the ecliptic path. This is the path that the sun takes as it moves across the sky during the year.
Another interesting question is when does the sun pass through Scorpius? The Sun passes through it each year for around a week in late November.
In the Greek Scorpio story, the Scorpion fights with Orion the Hunter and kills him. The God Zeus placed them both in the sky but kept them apart. Due to the animosity between the two, you will never see both in the sky at the same time.
Orion the Hunter only appears in the east after Scorpius sets in the west, and the opposite also applies. The Scorpio zodiac constellation does not rise in the east until Orion sinks in the west.
Features
Major stars in Scorpio
Here is a list of the major Scorpio stars in the sky.
Antares – α Scorpii (Alpha Scorpii)
The biggest of Scorpio stars, Antares, gets its name from the ancient Greek Άντάρης, which has been translated as “rival of Mars” or “like Mars”. It refers to the similar red hue that both celestial objects have.
Antares is a red supergiant star with a visual magnitude of 0.96 and is approximately 550 light-years away. It is the brightest star in the Scorpius constellation and lies at the heart of the Scorpion.
It has a mass of about 12 times that of the Sun. Antares is a two-star system consisting of Antares A – the red supergiant, and Antares B – a much smaller blue-white star of magnitude 5.5 (5).
Shaula – λ Scorpii (Lambda Scorpii)
Lambda Scorpii is another important star in Scorpious. Its traditional name, Shaula, comes from the Arabic al-šawlā´, which means “the raised (tail).” Shaula is the second brightest star in Scorpius and is about 700 light-years away from our Sun.
It is a multiple-star system with three visible components, Lambda Scorpii A, Lambda Scorpii B, and Lambda Scorpii C. The estimated age of the star system is about 10 to 13 million years. (29).
Acrab (Graffias) – β Scorpii (Beta Scorpii)
Another Scorpio constellation star, Beta Scorpii lies at the tip of one of the claws of the Scorpion. Its traditional name Acrab comes from the Arabic al-‘Aqrab, which means “the Scorpion.” It is also known as Graffias, which means “the claws.”
Beta Scorpii is a multiple-star system in Scorpius. It is a binary star with two components. It has a spectral type of B0.5V which makes it a blue star.
Acrab is the 92nd brightest star in the night sky and the 7th brightest star in Scorpius. The apparent magnitude is 4.90 (7) (8).
Dschubba – δ Scorpii (Delta Scorpii)
The next Scorpius constellation star to note is Delta Scorpii. Its traditional name, Dschubba, comes from the Arabic jabhat, which means “the forehead.” As such, it lies at the head of the Scorpion.
The star is about 490 light-years away and has a visual magnitude of 2.307. Orbiting Dschubba is a Class B object that orbits once every 20 days. It also has another celestial object that orbits it once every 10 years.
The Scorpius star Delta Scorpii has a magnitude of 2.32, making it the 79th brightest star in the sky (9).
Sargas – θ Scorpii (Theta Scorpii)
Sargas is a Luminous Giant Star-type star that forms part of the tail. The star has a spectral type, F1II, which makes it a yellow-to-white star. With an apparent magnitude of 1.87, Sargas is the 37th brightest star in the night sky and the 3rd brightest star in Scorpius.
You don’t need a telescope to see it. Sargas has a radius that is 26 times bigger than the Sun. The name is of Sumerian origin. It is also known as Girtab, both of which mean “Scorpion” (10).
ε Scorpii (Epsilon Scorpii)
Epsilon Scorpii is one of the orange giant stars in Scorpio, with a visual magnitude of 2.31. It lies about 63.7 light-years away. The star has a radius almost 13 times that of the Sun.
It is also known as Larawag, which has its roots in Wardaman traditional initiation ceremonies. Larawag is the signal watcher and gives the All-clear signal, allowing the secret part of the ceremony to continue (11).
Deep-sky objects in Scorpio
Apart from interesting stars in the Scorpio constellation, there are a number of deep-sky objects.
Messier 4 (M4, NGC 6121)
The Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux discovered M4, a large globular cluster, in 1746. It is a bright spherical collection of stars, which astronomers believe may be as many as 100,000.
It is relatively close to our solar system, at only 5,500 light-years away. The cluster can be easily spotted as it is close to the main star Antares. Messier 4 contains around 40,000 white dwarfs which are the cores of ancient, dead stars (12).
Butterfly Cluster – Messier 6 (M6, NGC 6405)
The beautiful Messier 6 is also known as the Butterfly Cluster. It is a bright open cluster located near the tail of the Scorpion. It lies about 1600 light-years from Earth. The American astronomer Robert Burnham named the cluster.
It gets its name from the shape, which resembles a butterfly with open wings. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.2. Messier 6 consists of around 80 stars and is about 100,000 million years old (13).
Ptolemy Cluster – Messier 7 (M7, NGC 6475)
Messier 7, also known as Ptolemy’s Cluster, is a bright open cluster that lies about 980 light-years from Earth. You will see it at the sting of the Scorpion. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.3 you can see it without a telescope.
People in the northern hemisphere will seldom see Messier 7 as part of the constellations Scorpius as it never rises very high above the horizon (14).
Messier 80 (NGC 6093)
Charles Messier, the French astronomer, discovered Messier 80 in the 18th century. It is about 32,600 light-years away.
It is one of the most densely populated star clusters in the galaxy. You will see it between the bright stars Alpha Scorpii, Akrab, Antares, and Beta Scorpii (15).
Cat’s Paw Nebula (Bear Claw Nebula) – NGC 6334 (Gum 64)
NGC 6334 is a Scorpio nebula that gets its name from the shape, which features 3 large bubbles resembling the pads of a cat’s paws. It is a large star-forming region, producing huge stars in the Milky Way.
The nebula lies about 5,500 light-years away. It was discovered in 1837 by the English astronomer John Herschel, during a South African expedition (16).
Butterfly Nebula (Bug Nebula) – NGC 6302 (Caldwell 69)
This is a stunning nebula that is a delight for any home stargazer to see through a telescope.
It is about 3,800 light-years away and is named after the pattern, which resembles a set of beautiful butterfly wings. Forming the wings are rolling areas of gas at temperatures of more than 36,000 degrees Fahrenheit (17).
Exoplanets in Scorpio
Exoplanets are planets that revolve around other stars other than our star, the sun. Exoplanets excite astronomers as they may offer conditions similar to our solar system, with the possibility of life.
Gliese 667Cc
Gliese 667Cc is a “super-Earth” that is about four times as large as Earth and is about 22 light-years away. It orbits a red dwarf called Gliese 667C. The star is part of a 3-star system. Studies done at the University of Puerto Rico at Arecibo’s Planetary Habitability Laboratory, show that this planet is exciting as it could be potentially habitable (18).
PSR B1620-26 b
This planet is also known as Methuselah due to its excessive age which is around 12.7 billion years old. It is interesting in that, unlike our planets, which revolve around one star, the Sun, this planet revolves around two stars. This type of planet is a circumbinary planet.
Gliese 667Ce and Gliese 667Cf
Also revolving around Gliese 667C are two other planets which could be habitable. Their names are Gliese 667Ce and Gliese 667Cf. They are about 2.7 times the mass of Earth. Habitable planets will have water, oxygen, and temperatures that could sustain life as we know it.
Meteor showers in Scorpio
Meteor showers occur when Earth crosses the orbital path of a comet. Bits of dust and debris from the remnants of the comet light up the sky when they enter and burn up in our atmosphere.
Alpha Scorpiids
This shower starts around 16 April and runs until 9 May. The peak is around 3 May. The shower radiates out from the bright star Antares and has an hourly rate of around 3. Meteors travel at a speed of about 35 km/s. This is a fairly faint meteor shower and viewers are sometimes disappointed. You can see it in the southern hemisphere and only in very few regions of the northern hemisphere (19).
Omega Scorpiids
This meteor shower occurs between 23 May and 15 June with the peak occurring on 31 May. The shower radiates from the star Omega1 Scorpii. It has an hourly rate of around 5 and a speed of 26km/s.
This is a fairly faint meteor shower and viewers are sometimes disappointed. You can see it in the southern hemisphere and only in very few regions of the northern hemisphere (20).
Location and visibility
Where is Scorpio constellation located?
Scorpio is one of the more easily identified constellations. You can see some of the bright stars that define the Scorpion with the naked eye. A visit to the local Planetarium where they can simulate a very bright night sky will make it even more exciting to locate Scorpio in the sky.
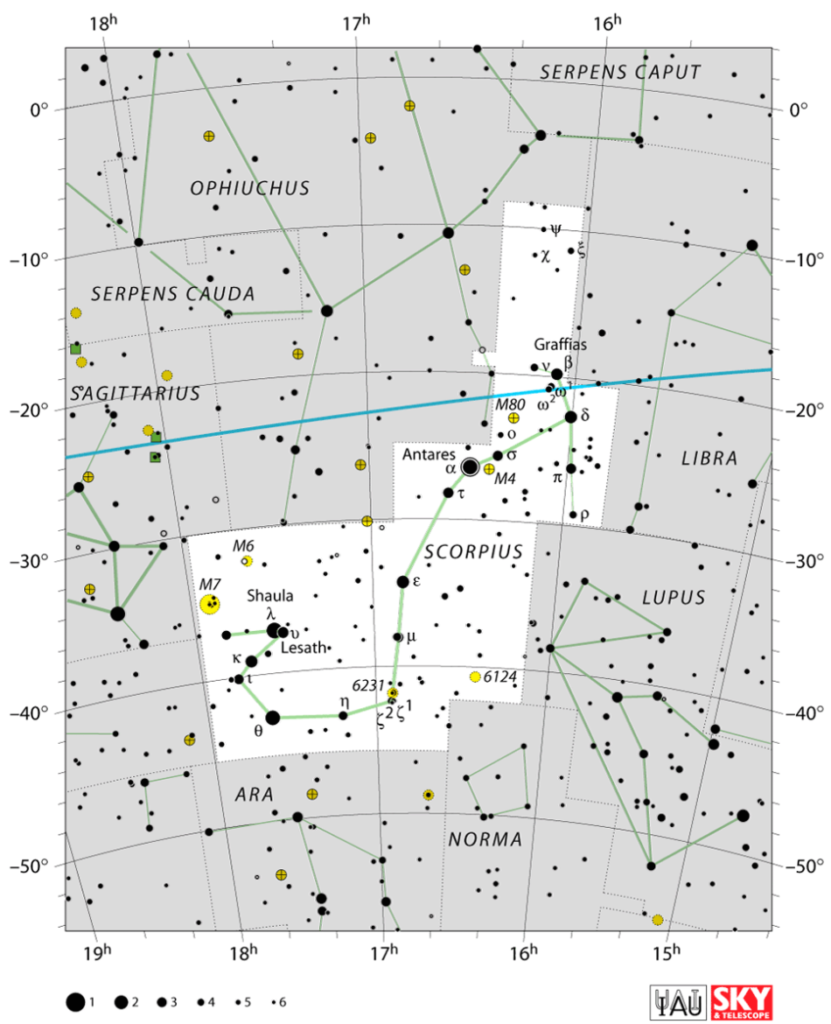
The Scorpio constellation is the 33rd biggest constellation in the sky, occupying an area of 497 square degrees. The Scorpius constellation location is in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere, SQ3.

A quadrant is essentially a quarter of a circle, which allows astronomers to measure the altitude of objects above the horizon. You can see the constellation at latitudes +40° and -90°.
The main neighboring constellations are Sagittarius and Libra. Sagittarius lies to the left, closer to the Scorpion’s tail. Libra lies to the right, closer to the head (21).
See the Scorpius constellation map to find your way around.
When is Scorpio constellation visible?
When is Scorpio visible? Scorpius is best seen in the southern hemisphere. The months for spotting it are March to October. Read on to learn when Scorpius is visible.
In early July, Scorpius reaches its highest point in the sky at about 10 pm. Because the stars return to the same place in the sky about a half-hour earlier with each passing week, in mid-July, it will be at its highest peak at around 9 pm.

When can you see Scorpius In the northern hemisphere? It is very difficult to see Scorpio in the northern hemisphere.
It rises just above the horizon and can only be seen in some regions of the northern USA states and Canada. The tail will be below the horizon, but you may see the head and claws at around 9.00 pm from July to August (22).
How to find Scorpio constellation?
Northern Hemisphere
Here are 5 steps on how to find the Scorpius constellation.
- To locate Scorpio you need to be in the northernmost regions and look very low on the horizon
- Look for the bright star Antares that is the heart of the Scorpion
- Above that you will see the two stars that define the pincers – Graffias and Dschubba
- Following down from Antares, imagine a curve that swoops below the horizon to form the tail
- You can alternatively find Sagittarius, and look for the bright stars of Scorpio straight across to the right
Southern Hemisphere
In the Southern Hemisphere, all constellations appear upside down, so where is Scorpio located?
- To find the Scorpio location, you can find Sagittarius and look to the left for the bright stars Graffias and Dschubba that define the claws
- Moving upwards, locate the heart star, Antares
- Draw a rough pattern of a question mark to outline the tail that curls around
- The star Shaula is at the tip of the tail where the sting is
- The star Lesath lies just below that
How to view Scorpio Constellation?
If you are out and about in a relatively dark area, you can spot the bright stars of Scorpio with the naked eye. Using a powerful pair of binos will give you a better chance of viewing the Scorpion.
The best way to enjoy Scorpio astronomy is through a telescope. For amateurs, there is a great choice of well-priced scopes that will give you fabulous Scorpio constellation images, even in your city garden.

Depending on your budget, you can spend from around $250 to $900 on a telescope that will last for many years.
The Orion SpaceProbe 130ST EQ Reflector Telescope is a great choice, offering exceptional value for money. It has a 5.1″ aperture for awe-inspiring views. The short 24” optical tube makes it very portable to take along on a stargazing trip.
The scope comes with 2 eyepieces, a 25mm, and a 10mm Sirius Plossl. The Shorty 2x Barlow doubles the magnification of the eyepieces. Also included is the Orion Telescope Observer’s Guide book to get you started.
History of observation
Who discovered Scorpio constellation?
Ancient Scorpius history shows that the Scorpion existed in Greek Scorpio myths that date back 3000 years. In fact, it goes far beyond that to the Sumerian civilization about 5000 years ago. They called it GIR-TAB, or “the Scorpion”.
The Greeks wrote about Scorpio constellation mythology in the story of Orion and the Scorpion. Orion the Hunter fought with the Scorpion and was killed.

In Chinese Scorpius myths, the constellation was part of the Azure Dragon. The Azure Dragon is one of the 4 symbols of the Chinese constellations. It represents the east and the spring season. It is also referred to in Feng Shui (23).
The ancient Babylonian Scorpio mythology astronomers knew it as MUL. GIR. TAB, meaning “the (creature with) a burning sting” (24).
For some interesting facts about Scorpius – in somewhat more recent times, the famous astronomer Ptolemy named the Scorpio constellation. He lived between 90 AD and 168 AD.
How old is Scorpio constellation?
Here are some more fascinating Scorpius constellation facts.
As long ago as 5000 BC, the Sumerian civilization had identified Scorpion stars in the constellation of the Scorpion. They called it GIR-TAB, or “the Scorpion” in the Scorpio constellation story.

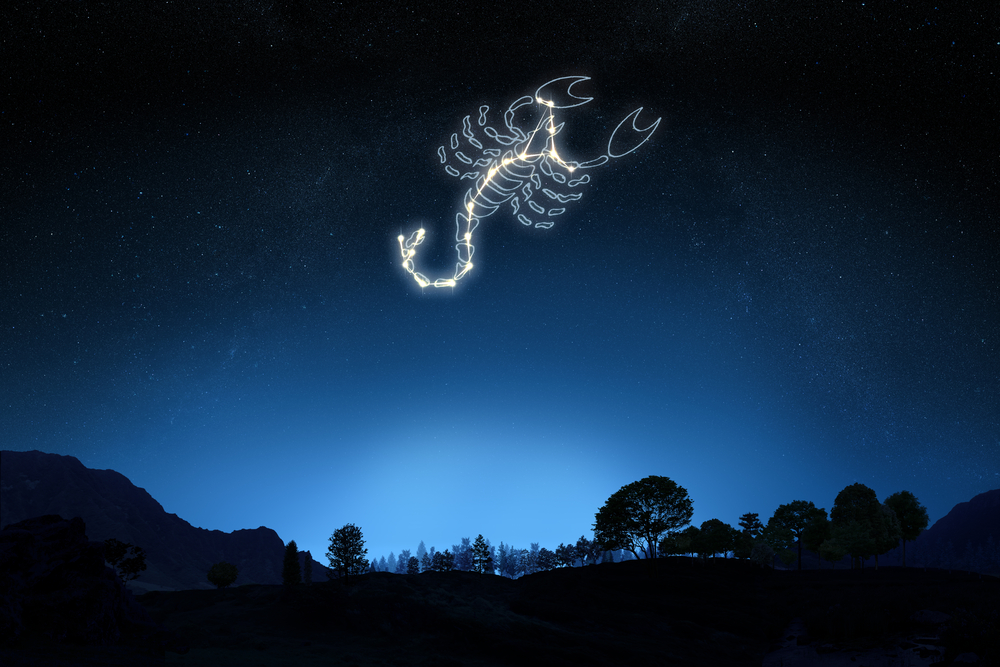
The iconic Scorpius mythology of the Greeks is around 3000 years old, and speaks of Orion the Hunter, who battled with a huge Scorpion and was eventually killed by the creature.
In somewhat more recent times, the famous Ptolemy named the Scorpio constellation in the 2nd century.
How did the Scorpio constellation get its name?
Many people ask – how did Scorpius get its name? Constellation names often come from ancient mythology stories. The Scorpion is not a complex constellation.
It closely resembles the real creature with a long curved tail with a sting at the end. The body has a beating heart and at the front of the head are two dangerous claws.
The word “Scorpion” is thought to have originated in Middle English between 1175 and 1225 AD from the Old French “Scorpion.” It also derives from the Italian “Scorpione”. Both words have roots in the Latin, Scorpius, which comes from the Greek word σκορπίος – skorpíos.
In Babylonian folklore, the creature was called MUL. GIR. TAB, which means – the (creature with) a burning sting” (25).
The Javanese people of Indonesia called Scorpius the Banyakangrem – the brooded swan. It also was known as Kalapa Doyong, the Leaning Coconut Tree (26).
Mythology and meaning
Scorpio myth
Like many of the constellations, there are several different Scorpio myth stories.
In Greek Scorpion mythology, Orion the Hunter grew arrogant, boasting that he would kill all the creatures of the Earth. Gaia, the Goddess of Earth, sent the Scorpion to destroy Orion and a massive battle followed.
The Scorpion won and the Gods placed Scorpio in the sky. Zeus took note of this battle and also sent Orion into the sky to serve as a warning to mortals to curb their arrogance.

Due to the animosity between the two, you will never see Orion and Scorpio both in the sky at the same time. Orion the Hunter only appears in the east after Scorpius sets in the west, and the opposite also applies, the Scorpion does not rise in the east until Orion sinks in the west.
In another Scorpio legend, the God Apollo, Artemis’s twin brother, grew angry with Orion the Hunter and sent the Scorpion to attack him. Orion had claimed that he was a stronger hunter than Artemis. Zeus, King of the Gods, was upset by this fray and put both Orion and Scorpius into the sky.
This Scorpio greek god made sure they appeared at different times as they were enemies. Even today, the Scorpius constellation myth is true and you will never see these two in the sky at the same time.
What does Scorpio symbolize?
Are you fascinated by mythical Scorpions, Scorpio history, and Scorpius meaning? In ancient Greek mythology, the Scorpion is a huge, powerful creature who was able to kill the more powerful Orion the Hunter.
What does Scorpius mean in these stories? The Scorpion in mythology is brave, fearless, and ready to take on any challenge. It is persistent and strategic, able to kill a hunter many times its size.

In astrology, the planet Pluto rules Scorpio. Pluto was one of the Scorpio gods who ruled the underworld.
Scorpios are goal-orientated and intuitive. When angered, they can sting with their tail – a lethal object. They become obstinate, aggressive, and manipulative. Scorpions can cause great destruction; handle with care!
People born under Scorpios star sign show great intelligence and understand the world at large. Marie Antoinette, Bill Gates, and Hillary Clinton are perfect examples of famous Scorpio personalities (27).
Future of Scorpio constellation
The Scorpio stars constellation remains one of the Zodiac signs and as time progresses and telescopes become more powerful, we will find more exciting Scorpio sky objects in the Scorpio galaxy.
Meteor showers are amazing sights to see and every year Scorpio offers a great show called the Alpha Scorpiids. This shower starts around 16 April and runs until 9 May. The peak is around 3 May.

The main star, Antares, is a red supergiant star that is approaching the end of its life. Once the supergiant burns up all its fuel, the star collapses and explodes.
An exploding star is called a supernova. A supernova is exceptionally bright and releases huge amounts of elements and debris into space (30) (31).
The stars in Scorpius constellation include U Scorpii. U Scorpii one of only 10 known recurring novas. These objects show a rapid increase in the brightness of a star. Its normal is 18, but it reaches magnitudes of around 8 during outbursts. Outbursts occurred in 1863, 1906, 1936, 1979, 1987, 1999 and 2010. It is exciting for astronomers to see when the next one occurs! (32)